Abstract
Parasitic plants exchange various types of RNAs with their host plants, including mRNA, and small non-coding RNA. Among small non-coding RNAs, miRNA production is known to be induced at the haustorial interface. The induced miRNAs transfer to the host plant and activate secondary siRNA production to silence target genes in the host. In addition to interfacial transfer, long-distance movement of the small RNAs has also been known to mediate signaling and regulate biological processes. In this study, we tested the long-distance movement of trans-species small RNAs in a parasitic-plant complex. Small RNA-Seq was performed using a complex of a stem parasitic plant, Cuscuta campestris, and a host, Arabidopsis thaliana. In the host plant’s parasitized stem, genes involved in the production of secondary siRNA, AtSGS3 and AtRDR6, were upregulated, and 22-nt small RNA was enriched concomitantly, suggesting the activation of secondary siRNA production. Stem-loop RT-PCR and subsequent sequencing experimentally confirmed the mobility of the small RNAs. Trans-species mobile small RNAs were detected in the parasitic interface and also in distant organs. To clarify the mode of long-distance translocation, we examined whether C. campestris-derived small RNA moves long distances in A. thaliana sgs3 and rdr6 mutants or not. Mobility of C. campestris-derived small RNA in sgs3 and rdr6 mutants suggested the occurrence of direct long-distance transport without secondary siRNA production in the recipient plant.
Keywords: Cuscuta campestris, long-distance movement, parasitic plant, secondary siRNA, sRNA
Introduction
Stem holoparasitic plants from the family Cuscuta (Convolvulaceae) attack broad range of host plants by suppressing host growth and sometimes cause death. After germination, Cuscuta forms a thread-like stem, which searches for nearby host plants to parasitize. Upon attachment to the host stem, a specialized, intrusive organ called the haustorium starts to develop and grows into the host’s stem. Long, unicellular, searching hyphae develop at the haustorium tip, which connects to the host’s vascular tissues, to withdraw water and nutrients for survival. In addition to water and nutrients, vascular connections allow Cuscuta to exchange larger molecules, such as viruses and viroids (Birschwilks et al. 2006), proteins (Haupt et al. 2001; Liu et al. 2019), and various types of RNAs with the host (David-Schwartz et al. 2008; Kim et al. 2014; Roney et al. 2007; Shahid et al. 2018).
The exchange of mRNAs has been shown to occur between Cuscuta pentagona and host plants, including Arabidopsis thaliana and Solanum lycopersicum (Kim et al. 2014). The movement of the mRNAs within a single plant regulates developmental processes (Banerjee et al. 2009; Haywood et al. 2005; Kim et al. 2001; Li et al. 2011; Notaguchi et al. 2012), and it has been well-established that endogenous mRNAs are transported systemically via the phloem (for review, see Kehr and Kragler 2018; Lough and Lucas 2006). Unrestricted movement of the phloem-mobile molecules between Cuscuta and host plants via the haustoria provides evidence of a symplastic pathway (Haupt et al. 2001). mRNAs likely move via this pathway. The trans-species movement of mRNAs strongly suggests that RNA-based control is involved in establishing the parasitic complex.
In addition to the mRNAs, the exchange of small RNAs (sRNAs) between pathogenic organisms and host plants has previously been found. The plant pathogenic fungus Botrytis cinerea generates sRNAs that target host mRNAs during pathogenic interactions, to suppress the host plants’ immunity (Weiberg et al. 2013). Conversely, cotton plants infected with the pathogenic fungus Verticillium dahliae have been shown to export microRNAs (miRNAs) to the fungal hyphae, silencing the expression of genes essential for fungal virulence (Zhang et al. 2016). The movement of artificially expressed sRNAs has also been observed in host-induced gene silencing (HIGS), by which host-derived siRNA or artificial miRNA are transferred to the opposing organisms and silence target genes against nematodes (Huang et al. 2006), insects (Baum et al. 2007), fungi (Nowara et al. 2010), and the parasitic plant Cuscuta pentagona (Alakonya et al. 2012).
Analysis of the miRNAs in the C. campestris-A. thaliana parasitic complex revealed that C. campestris miRNAs were significantly up-regulated in the interface, and the induced miRNAs caused the formation of secondary small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) and decreased the mRNA accumulation in the host plant (Shahid et al. 2018). Host genes targeted by parasite-derived miRNAs included defense-related, hormone signaling, and vascular development genes (Shahid et al. 2018). Analysis of haustorium-induced miRNAs using four different Cuscuta species, also demonstrated that haustorium-induced miRNAs interacted with conserved target sites within the host mRNAs’ coding sequences (Johnson et al. 2019). Cuscuta haustorium-induced miRNAs often have variations in a three-nucleotide period, which compensates for synonymous-site variations in the host mRNAs. These studies clearly demonstrated that small RNA (sRNA)-based mechanisms are involved in establishing parasitic interfaces and in successful parasitization of diverse host species (Johnson et al. 2019). However, although these studies have shown the induction of miRNAs in the parasitic interface, it has not yet been elucidated whether sRNAs derived from donor plants in parasitic complexes are translocated to distant tissues in the recipient plants.
Here we report the plant-to-plant movement of trans-species mobile sRNAs in the C. campestris-A. thaliana parasitic complex. Our analyses demonstrated that trans-species sRNA from the donor plant moved to the recipient plant and were transported to distant organ such as apical region. C. campestris-derived mobile sRNAs were also detected in the apical region of A. thaliana mutants defective in secondary siRNA-biogenesis (sgs3 and rdr6). The result demonstrated that the long-distance movement of trans-species sRNA in the recipient plant is independent of secondary siRNA production and likely due to the direct transport.
Materials and methods
Plant materials and growth conditions
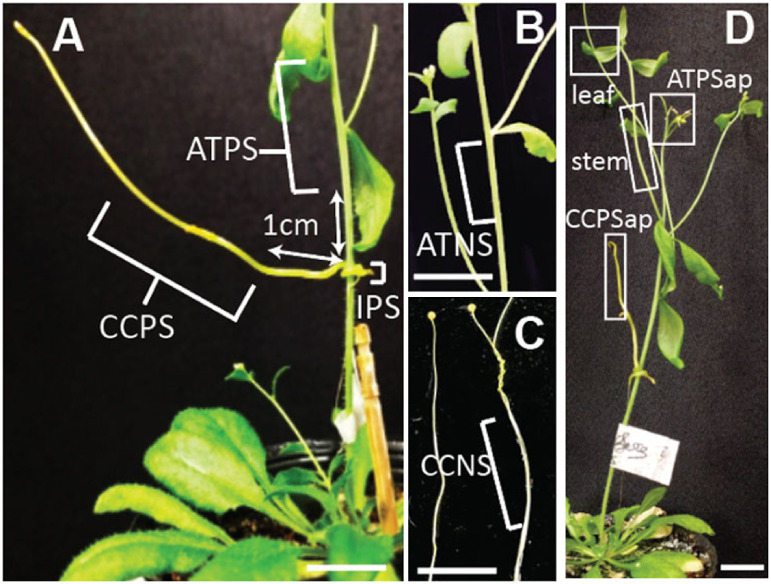
Seeds of Arabidopsis thaliana (ecotype Col-0), sgs3-11, and rdr6-11 (Peragine et al. 2004) were obtained from the Arabidopsis Biological Resource Center (https://abrc.osu.edu/). A. thaliana were grown in soil (Sukoyaka-baido, Yammar Co. Ltd., Osaka, Japan) mixed with the same volume of vermiculite (GS30L, NITTAI Co., Ltd., Osaka, Japan). C. campestris seeds were grown on soil (Sukoyaka-baido, Yammar Co. Ltd.) mixed with the same volume of vermiculite (GS30L, NITTAI Co., Ltd.). Eight-day-old C. campestris seedlings were used to parasitize 60-day-old, mature A. thaliana plants as previously described (Hozumi et al. 2017). The parasitic process of C. campestris on the A. thaliana inflorescence stems was induced as previously described (Hozumi et al. 2017). The parasitic stems (PS) of C. campestris were defined as those that were 1 cm away from the parasitic interface and 1 cm from the shoot apical tip. The nonparasitic stems (NS), were defined as being 1 cm from the basal tip and 1 cm from the apical tip of the C. campestris seedlings grown for 9 days without the A. thaliana host. The parasitized stems (PS) of A. thaliana were inflorescence stems 1 cm from the parasitic interface and 1 cm below the inflorescence. The nonparasitized stems (NS) of A. thaliana were inflorescence stems of 4-week-old plants, 1 cm from the point where C. campestris was attached for 1 day and removed. All samples were taken from 10-day-old complexes. To harvest the apical regions, A. thaliana inflorescence stems, including the flowers, were cut 1 cm below the tip. The harvested tissues were immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80°C. Leaf, stem, and root of 4-week-old A. thaliana plant were harvested 10 days after C. campestris attachment and stored at −80°C.
