Abstract
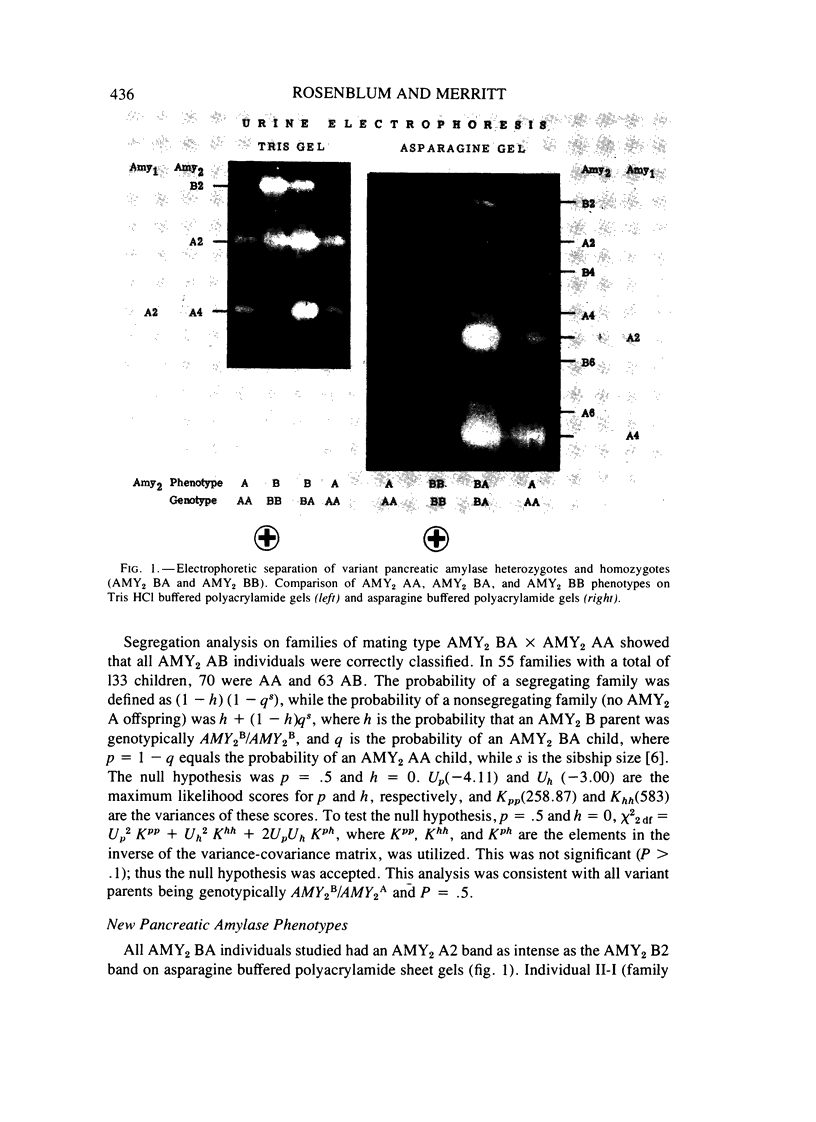
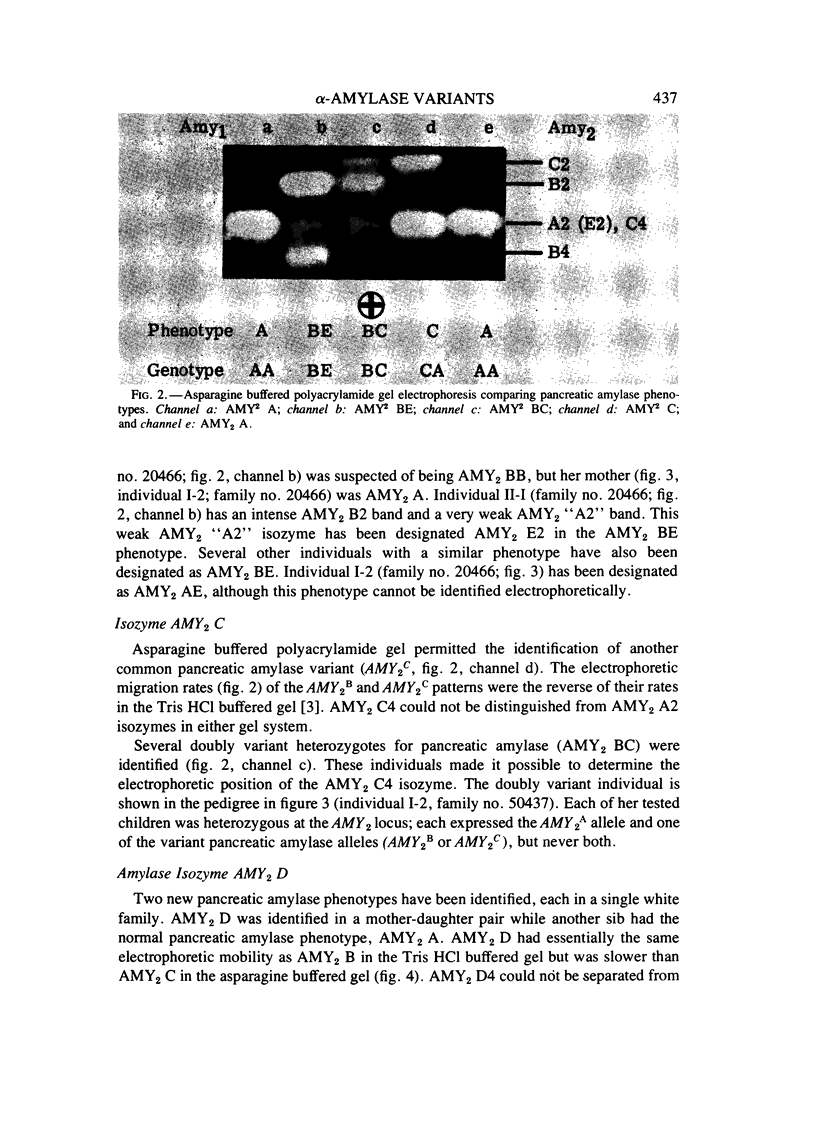
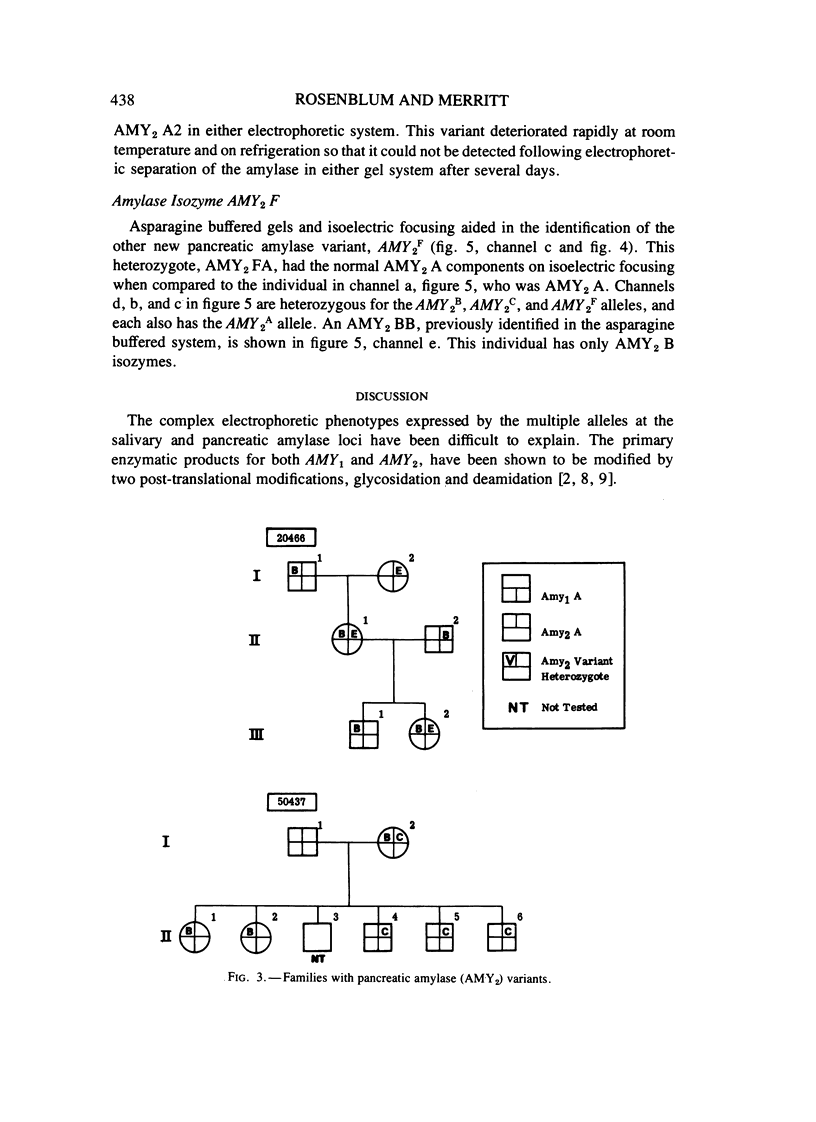
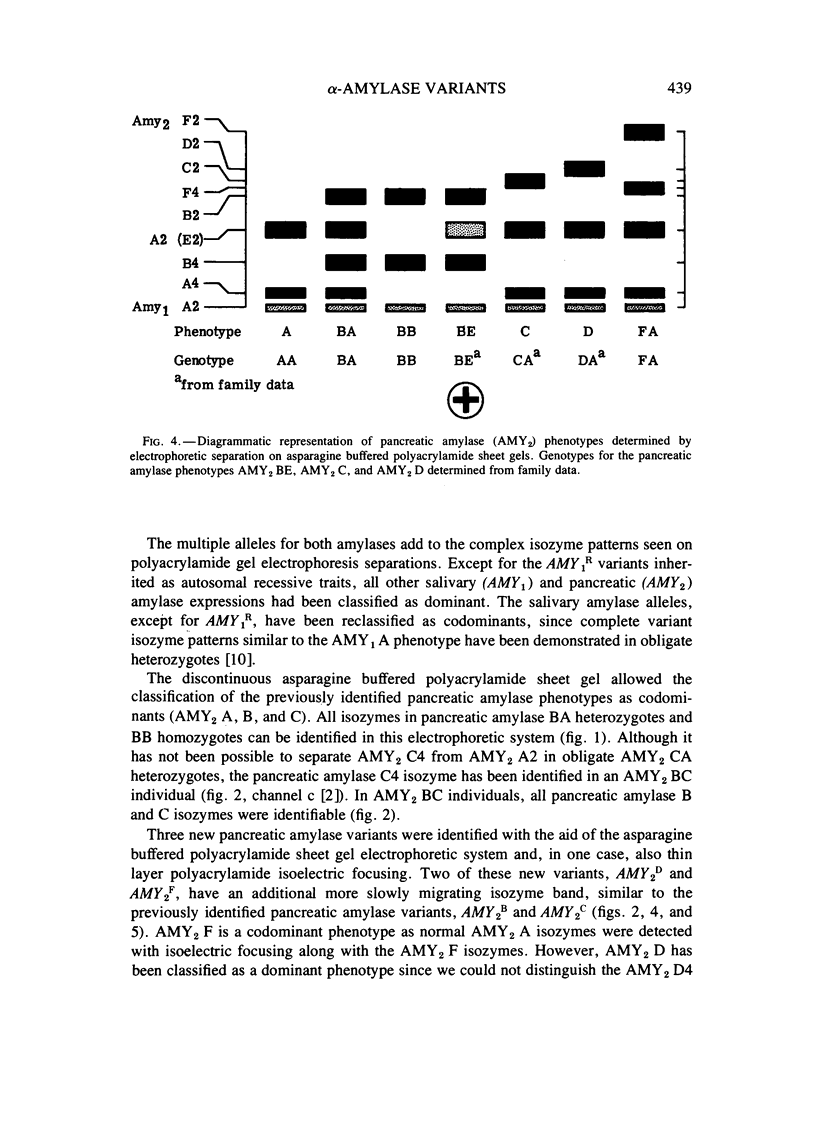
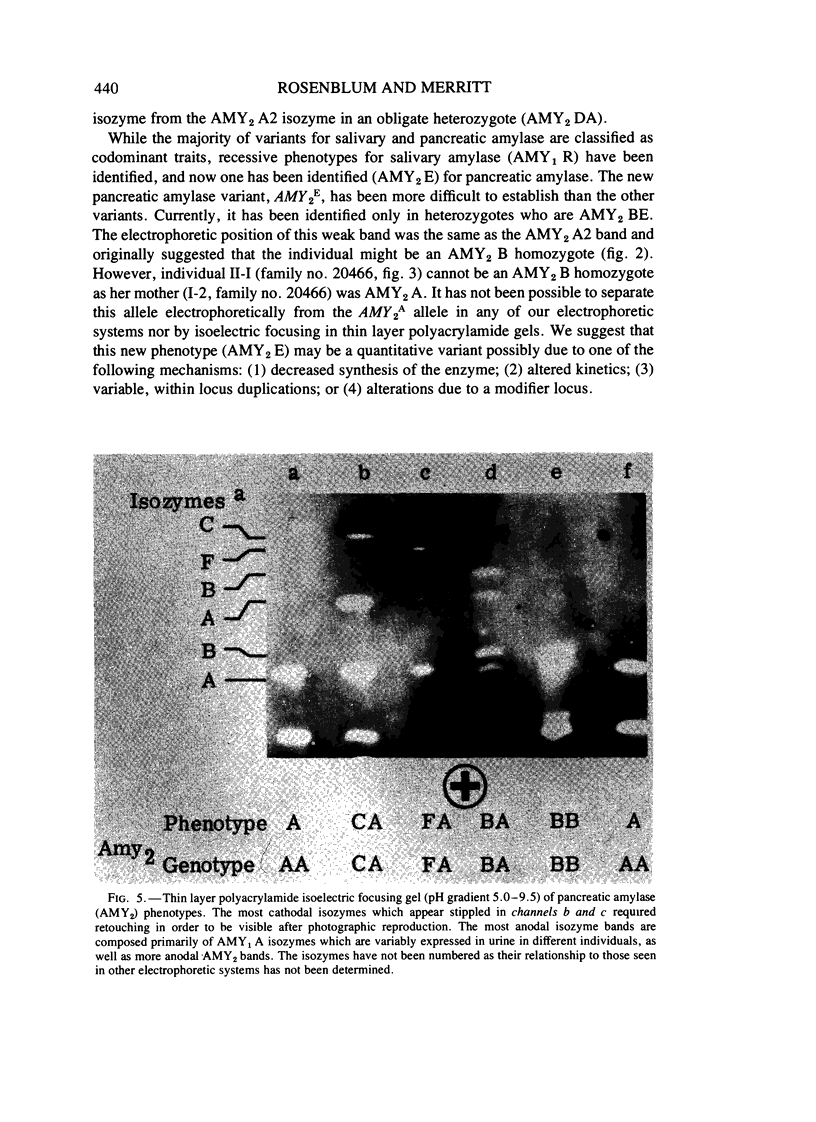
The genetic heterogeneity of human pancreatic alpha-amylase (alpha-1,4-glucan 4-glucanohydrolase, E.C. 3.2.1.1) has been better defined through the development of an asparagine buffered electrophoretic gel system. Three alleles had been identified for the pancreatic amylase locus, AMY2, with two variant alleles as autosomal dominant traits on Tris HCl buffered sheet gels. The asparagine buffered sheet gel now allows the differentiation of the genotypes AMY2B/AMY2B,AMY2B/AMY2A, and