| Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) | Used by DRC/ Sustainable AntiRetroviral Access Program (SARA)/Kalembelembe Pediatric Hospital (KLL)
Summary of disclosure process:
When to disclose: Begin disclosure from when child is 5 years old, full disclosure by 11 years. Earlier start of disclosure process if a child asks questions, has an aggressive attitude or decreased adherence to treatment and care.
Who discloses: Health-care workers (HCWs), parents/caregiver with HCW's assistance if necessary
How disclosure is done: Approach comprises four steps, step duration depends on a child's level of psychological development.
- ▪
Step 1: Obtain good adherence to care and treatment and maintain confidentiality. - ▪
Step 2: Child learns about the functioning of the human body, acute and chronic illness. The child should understand that he/she has a chronic illness and the disease can be controlled by treatment. - ▪
Step 3: Disclosure (naming HIV) - ▪
Step 4: Support following disclosure.
Tools used during the disclosure process, adapted to the child's age: tales for younger children (5–8 years old); illustrated explanations (children 8–10 years old); comic strips for children older than 10 years (following full disclosure).
Key lessons learnt during implementation:
- ▪
Principal barriers to disclosure are parents' underestimation of children's knowledge of HIV and lack of initiative from HCWs.
|
| India/ WAG CHELSEA (Women's Action Group CHELSEA, where CHELSEAs tands for children, health, education, ladies, senior citizens, environment, awareness) | An approach used for provision of information to young children up to 9 years of age. This is done through:
- ▪
A series of informal group sessions targeted at children 5–9 years of age - ▪
Objective of sessions: To provide relevant information in a graded, child-friendly manner, and to help find answers to common questions. - ▪
Sessions are interactive and start with some simple activities like a poem/simple dance to relax the participants. - ▪
Subjects covered: General health and hygiene, healthy lifestyle, care during sickness and nutritious foods. The topic of illness caused by HIV is introduced without disclosing the child/parent's status. - ▪
At the end of each session children are asked to draw what they have learnt. - ▪
Follow-up review (with parent) of child's behaviour. Parents are prepared to answer questions that children may ask after sessions.
Tools used: Stories, mostly using animal characters; flash cards; role-play by counsellors; puppet shows; games/activities
Advantages of sessions:
- ▪
Prepare the background for full disclosure - ▪
Help explore children's feelings (e.g. guilt, sadness, anger) and provide an opportunity for expressing and dealing with them - ▪
Facilitate bonding and establishment of communication channels and support among the children and between children and counsellors.
|
| Kenya/ Muangalizi project, EDARP | A community health worker (CHW) model
When to disclose:
- ▪
Start process when caregiver and child are ready (when a child can process basic abstract information, preferably from 5 years of age). - ▪
Full disclosure to children from 10 years of age, preferably done at the time of diagnosis of HIV.
Who discloses: Caregiver disclosure preferred (or), facilitated by the health-care provider.
How disclosure is done: Process and not event, partial then complete.
- ▪
Help the caregiver understand the why, when, how of HIV communication. - ▪
Prepare the caregiver by supporting sustainable coping mechanisms. Anticipate challenges, model communication. - ▪
Address myths that the child may have; begin with what the child knows. - ▪
Disclose to significant adults to whom the child might disclose. - ▪
Provide follow-up support for the child and caregiver. Look out for adverse reactions. Observe play to assess knowledge and coping mechanisms. CHW to provide routine feedback on progress of the child.
Results and key lessons learnt:
- ▪
Trend: increased rates of disclosure with increasing age. - ▪
Challenges at operational level include HIV-related stigma, lack of an operational definition of disclosure, and lack of clear guidance on the disclosure process
|
| Sweden | When to disclose: Full disclosure before a child is 10 years old
Who discloses: HCW parent/caregiver
How disclosure is done: The “HIV school” is an annual residential school/extended weekend camp from when a child is 10–13 years old.
- ▪
The children learn self-awareness and awareness of others through play therapy; receive age-related education on physical development; sexual and personal relationships; viruses and infectiousness, and infectious disease control; acquire knowledge on HIV; receive grief and loss therapy; and meet other children in the same situation, exchange experiences and give each other support.
|
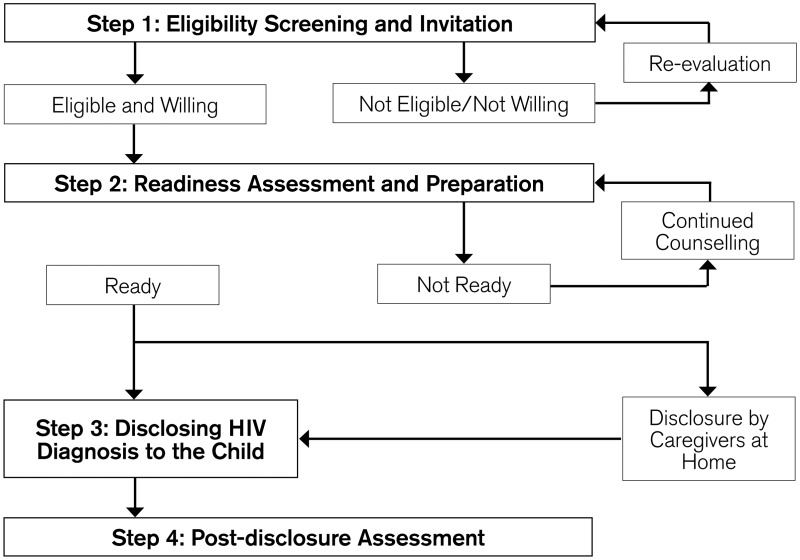
| Thailand disclosure model (see ) | Model was developed in 2005. It has been implemented and evaluated in two paediatric HIV clinics.
Summary of disclosure process:
When to disclose:
- ▪
Give information on the effect of illness on the immune system, and the necessity of taking medication to children less than 7 years old. - ▪
Start the disclosure process once a child is above 7 years of age.
Who discloses: Mostly caregiver or HCW in the presence of the caregiver
How disclosure is done: Model comprises four steps:
Eligibility screening and invitation Readiness assessment and preparation Disclosing the diagnosis of HIV to the child Post-disclosure assessment.
Comments:
- ▪
Model emphasizes counselling and communication, and is broken down into steps with written manuals for each step. - ▪
Child's readiness for disclosure is determined by caregiver and HCW, through a process of counselling and reviewing the child's clinical profile. - ▪
Caregivers are counselled and prepared to deal with the child's reactions, should they occur. - ▪
“Disclosure” is defined as telling children about their HIV status, and also providing information on HIV, self-care and HIV prevention.
Key lessons learnt during implementation:
- ▪
Making a decision to disclose is a difficult process for caregivers. They require time and support. - ▪
With good caregiver preparation, disclosure to the child is mostly smooth and without serious or untoward incidences. - ▪
It seems appropriate to start the disclosure process when a child is 7 years old. The disclosure process takes 1–2 years.
|
| MSF : Some tools and guidelines in used in Asia | Example 1: Guidelines developed by international NGOs working with children living with HIV. Provides guidance for both HCWs and caregivers. Guidelines have four major components.
Example 2: MSF guidelines, developed based on MSF field experience and aimed at facilitating the development of paediatric clinics at MSF sites. Guidelines have five components and include tools/job aids, widely used but not evaluated.
Example 3: HIV guidance for communication “Debbie book”
Example 5: Paediatric ART counselling training modules: have a section on basic counselling and disclosure |