sRNA-Seq
Total RNA was isolated from the tissues using the miRCURY™ RNA isolation kit- Cell & Plant (Exiqon, Copenhagen, Denmark), following the manufacturer’s protocol with the addition of 8 µl ml−1 β-mercaptoethanol (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., Osaka, Japan), and 8 µl ml−1 RNase inhibitor, Recombinant (TOYOBO, Osaka, Japan) in the extraction buffer. Total RNA was treated with a DNA-free DNA Removal Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, https://www.thermofisher.com), according to the manufacturer’s protocol, to remove the residual DNA. The RNA quality and integrity were checked using High Sensitivity RNA Screen Tape (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA) and TapeStation 4200 (Agilent). Samples with at least two replications of each tissue with integrity indices above 6.5, were used to construct the sequencing library. Sequencing libraries for sRNA-Seq were prepared from the total RNA using the TruSeq Small RNA kit (Illumina, San Diego, CA), following the manufacturer’s protocol. Small RNAs from C. campestris and A. thaliana were isolated using 6% (w/v) TBE urea gel, stained with SYBR Gold (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Quantification of the sRNAs was conducted using an Agilent High Sensitivity DNA kit (Agilent) or KAPA Library Quantification Kit (Illumina). Sequencing was performed using HiSeq 2500 system (Illumina). sRNA-Seq data of the C. campestris-A. thaliana parasitic complex was registered with the accession number DRA010061.
Processing and filtering of reads
Quality and read length distribution of the raw data in the FASTQ format were checked using FastQC (https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/). Barcode removal and adapter sequence trimming was performed with the FASTX-Toolkit (http://hannonlab.cshl.edu/fastx_toolkit/download.html; Schmieder and Edwards 2011), followed by quality control (-q 20 -p 80). Sequences that were 19–24 nt long were filtered using Prinseq-lite (https://sourceforge.net/projects/prinseq/files/; Schmieder and Edwards 2011).
sRNA read mapping
Quality-filtered reads (Supplementary Data S1) were mapped using ShortStack (version 3.8.3; Shahid and Axtell 2013) with the default settings at the scaffold of the C. campestris genome, cucam_0.32.annot.scafold, from the Cuscuta campestris genome project (Vogel et al. 2018). De novo assembly of ShortStack mapping provided the information on sRNA producing “Loci”, which are hereafter referred to as “SS-loci” standing for ShortStack-loci, with DICER call (Supplementary Data S2-1, S2-2). All the loci with DICER-call were selected and annotated with transcript information using GffCompare (https://ccb.jhu.edu/software/stringtie/gffcompare.html; Pertea and Pertea 2020). All the libraries’ sRNA mapping results were merged and sorted according to the SS-loci (Supplementary Data S3-1, S3-2).
Read length profiling
To analyze read length profiles of genes differentially mapped with sRNA-Seq reads between PS and NS libraries, IDs of reference genes commonly appeared in all mapping results of NS and PS libraries to the genome sequences of respective plants (Supplementary Data S3-1, S3-2) were identified. Numbers of reads associated with SS-loci annotated to the same reference gene were summed and regarded as numbers of reads mapped to that reference gene. Average of the reads per million (RPM) values of the reference genes were compared between PS and NS libraries, and reference genes of which RPM values showed more than one or two-fold changes were selected (Supplementary Data S4-1). Numbers of 20-, 21-, 22-, 23-, and 24-nt-long reads of differentially mapped genes were extracted (Supplementary Data S4-2, S4-3), and RPM values were calculated (Supplementary Data S4-4). Significance of the differences in the proportion of reads of each length was examined using prop.test function of R version 4.0.3 (R Core Team 2020) for all the pairwise combinations of NS and PS libraries. If p-values were smaller than 0.05 in all of the combinations, the proportion of the reads of given length was regarded to have significant difference at 5% level.
qRT-PCR
The target mRNAs’ accumulation levels were checked using qRT-PCR, as described previously (Shimizu et al. 2018). The CcRPS18 and AtACTIN2 were used as the reference genes to measure the relative expression of the individual plants. The sequences of the primers used for qRT-PCR are provided in Supplementary Data S5. Statistical analyses were performed using Microsoft Excel 2016 functions.
Screening of trans-species mobile sRNAs
Candidates for parasite-derived mobile sRNAs were prioritized as follows. To identify parasite-derived mobile sRNA-generating loci, the SS-loci commonly present in the mapping results of the reads derived from the libraries of nonparasitic stems of C. campestris (CCNS), parasitic stems of C. campestris (CCPS), interface of parasitic stems (IPS), and parasitized stems of A. thaliana (ATPS) but absent in that of nonparasitized stems of A. thaliana (ATNS) were prioritized for further screening (Supplementary Data S3-1). The reads associated with the SS-loci of the recipient host in parasitic condition (ATPS) (Supplementary Data S6-1) were retrieved (Supplementary Data S6-2), and again mapped to both cucam_0.32.annot.scaffold and TAIR10_whole_genome (https://www.arabidopsis.org; Lamesch et al. 2012) using ShortStack v3.8.3 with –mismatches 0 –nohp settings. Reads matched to both genomes (A. thaliana and C. campestris) could not be distinguished from each other, and were thus excluded from further analyses. Reads that matched exclusively to C. campestris were regarded as originating from the donor parasite (Supplementary Data S6-3). The number of the reads mapped in each library was counted (Supplementary Data S6-4). Finally, sRNAs reads, of which numbers mapped to C. campestris genome using CCNS, CCPS, IPS and ATPS libraries were more than four, and of which number mapped to C. campestris genome using ATNS library equaled to zero, were regarded as transferred from C. campestris to A. thaliana (Supplementary Data S7).
Candidates for host-derived mobile sRNAs were prioritized as follows. To identify host-derived mobile sRNA-generating loci, the SS-loci commonly present in the mapping results of the reads derived from the libraries of nonparasitized stems of A. thaliana (ATNS), parasitized stems of A. thaliana (ATPS), interface of parasitic stems (IPS), and parasitic stems of C. campestris (CCPS) but absent in that of nonparasitic stems of C. campestris (CCNS) were prioritized for further screening (Supplementary Data S3-2). The reads associated with the SS-loci of the recipient parasite in parasitic conditions (CCPS) (Supplementary Data S6-5) were retrieved (Supplementary Data S6-6) and again mapped to both TAIR10_whole_genome and cucam_0.32.annot.scaffold using ShortStack v3.8.3 with the –mismatches 0 –nohp settings. Reads matched to both genomes (A. thaliana and C. campestris) could not be distinguished from each other, and discarded. Reads that matched exclusively to A. thaliana were regarded as originating from the donor host (Supplementary Data S6-7). The number of the reads mapped in each library was counted (Supplementary Data S6-8). Finally, sRNAs reads, of which numbers mapped to A. thaliana genome using ATNS, ATPS, IPS and CCPS libraries were more than four, and of which number mapped to A. thaliana genome using CCNS library equaled to zero, were regarded as transferred from A. thaliana to C. campestris (Supplementary Data S8).