AMY2B/AMY2C, thus classifying these three alleles as codominants. Asparagine buffered polyacrylamide gels and thin layer polyacrylamide isoelectric focusing aided in the identification of three new pancreatic amylase variants: AMY2D,AMY2E, and AMY2F. AMY2E has been identified only in AMY2B and AMY2E individuals. This allele is proposed as a quantitative activity variant with essentially the same electrophoretic mobility as AMY2A. The other new autosomal variants have each been identified in single white families. AMY2D is dominant and AMY2F is a codominant trait as shown on thin layer polyacrylamide isoelectric focusing gels.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Karn R. C., Rosenblum B. B., Ward J. C., Merritt A. D., Shulkin J. D. Immunological relationships and post-translational modification of human salivary amylase (Amy) and pancreatic amylase (Amy) isozymes. Biochem Genet. 1974 Dec;12(6):485–499. doi: 10.1007/BF00486066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn R. C., Shulkin J. D., Merritt A. D., Newell R. C. Evidence for post-transcriptional modification of human salivary amylase (amyl) isozymes. Biochem Genet. 1973 Dec;10(4):341–350. doi: 10.1007/BF00485989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON N. E. Genetic tests under incomplete ascertainment. Am J Hum Genet. 1959 Mar;11(1):1–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt A. D., Lovrien E. W., Rivas M. L., Conneally P. M. Human amylase loci: genetic linkage with the Duffy blood group locus and assignment to linkage group I. Am J Hum Genet. 1973 Sep;25(5):523–538. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt A. D., Rivas M. L., Bixler D., Newell R. Salivary and pancreatic amylase: electrophoretic characterizations and genetic studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1973 Sep;25(5):510–522. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. C., Merritt A. D., Bixler D. Human salivary amylase: genetics of electrophoretic variants. Am J Hum Genet. 1971 Jul;23(4):403–409. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]