Target prediction
Target mRNAs of parasite-derived mobile sRNAs (CcsRNAs) were predicted in the host’s CDS (TAIR10_CDS) using targetfinder.pl v0.1 (https://github.com/carringtonlab/TargetFinder; Fahlgren and Carrington 2010) and predicted targets whose scores were smaller than 4.5 (Shahid et al. 2018) were prioritized (Supplementary Data S9-1). Target mRNAs of host-derived mobile sRNAs (AtsRNAs) were also predicted in the same way using parasite CDS (https://www.plabipd.de/project_cuscuta2/start.ep) (Supplementary Data S9-2). Gene Ontology annotation enrichment analysis was performed using “GO Term Enrichment for Plants” tool in TAIR (https://www.arabidopsis.org/tools/go_term_enrichment.jsp) based on the similarity of target genes to A. thaliana genes.
Stem-loop PCR and confirmation of sRNA sequences
Confirmation of the sRNAs’ sequences was performed by stem-loop reverse transcription (RT)-PCR, as previously described (Varkonyi-Gasic et al. 2007). In brief, total RNA was used for the cDNA synthesis with sequence-specific stem-loop RT primers, which had 3′ overhangs that were complementary to the 3′ end of the sRNAs’ sequence (Kramer 2011). A master mix of 5× RT buffer, 10 mM dNTP mix, nuclease-free water, and ReverTra Ace –α– (Toyobo) RT enzyme was prepared. Then 1 µl of 10 µM stem-loop RT primer and 1 µl of total RNA (1 µg) was added to an aliquot of the master mix to make a total volume of 20 µl. The reaction was performed by 30 min incubation at 16°C, followed by 60 cycles of pulsed RT at 30°C for 30 s, 42°C for 30 s, and 50°C for 1 s. The reaction was stopped by incubating at 85°C for 5 min. The end-point PCR was performed by using the KOD-Neo-plus DNA polymerase (Toyobo), followed by incubation at 94°C for 2 min, and then followed by 40 cycles at 94°C for 15 s and 60°C for 30 s. The PCR products were run on 6% (w/v) agarose gel in 0.5% TBE. The 60–64 nt lengths of the gel band, which included the stem-loop primer part, were cut and cloned using the Zero Blunt TOPO PCR Cloning Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific) for Sanger sequencing. Sequences of the primers used for the stem-loop PCR are provided in Supplementary Data S5.
Results
Read length profile and expression of sRNA biogenesis-related genes
Small RNA (sRNA)-Seq analyses were performed using RNA obtained from the stems of C. campestris and A. thaliana in a C. campestris-A. thaliana parasitic complex (Figure 1A). The stems harvested from the parasitic complexes are hereafter referred to as PS (Figure 1A). RNA was also prepared from the stems of the respective plants grown without parasitic cohorts, referred to as NS (Figure 1B, C).
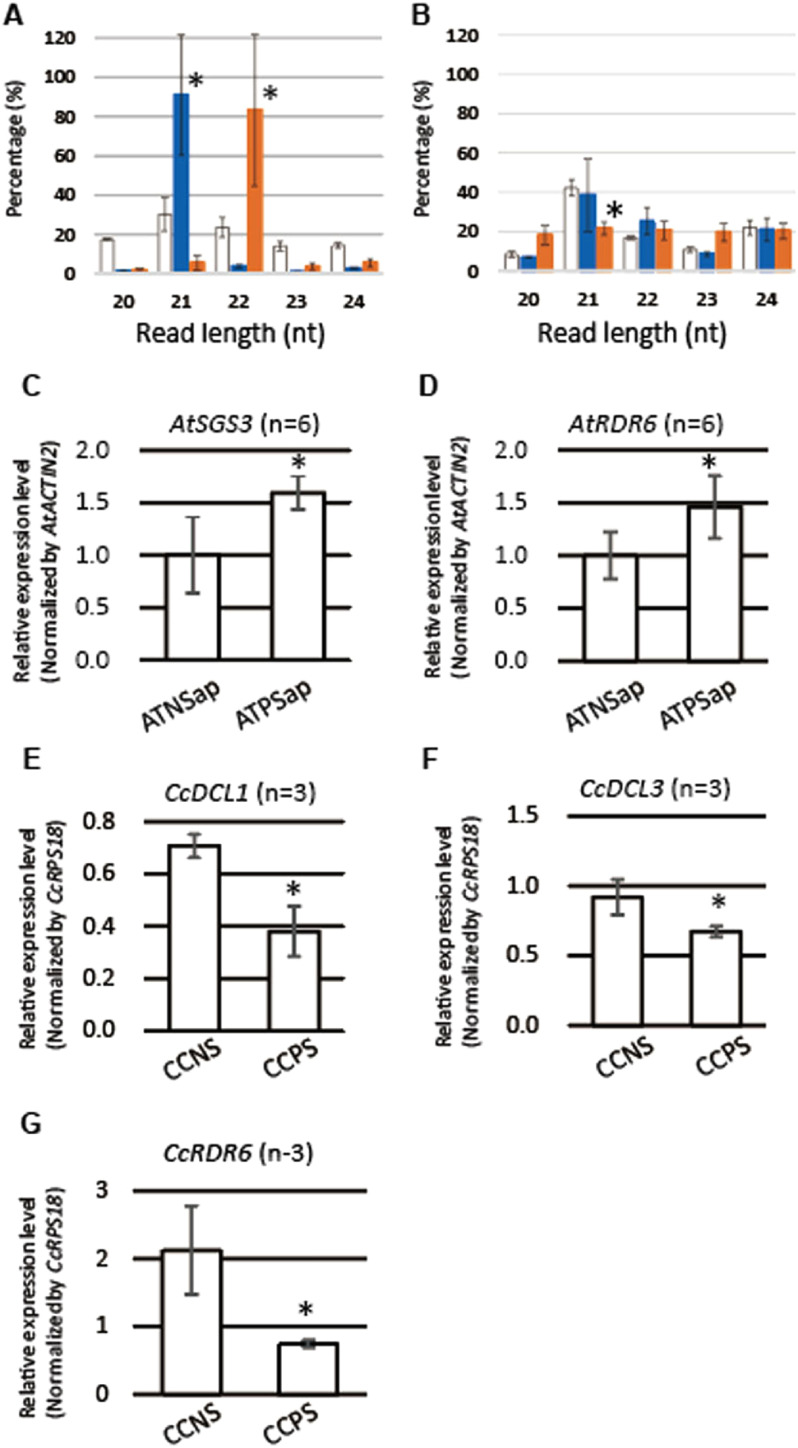
Figure 1. Tissues for sRNA-Seq analyses (A–C). (A) Arabidopsis thaliana parasitized stem (ATPS) and Cuscuta campestris parasitic stem (CCPS) were harvested >1 cm away from the parasitic interface (IPS). (B) A. thaliana nonparasitized stems (ATNS) were harvested from inflorescence stems of 4-week-old A. thaliana. (C) C. campestris nonparasitic stems (CCNS) were harvested from 9-day-old soil-grown C. campestris seedlings. (D) Tissues and organs used for RT-PCR and stem-loop RT-PCR. ATPSap, apical regions of Arabidopsis thaliana parasitized stem; CCPSap, Cuscuta campestris parasitic stem containing apical region. Leaf, stem, and root (below soil surface) of 4-week-old A. thaliana plant were harvested 10 days after C. campestris attachment. Scale bars, 1 cm.
We found that sRNA reads associated with genes, where reads per million (RPM) values increased more than 2-fold in ATPS compared to ATNS, were enriched with 22-nt reads (Figure 2A, Supplementary Figure S1A). On the contrary, sRNA reads associated with genes that decreased more than 2-fold in ATPS were enriched with 21-nt reads (Figure 2A, Supplementary Figure S1B). In C. campestris, no significant enrichment was observed for any length of sRNA reads (Figure 2B). Percentage of 21-nt reads significantly decreased that associated with genes that increased more than 2-fold (Figure 2B, Supplementary Figure S1C). We next investigated whether changes in read-length profile related to the changes in the expression of sRNA biogenesis genes in the parasitized stems containing apical regions (Figure 1D). Expression levels of A. thaliana DICER-LIKE 1 (AtDCL1), AtDCL2, AtDCL3, and AtDCL4 did not change significantly (Supplementary Figure S2A–D). A. thaliana SUPPRESSOR OF GENE SILENCING 3 (AtSGS3) and RNA-DEPENDENT RNA POLYMERASE 6 (AtRDR6), which play crucial roles in the ta-siRNA production pathway (Allen et al. 2005), were significantly upregulated in the apical region of ATPS (Figure 2C, D). This finding, together with the enrichment of the 22-nt reads which are involved in the triggering of siRNA production (Chen et al. 2010; Cuperus et al. 2010), implies that production of secondary siRNA in the host plant is activated by parasitism. In the parasitic plant, C. campestris, CcDCL1, CcDCL3, and CcRDR6 were significantly downregulated (Figure 2E–G). Decrease in the proportion of 21-nt reads in CCPS may be associated with the down regulation of CcDCL1 and CcRDR6. Response of C. campestris sRNA biogenesis process to parasitism was moderate compared to the host.
Figure 2. Length distribution of sRNA reads and expression of sRNA biogenesis genes. (A) ATPS reads mapped to Arabidopsis thaliana genes, of which reads per million (RPM) values changed more than two-fold compared to ATNS. White bar, all reads; blue bar, reads mapped to A. thaliana genes of which RPM values decreased more than two-fold (< 0.5) compared to ATNS; orange bar, reads mapped to A. thaliana genes of which RPM values increased more than two-fold (>2) compared to ATNS. Values indicate means and standard deviations of two replicates. Asterisks indicate significant difference from the value of all reads at 5% level (p<0.05). (B) CCPS reads mapped to Cuscuta campestris genes, of which RPM values changed more than two-fold compared to CCNS. White bar, all reads; blue bar, reads mapped to C. campestris genes of which RPM values decreased more than two-fold (<0.5) compared to CCNS; orange bar, reads mapped to C. campestris genes of which RPM values increased more than two-fold (>2) compared to CCNS. Values indicate means and standard deviations of three replicates. Asterisk indicates significant difference from the value of all reads at 5% level (p<0.05). Expression levels of (C) AtSGS3, (D) AtRDR6, (E) CcDCL1, (F) CcDCL3, and (G) CcRDR6. ATNSap, apical region of nonparasitized stem of Arabidopsis thaliana; ATPSap, apical region of parasitized stem of Arabidopsis thaliana, CCNSap, nonparasitic stem of Cuscuta campestris containing apical region, CCPSap, parasitic stem of Cuscuta campestris containing apical region. In parenthesis, numbers of replicates are indicated. Asterisks indicate significant difference, as examined by the Student’s t-test (p<0.05).
Screening of mobile sRNAs in parasitic complex
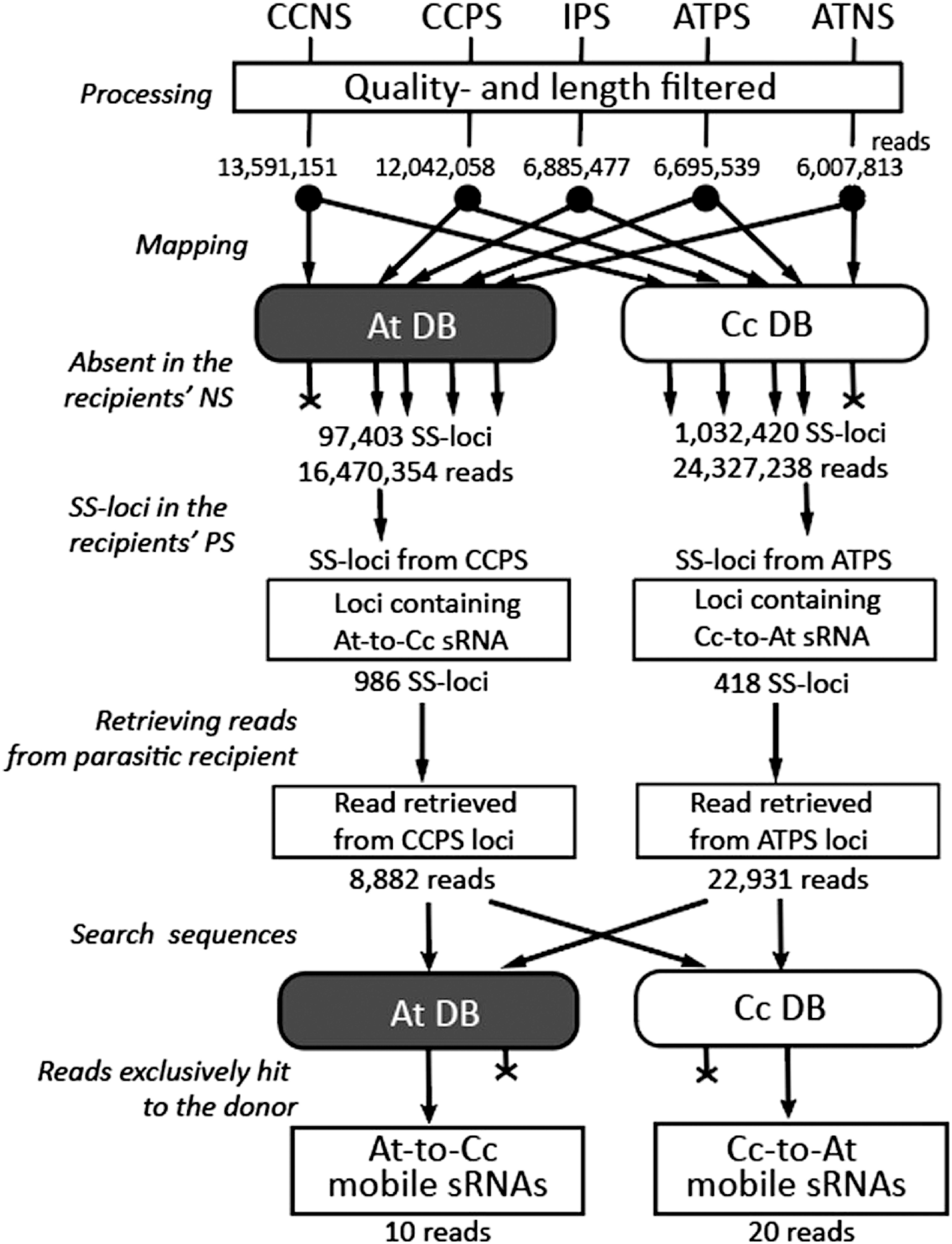
A detailed procedure to prioritize trans-species mobile sRNA candidate is described in the Materials and methods. Briefly, reads obtained from a single sequencing library were quality-filtered, and mapped to the genome databases of both the parasite and host (Figure 3, Supplementary Data S1, S2). One of the two plants in the parasitic complex which produces mobile sRNAs are hereafter referred to as “donor plant”, and the other which receives mobile sRNAs are hereafter referred to as “recipient plant”. Reads corresponding to the mobile sRNA were chosen according to the following criteria: i) sRNA reads obtained from the PS library of recipient plant were mapped to the genome of donor plant; ii) The same loci of the donor plants did not have any mapped reads from NS library of the recipient plant. The sRNA reads that mapped on both genomes were excluded from the analysis, and the reads that exclusively matched to the donor genome regions were selected (Figure 3). Based on these criteria, we prioritized 20 sRNAs from C. campestris and 10 sRNAs from A. thaliana (Supplementary Data S7, S8).
Figure 3. Flowchart of mobile sRNA screening in the Cuscuta campestris-Arabidopsis thaliana parasitic complex. sRNA-Seq reads obtained from the indicated tissues (Reads) were quality- and length-filtered (Processing), and mapped to the donor and recipient genome databases (Mapping). ShortStack-loci (SS-loci) absent in the nonparasitic recipient were selected (Absent in the recipients’ PS), and reads were retrieved from the parasitic recipient libraries (SS-loci in the recipients’ PS, Retrieve reads from parasitic recipient). The retrieved reads were searched in both donor and recipient genomes (Search sequences) and the reads, which were exclusive hits of the donor genome, were regarded as plant-to-plant mobile sRNAs (Reads exclusively hit to the donor). Cc, Cuscuta campestris; At, Arabidopsis thaliana, DB, genome sequence database. Numbers indicate numbers of reads or loci that remained after the procedures just before.
Validation of the trans-species mobility of sRNAs and target prediction
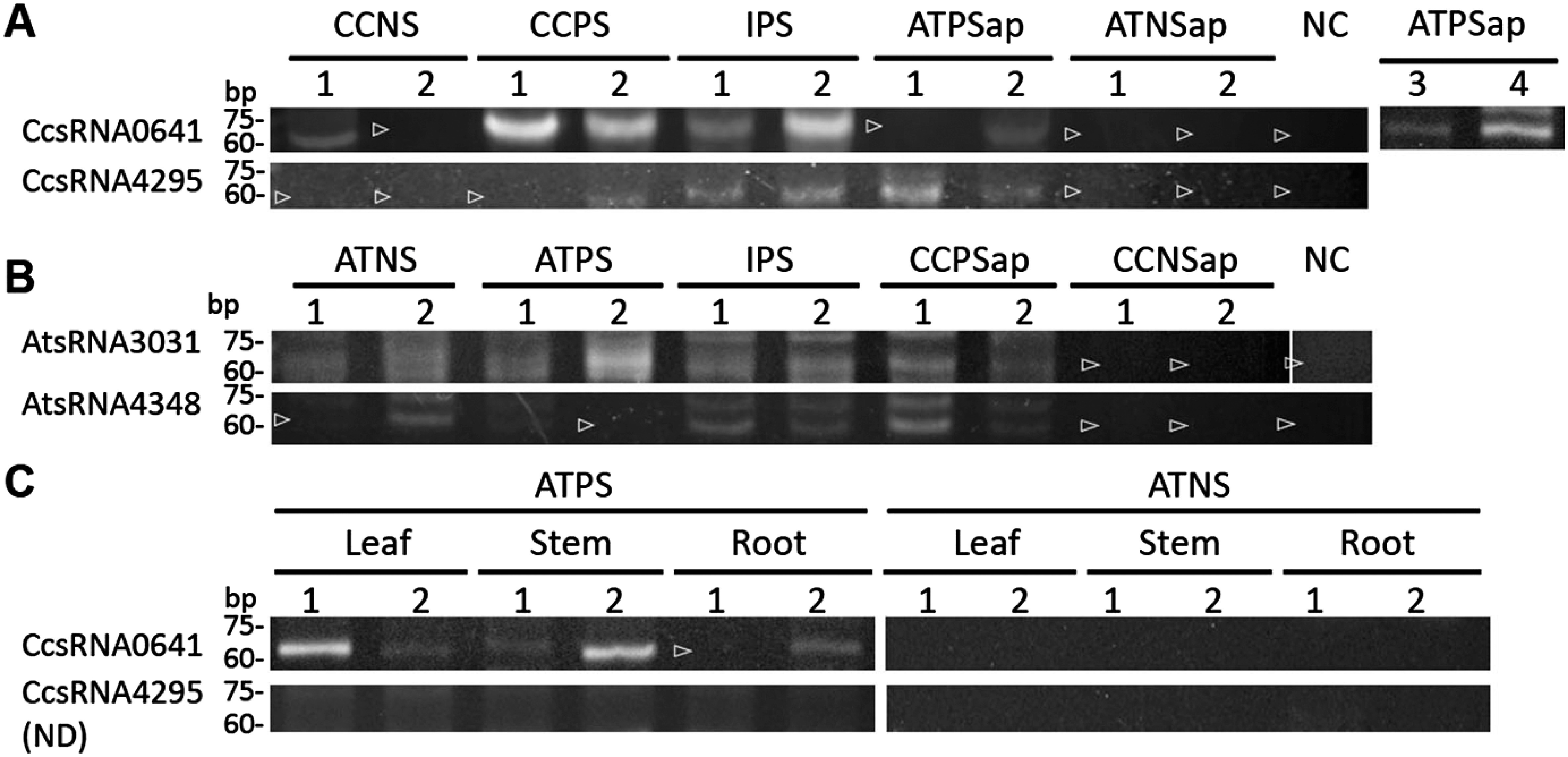
We further prioritized seven out of 20 C. campestris-derived mobile-sRNA candidates, and six out of 10 A. thaliana-derived mobile-sRNA candidates, according to the abundance in the PS libraries of the donor plants for the experimental validation of the movement (Table 1). To detect sRNAs, RT-PCR using sRNA-sequence-specific stem-loop primers was performed (Varkonyi-Gasic et al. 2007) followed by sequencing of the PCR products. Of the seven candidates of C. campestris-derived sRNAs (CcsRNAs) tested, two were confirmed to move (Figure 4A, Table 1). CcsRNA0641, which was mapped to a non-coding region (Table 1), was detected in one of the two CCNS samples, both CCPS samples, both IPS samples, and three out of the four ATPS apical region (ATPSap) samples, but not in either of the ATNS apical region (ATNSap) samples (Figure 4A). Sequences of sRNAs detected in all tissues were identical to that obtained by sRNA-Seq (Table 1), suggesting that these sRNAs were produced in the donor C. campestris and transported to the recipient A. thaliana. Although CcsRNA4295, mapped to a non-coding region, was not detected in CCNS, it was detected in one of the two CCPS samples, both IPS samples, and both ATPSap samples, but not in either of the ATNSap samples, thus regarded as trans-species mobile sRNAs. Of the six candidates of A. thaliana-derived sRNAs (AtsRNAs) tested, two were confirmed to move (Figure 4B). AtsRNA3031 and AtsRNA4348, which were mapped to different intergenic regions, were detected in ATNS, ATPS, IPS, and CCPSap, but not in CCNSap, suggesting that these sRNAs were produced in the donor, A. thaliana, and transported to the recipient, C. campestris. We then checked how far trans-species sRNAs move in the recipient plant. CcsRNA0641 was detected in both leaf samples, both stem samples, and one of the two root samples (Figure 4C), suggesting that CcsRNA0641 moved to distance organs in the recipient plant. On the other hand, CcsRNA4295 was not detected in leaf, stem, or root (Figure 4C), although it was detected in apical region (Figure 4A). This result implied that sRNAs translocation efficiency differs among sRNAs. We did not tested movement of A. thaliana-derived sRNA in the recipient C. campestris, because C. campestris did not have leaves or roots.
Table 1. Mobile sRNA candidates and summary of the trans-species mobility.
| sRNA ID | Sequence, Donor genomic loci, Description | Length (nt) | Length of SL- PCRa (nt) | Av RPM in donor PSb | Mobilityc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CcsRNA0613 | ACUGCGAUUCCUACUUCUGCCA | 22 | 62 | 192.3 | N |
| Ccam0.32_scaffold87b:766744-766765 | |||||
| Cc015853 SNF2 domain protein | |||||
| CcsRNA0641 | ACUUGCGUUCAAAGUUUCGAU | 21 | 61 | 358.3 | M |
| Ccam0.32_scaffold327b:26842-26992 | |||||
| Non-coding region | |||||
| CcsRNA0897 | AGGGGCGAAAGACUAAUCGAACC | 23 | 63 | 420.7 | N |
| Ccam0.32_scaffold428:135804-135828 | |||||
| Non-coding region | |||||
| CcsRNA1003 | AGUUUUUCCACUCGCCAACUCGC | 23 | 63 | 245.7 | N |
| Ccam0.32_scaffold158:308476-308499 | |||||
| Reverse transcriptase | |||||
| CcsRNA3151 | GAUGCUCUUCCAACCGCUGGAC | 22 | 62 | 93.0 | N |
| Ccam0.32_scaffold490:38023-38045 | |||||
| RNase H family protein | |||||
| CcsRNA4295 | GUUUGAAUUGUAGUCUGGAGA | 21 | 61 | 458.3 | M |
| Ccam0.32_scaffold3003:6576-6597 | |||||
| Non-coding region | |||||
| CcsRNA5627 | UUUGAAUUGUAGUCUGGAGA | 20 | 60 | 405.3 | N |
| Ccam0.32_scaffold757:3409-3433 | |||||
| Non-coding region | |||||
| AtsRNA1127 | ACCCGUUAAUGACUGUUAAUCUGU | 24 | 64 | 60.0 | N |
| Chr5:8313181-8313483 | |||||
| AT5G24352 protein kinase | |||||
| AtsRNA2146 | AUAAAACAUGAUCAAAGGGUG | 21 | 61 | 43.0 | N |
| Chr5:9741714-9741938 | |||||
| Non-coding region | |||||
| AtsRNA3031 | CAUCCGUUGACCAUGUUUUAU | 21 | 61 | 48.5 | M |
| Chr3:8842983-8843011 | |||||
| Non-coding region | |||||
| AtsRNA4110 | GAGUUUUUCAGUAUCUGUUCUU | 22 | 62 | 21.0 | N |
| Chr1:11793991-11794171 | |||||
| AT1G32610 glycoprotein family protein | |||||
| AtsRNA4348 | GCCCAUUUUAAACCUGUGUU | 20 | 60 | 8.0 | M |
| Chr1:13152671-13152836 | |||||
| Non-coding region | |||||
| AtsRNA4501 | GCUUUCUCCAAUCUGCUAGAA | 21 | 61 | 16.5 | N |
| Chr2:16467151-16467318 | |||||
| AT2G39440 ribonuclease H2 subunit C |
aLength of stem-loop RT-PCR product. bAverage reads per million (RPM) in the parasitic- or parasitized stems of the donor plants. cExperimentally examined mobility to the recipient plant in this study; M, mobile; N, not mobile.
Figure 4. Detection of donor-derived sRNAs in the recipient plant by stem-loop PCR. (A) Cuscuta campestris (donor)-derived sRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana (recipient). (B) A. thaliana (donor)-derived sRNAs in C. campestris (recipient). (C) Detection of CcsRNA0641, and absence of CcsRNA4295 in leaf, stem, and root of A. thaliana (recipient). CCNS, nonparasitic stem of C. campestris; CCPS, parasitic stem of C. campestris; CCNSap, nonparasitic stem of C. campestris containing apical region; CCPSap, parasitic stem of C. campestris containing apical region; IPS, parasitic interface; ATNS, nonparasitized stem of A. thaliana; ATPS, parasitized stem of A. thaliana; ATNSap, apical region of ATNS; ATPSap, apical region of ATPS; NC, no template control. Numbers on top of the lanes indicate replicates. Open arrowheads indicate that no amplification products were detected. ND, not detected.
Target transcripts were predicted for the mobile sRNAs in which trans-species movement were confirmed (Supplementary Data S9). Predicted targets of CcsRNA0641 included disease resistance protein family genes and sRNA degrading nuclease gene, and those of CcsRNA4295 included Golgi nucleotide sugar transporter gene and an ARF-GAP domain 6 gene. Predicted targets of AtsRNA3031 included metallopeptidase M24 family protein gene and RNA-binding (RRM/RBD/RNP motifs) family protein gene, and those of AtsRNA4348 included several leucine-rich repeat protein kinase family protein genes. However, gene ontology analysis did not show any enrichment of specific terms associated with molecular functions, cellular components, or biological processes.
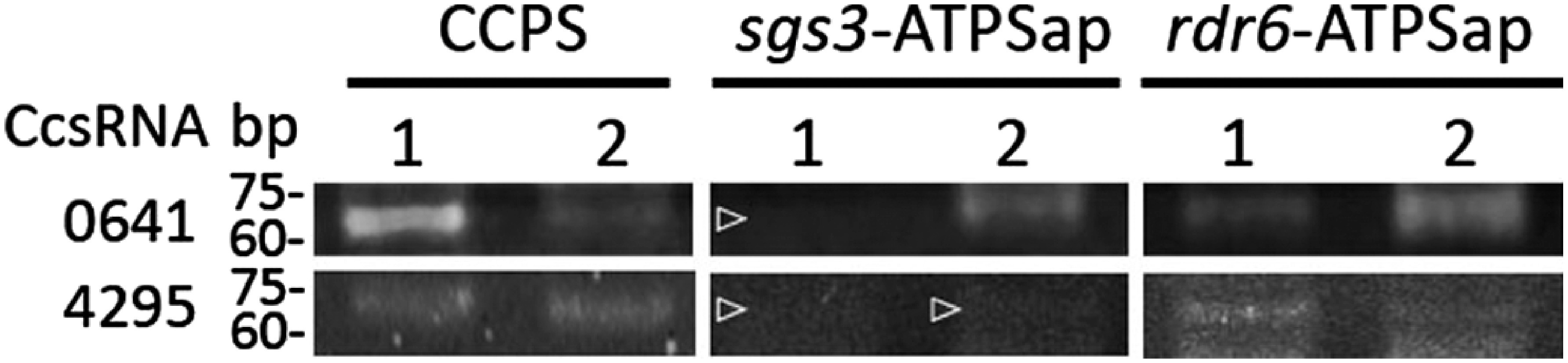
To test whether secondary siRNAs production in the recipient plant was involved in the movement of trans-species mobile sRNAs or not, we checked the phasing, which means a periodicity of sRNA abundance of sRNAs mapped to predicted target genes (Supplementary Data S9) since phasing has been demonstrated to be a signature of secondary siRNAs produced via the SGS3-RDR6-dependent pathway (Allen et al. 2005). However, no significant phase scores were provided to the SS-loci corresponding to predicted target genes (Table 2), reinforcing the notion that donor-derived mobile sRNAs did not trigger secondary siRNA production in the PS of the recipient plant. Finally, we examined the detection of C. campestris (donor)-derived mobile sRNAs in sgs3 and rdr6 mutants of the recipient A. thaliana. The presence of CcsRNA0641 and CcsRNA4295 in the donor, C. campestris, was confirmed in both of the CCPS samples. CcsRNA0641 was detected in one of the two apical region samples of sgs3, and both apical region samples of rdr6 (Figure 5). On the other hand, CcsRNA4295 was not detected in sgs3, but was detected in both samples of rdr6 (Figure 5). Therefore, the long-distance movement of CcsRNA0641 in the recipient plant did not require SGS3-RDR6-dependent secondary siRNA production, but that of CcsRNA4295 might be depended on SGS3.
Table 2. Non-phasing of sRNAs mapped onto the target genes of experimentally validated trans-species mobile sRNAs.
| sRNA | Num predicted targetsa | Num target mappedb | Max phase scorec | 20d | 21d | 22d | 23d | 24d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CcsRNA0641 | 6 | 1 | None | 7 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| CcsRNA4295 | 10 | 4 | None | 10 | 8 | 22 | 19 | 21 |
| AtsRNA3031 | 6 | 5 | 1.4 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 41 |
| AtsRNA4348 | 21 | 15 | 1.2 | 21 | 40 | 86 | 63 | 288 |
aNumbers of predicted target genes with target score equal to or smaller than 4.5, bNumbers of target genes actually mapped by sRNA reads, cMaximum phase score found in the ShortStack output (a score of 30 or more indicates a well-phasing locus), dNumber of reads of indicated length (nt).
Figure 5. Detection of Cuscuta campestris-derived sRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana sgs3 and rdr6 mutants. CCPS, parasitic stem of C. campestris; sgs3-ATPSap, apical region of parasitized stem of A. thaliana sgs3 mutant; rdr6-ATPSap, apical region of parasitized stem of A. thaliana rdr6 mutant. Numbers on top of the lanes indicate replicates. Open arrowheads indicate that no amplification products were detected.
Discussion
In this study, we aimed to identify trans-species mobile sRNAs that moved long distances in recipient plants. We first performed sRNA-Seq analysis of the C. campestris-A. thaliana parasitic complex. The length distribution of A. thaliana sRNA reads mapped to the genes of which RPM values increased more than 2-fold revealed that the 22-nt sRNAs were enriched, while A. thaliana reads associated with genes that decreased more than 2-fold were enriched with 21-nt sRNA (Figure 2A). The 22-nt miRNA are associated with secondary siRNA accumulation (Chen et al. 2010; Cuperus et al. 2010). Enrichment of 22-nt miRNA was reported in the C. campestris miRNAs induced in the haustorial interface between C. campestris and A. thaliana (Shahid et al. 2018). However, in the case of ATPS, most of the 22-nt sRNA reads were not annotated with canonical miRNAs (Supplementary Data S2-2). In ATPS, majority (95%) of the 22-nt sRNA reads were mapped to non-exon regions of ribosomal protein genes and ribosomal RNA genes (Supplementary Data S3-2). SGS3 and RDR6 were shown to be involved in the RNA quality control by degrading aberrant RNAs of SMXL4 and SMXL5 and siRNA production (Wu et al. 2017). Thus, upregulation of AtSGS3 and AtRDR6 in ATPSap (Figure 2C, D) is probably involved in producing 22-nt siRNAs from aberrant transcripts of ribosomal protein genes and ribosomal RNA genes.
Two C. campestris-derived sRNAs and two A. thaliana-derived sRNAs were detected in the PSs of recipient plants, which indicated that trans-species sRNA movement occurred bidirectionally (Figure 4A, B). One of the C. campestris-derived sRNAs, CcsRNA0641, was detected in leaf, stem, and root, as well as in the apical region of the recipient A. thaliana (Figure 4A, C). The other C. campestris-derived sRNAs, CcsRNA4295, was detected in the apical region but not in leaf, stem, or root (Figure 4A). Since abundance of CcsRNA4295 transferred into the apical region was comparable to that of CcsRNA0641 (Table 1), active targeting mechanisms may be involved. Detection of both sRNAs in the apical region suggested that donor-derived sRNAs could be directly transported to the distant organs of the recipient plants. To test this hypothesis, we attempted to clarify whether the movement of C. campestris-derived sRNAs in the recipient A. thaliana requires secondary siRNA biogenesis. We first checked the occurrence of phased sRNA production from the predicted target genes of CcsRNA0641, which showed no phasing (Table 2) suggesting that CcsRNA0641 did not trigger secondary siRNA production. Second, we examined the detection of CcsRNA0641 in the apical region of A. thaliana sgs3 and rdr6 mutants (Figure 5). The results demonstrated that CcsRNA0641 was detected in ATPSap in the absence of SGS3 or RDR6, indicating that CcsRNA0641 was not a secondary siRNA product. The movement of CcsRNA0641 should be accounted for by the direct transport of donor-derived sRNAs.
The other C. campestris-derived mobile sRNAs, CcsRNA4295, did not trigger phased siRNA production (Table 2). However, CcsRNA4295 was detected in the apical region of the rdr6 mutant, but not in the sgs3 mutant (Figure 5), suggesting that AtSGS3 is necessary for long-distance movement CcsRNA4295. Previous studies on ta-siRNA biogenesis revealed that sgs3-11 was epistatic to rdr6-11 (Yoshikawa et al. 2005). SGS3 protein binds to the fragments derived from miRNA-cleaved RNAs and protects them from degradation. RDR6 subsequently transcribes SGS3-bound fragments to form double-stranded RNA (Yoshikawa et al. 2005). Our results showed that AtRDR6 is not necessary for the movement of CcsRNA4295, suggesting that downstream siRNA production is not necessary, according to the ta-siRNA biogenesis model. On the other hand, AtSGS3 is probably necessary for a process different from siRNA production, for example, in protecting CcsRNA4295 from degradation, which facilitates its long-distance movement. The exact roles of SGS3 in the movement of sRNA in the parasitic plant complex remain elusive.
Several possible routes for the trans-species delivery of siRNA or miRNA have been hypothesized (Wang and Dean 2020). One is via the secretion and uptake of extracellular vesicle (Cai et al. 2018). Alternatively, symplastic continuity has been also hypothesized to serve as a transporting route. This notion tempted us to hypothesize that trans-species mobile sRNAs also invoke phloem transport. Given that phloem serves as a transport route, sRNAs movement direction should follow the sugar concentration gradient, from the source (host) to the sink (parasite). However, our results showed that sRNAs could move bidirectionally (Figure 4A, B). Long-distance movement of the endogenous mRNA of A. thaliana revealed that many mRNAs moved in the direction opposite the source-to-sink direction (Thieme et al. 2015). Thus, the source-sink relationship between the host and parasite may not be the only determinant of the sRNAs movement’s direction, as active targeting may also be involved.
In summary, our results indicate that donor-derived sRNAs moved to, and in so doing, moved long distances in the recipient plant. Despite the upregulation of the SGS3-RDR6 pathway of secondary siRNA biogenesis in the host plant, the dependency of the mobility of parasite-derived sRNA in the recipient host plant on the SGS3-RDR6 pathway differed with sRNA species. We hypothesize that mobile sRNAs should repress the expression or translation of target genes in distant organs, although experimental proof is still required. A more comprehensive analysis of the trans-species sRNAs will provide deeper insights into the sRNA-mediated interactions between parasitic and host plants. It will also provide new insights into the RNA-transfer-based plant breeding technology.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Advanced Genomics Center (Osaka Prefecture University) for the RNA quality check, and Dr. Asaka Akita (NIBB) for the technical assistance in sRNA-Seq. This study was partly supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (18H03950 and 19H00944, JSPS to K.A.), and the NIBB Cooperative Research Program (17-429, NIBB, to K.A.).
Abbreviations
- miRNA
microRNA
- NS
nonparasitic or nonparasitized stem
- nt
nucleotide
- PS
parasitic or parasitized stem
- RPM
reads per million
- RT-PCR
reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
- siRNA
short interfering RNA
- sRNA
small RNA
- SS-loci
ShortStack-loci
- ta-siRNA
trans-acting short interfering RNA
Supplementary Data
References
- Alakonya A, Kumar R, Koenig D, Kimura S, Townsley B, Runo S, Garces HM, Kang J, Yanez A, David-Schwartz R, et al. (2012) Interspecific RNA interference of SHOOT MERISTEMLESS-like disrupts Cuscuta pentagona plant parasitism. Plant Cell 24: 3153–3166 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen E, Xie Z, Gustafson AM, Carrington JC (2005) microRNA-directed phasing during trans-acting siRNA biogenesis in plants. Cell 121: 207–221 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee AK, Lin T, Hannapel DJ (2009) Untranslated regions of a mobile transcript mediate RNA metabolism. Plant Physiol 151: 1831–1843 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum JA, Bogaert T, Clinton W, Heck GR, Feldmann P, Ilagan O, Johnson S, Plaetinck G, Munyikwa T, Pleau M, et al. (2007) Control of coleopteran insect pests through RNA interference. Nat Biotechnol 25: 1322–1326 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birschwilks M, Haupt S, Hofius D, Neumann S (2006) Transfer of phloem-mobile substances from the host plants to the holoparasite Cuscuta sp. J Exp Bot 57: 911–921 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai Q, Qiao L, Wang M, He B, Lin FM, Palmquist J, Huang SD, Jin H (2018) Plants send small RNAs in extracellular vesicles to fungal pathogen to silence virulence genes. Science 360: 1126–1129 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen HM, Chen LT, Patel K, Li YH, Baulcombe DC, Wu SH (2010) 22-Nucleotide RNAs trigger secondary siRNA biogenesis in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107: 15269–15274 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuperus JT, Carbonell A, Fahlgren N, Garcia-Ruiz H, Burke RT, Takeda A, Sullivan CM, Gilbert SD, Montgomery TA, Carrington JC (2010) Unique functionality of 22-nt miRNAs in triggering RDR6-dependent siRNA biogenesis from target transcripts in Arabidopsis. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17: 997–1003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David-Schwartz R, Runo S, Townsley B, Machuka J, Sinha N (2008) Long-distance transport of mRNA via parenchyma cells and phloem across the host-parasite junction in Cuscuta. New Phytol 179: 1133–1141 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahlgren N, Carrington JC (2010) miRNA target prediction in plants. Methods Mol Biol 592: 51–57 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haupt S, Oparka KJ, Sauer N, Neumann S (2001) Macromolecular trafficking between Nicotiana tabacum and the holoparasite Cuscuta reflexa. J Exp Bot 52: 173–177 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haywood V, Yu TS, Huang NC, Lucas WJ (2005) Phloem long-distance trafficking of GIBBERELLIC ACID-INSENSITIVE RNA regulates leaf development. Plant J 42: 49–68 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hozumi A, Bera S, Fujiwara D, Obayashi T, Yokoyama R, Nishitani K, Aoki K (2017) Arabinogalactan proteins accumulate in the cell walls of searching hyphae of the stem parasitic plants, Cuscuta campestris and Cuscuta japonica. Plant Cell Physiol 58: 1868–1877 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang G, Allen R, Davis EL, Baum TJ, Hussey RS (2006) Engineering broad root-knot resistance in transgenic plants by RNAi silencing of a conserved and essential root-knot nematode parasitism gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 14302–14306 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson NR, dePamphilis CW, Axtell MJ (2019) Compensatory sequence variation between trans-species small RNAs and their target sites. eLife 8: e49750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehr J, Kragler F (2018) Long distance RNA movement. New Phytol 218: 29–40 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim G, LeBlanc ML, Wafula EK, dePamphilis CW, Westwood JH (2014) Plant science: Genomic-scale exchange of mRNA between a parasitic plant and its hosts. Science 345: 808–811 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim M, Canio W, Kessler S, Sinha N (2001) Developmental changes due to long-distance movement of a homeobox fusion transcript in tomato. Science 293: 287–289 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer MF (2011) Stem-loop RT-qPCR for miRNAs. Curr Protoc Mol Biol 95: 15.10.1–15.10, 15 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamesch P, Berardini TZ, Li D, Swarbreck D, Wilks C, Sasidharan R, Muller R, Dreher K, Alexander DL, Garcia-Hernandez M, et al. (2012) The Arabidopsis information resource (TAIR): Improved gene annotation and new tools. Nucleic Acids Res 40(D1): D1202–D1210 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C, Gu M, Shi N, Zhang H, Yang X, Osman T, Liu Y, Wang H, Vatish M, Jackson S, et al. (2011) Mobile FT mRNA contributes to the systemic florigen signaling in floral induction. Sci Rep 1: 73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu N, Shen G, Xu Y, Liu H, Zhang J, Li S, Li J, Zhang C, Qi J, Wang L, et al. (2019) Extensive inter-plant protein transfer between Cuscuta parasites and their host plants. Mol Plant 13: 573–585 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lough TJ, Lucas WJ (2006) Integrative plant biology: Role of phloem long-distance macromolecular trafficking. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57: 203–232 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notaguchi M, Wolf S, Lucas WJ (2012) Phloem-mobile Aux/IAA transcripts target to the root tip and modify root architecture. J Integr Plant Biol 54: 760–772 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowara D, Gay A, Lacomme C, Shaw J, Ridout C, Douchkov D, Hensel G, Kumlehn J, Schweizer P (2010) HIGS: Host-induced gene silencing in the obligate biotrophic fungal pathogen Blumeria graminis. Plant Cell 22: 3130–3141 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peragine A, Yoshikawa M, Wu G, Albrecht HL, Poethig RS (2004) SGS3 and SGS2/SDE1/RDR6 are required for juvenile development and the production of trans-acting siRNAs in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev 18: 2368–2379 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pertea G, Pertea M (2020) GFF Utilities: GffRead and GffCompare. F1000 Res 9: ISCB Comm J-304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team (2020) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria
- Roney JK, Khatibi PA, Westwood JH (2007) Cross-species translocation of mRNA from host plants into the parasitic plant dodder. Plant Physiol 143: 1037–1043 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmieder R, Edwards R (2011) Quality control and preprocessing of metagenomic datasets. Bioinformatics 27: 863–864 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahid S, Axtell MJ (2013) Identification and annotation of small RNA genes using ShortStack. Methods 67: 20–27 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahid S, Kim G, Johnson NR, Wafula E, Wang F, Coruh C, Bernal-Galeano V, Phifer T, dePamphilis CW, Westwood JH, et al. (2018) MicroRNAs from the parasitic plant Cuscuta campestris target host messenger RNAs. Nature 553: 82–85 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu K, Hozumi A, Aoki K (2018) Organization of vascular cells in the haustorium of the parasitic flowering plant Cuscuta japonica. Plant Cell Physiol 59: 715–723 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thieme CJ, Rojas-Triana M, Stecyk E, Schudoma C, Zhang W, Yang L, Miñambres M, Walther D, Schulze WX, Paz-Ares J, et al. (2015) Endogenous Arabidopsis messenger RNAs transported to distant tissues. Nat Plants 1: 15025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varkonyi-Gasic E, Wu R, Wood M, Walton EF, Hellens RP (2007) Protocol: A highly sensitive RT-PCR method for detection and quantification of microRNAs. Plant Methods 3: 12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel A, Schwacke R, Denton AK, Usadel B, Hollmann J, Fischer K, Bolger A, Schmidt MH, Bolger ME, Gundlach H, et al. (2018) Footprints of parasitism in the genome of the parasitic flowering plant Cuscuta campestris. Nat Commun 9: 2515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M, Dean RA (2020) Movement of small RNAs in and between plants and fungi. Mol Plant Pathol 21: 589–601 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiberg A, Wang M, Lin FM, Zhao H, Zhang Z, Kaloshian I, Huang HD, Jin H (2013) Fungal small RNAs suppress plant immunity by hijacking host RNA interference pathways. Science 342: 118–123 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu YY, Hou BH, Lee WC, Lu SH, Yang CJ, Vaucheret H, Chen HM (2017) DCL2- and RDR6-dependent transitive silencing of SMXL4 and SMXL5 in Arabidopsis dcl4 mutants causes defective phloem transport and carbohydrate over-accumulation. Plant J 90: 1064–1078 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa M, Peragine A, Park MY, Poethig RS (2005) A pathway for the biogenesis of trans-acting siRNAs in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev 19: 2164–2175 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang T, Jin Y, Zhao JH, Gao F, Zhou BJ, Fang YY, Guo HS (2016) Host-induced gene silencing of the target gene in fungal cells confers effective resistance to the cotton wilt disease pathogen Verticillium dahliae. Mol Plant 9: 939–942 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.