This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-.

StatPearls [Internet].
Show detailsContinuing Education Activity
Segond fractures are a type of avulsion fracture on the lateral aspect of the knee. They are relatively common and are highly associated with an underlying anterior cruciate ligament injury. This activity reviews the cause, evaluation, treatment, and prognosis of Segond fractures. It also highlights the requirement of an interprofessional team approach to dealing with this condition.
Objectives:
- Identify the etiology and epidemiology of Segond fractures.
- Review the appropriate history, physical, and evaluation of Segond fractures.
- Outline the treatment and management options available for Segond fractures.
- Summarize interprofessional team strategies for improving care coordination and communication to improve patient outcomes.
Introduction
Segond fractures are defined as an avulsion type fracture of the lateral proximal tibia at the attachment of the anterolateral ligament.[1] They are especially important because they are pathognomonic of a more complex knee injury, an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) rupture.[2] Segond fractures confirmed on plain radiographs necessitate further evaluation and investigation to disprove concomitant knee injuries, as Segond fractures are almost never isolated injuries. The one exception to this is in the pediatric population, where Segond fractures are rarely noted to be isolated injuries. This is, however, not the norm, and even children should undergo thorough evaluation and investigation for knee ligamentous injury.[3]
Etiology
Segond fractures are usually caused by a forced mechanism of internal rotation with varus stress to the knee. It was first described by Paul Segond in his published works in 1879, following a cadaveric study of knee injuries.[2] This has later been correlated with ACL ruptures via the invention of more advanced imaging techniques. Segond also described a fibrous band at the point of the avulsion injury that has been defined as the anterolateral ligament.[4] More recent MRI studies however have been unable to identify any distinct ligamentous attachments associated with the anterolateral ligament, but do show evidence of posterior capsule and iliotibial band fibers attaching to the Segond fragment. These findings however are controversial.[5]
Epidemiology
Segond fractures have a high association with ACL ruptures, being present in 75% to 100% of cases. Conversely, 9-12% of ACL ruptures have an associated Segond fracture.[6][7]
ACL ruptures are a common orthopedic injury with an annual incidence of 68.6 per 100 000 people per year in the United States.[8] Incidence is slightly higher in male patients, with a peak incidence occurring later in men than in women - occurring in men aged 19-25 years of age with an incidence of 0.00241 and in women aged 14-18 with an incidence of 0.002276.
History and Physical
As Segond fractures have such a strong correlation with ACL ruptures, it is of no surprise that their history and mechanism of injury are also the same. Patients commonly describe a ‘pop’ following a twisting mechanism. They generally have an associated discomfort, swelling, decreased range of motion at the knee, and difficulty mobilizing.
There is no specific physical test for a Segond fracture, as they are generally noted on radiographs of the knee. However, as Segond fractures are often pathognomonic of ACL ruptures, testing for an intact ACL is imperative. Lachmann's test is the most sensitive physical examination maneuver in assessing for ACL tears, but there is also utility in the anterior drawer test. Integrity of all other ligaments of the knee should be assessed as well, including posterior drawer, varus/valgus stress testing, and pivot shift testing.
Evaluation
A Segond fracture can normally be diagnosed with a plain radiograph. A bony fragment (avulsion fracture) is seen in the anteroposterior view of the knee on the lateral aspect of the proximal tibia.
As previously discussed, with likely underlying ligamentous and or meniscal injuries, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is necessary for further evaluation, which may also highlight the more subtle Segond fractures.
Computed tomography is not usually used in the diagnosis of Segond fractures. While there is a much higher sensitivity for diagnosing fractures with CT Scan, MRI is the imaging modality of choice to identify the specific associated ligamentous injuries in the knees.
Treatment / Management
Initial treatment should be supportive. This includes resting the affected knee, elevating it whenever possible, simple analgesia, and icing the knee. Patients are highly likely to require walking aids, such as crutches. Having a knee brace early can also help support the knee before the consideration of surgery.
Surgical intervention is directed at underlying injuries rather than the Segond fracture itself. There is no evidence that Segond fractures need to be fixed. Furthermore, evidence suggests that ACL reconstructions are not at greater risk of failure with the presence of a Segond fracture.[9] While Segond fractures suggest higher instability associated with ligamentous knee injuries pre-operatively, the post-operative comparison suggests no difference in tested stability after the ligamentous injury is addressed.[10]
Direct repair of Segond fractures by repairing the anterolateral ligament is an option, as some suggest that it may restore rotational stability to the knee. Segond fractures can be repaired by either direct suture repair, suture anchor techniques, or screw fixation dependant on the size and characteristics of the fracture. Surgical repair of Segond fractures has shown good results with minimal complications, however, these were not compared to a control group.[2]
All surgical interventions should be undertaken following shared decision making with the patient and following informed consent. The decision to proceed with surgery is often largely swayed by the patient’s co-morbidities, activity levels, the patient’s expectations, and their likelihood of a favorable outcome.
Regardless of whether a patient elects for operative versus non-operative management, all patients need some form of rehabilitation from an interprofessional team approach. They will need to see a therapist for rehabilitation and may benefit from bracing to add stability and comfort to the knee.[11]
Differential Diagnosis
"Arcuate sign" is an avulsion fracture of the fibular head and is frequently mistaken for a Segond fracture on radiographs. The arcuate ligament complex or the posterolateral ligaments may avulse from the fibular head during a traumatic deformity to the knee. Like Segond fractures, this finding is pathognomonic for ligamentous knee injury and instability and should be investigated in a similar fashion. There are, however, subtle differences on plain radiographs, as an arcuate avulsion is normally more horizontal, lateral, and posterior than would be seen in a true Segond fracture.
Prognosis
The prognosis for a Segond fracture itself is good. As previously discussed, there has not been shown to be any benefit to fixing this fracture. Furthermore, the presence of Segond fractures do not appear to represent a higher risk of requiring revision surgery.[11] The main concern with regards to prognosis is appropriately addressing the associated ligamentous injuries in the knee. If addressed appropriately, patients will generally have a favorable outcome. Any alteration of the mechanics of the knee often leads to an increased risk of osteoarthritis (OA). It is well known that an ACL rupture leads to OA in a high proportion of patients. Unfortunately, ACL reconstruction has not been shown to completely reduce the risk of developing OA but has been shown to reduce its prevalence.[12]
Complications
The most common short-term complications from a Segond fracture are ongoing pain and stiffness. If the patient undergoes an ACL reconstruction, additional short to mid-term complications exist associated with the surgical procedure. Generally, however, ACL reconstruction is considered a safe procedure, with a 0.75% risk of a wound complication. Although thromboprophylaxis for ACL reconstruction is felt to be unnecessary, one paper has quoted deep vein thrombosis levels at 0.30% and pulmonary embolism levels at 0.18%.[13] The topic of thromboprophylaxis after ligamentous repair of the knee is controversial, and the decision to provide anticoagulation postoperatively should be made on a case by case basis by the surgeon considering each patient's specific medical comorbidities.
Deterrence and Patient Education
Patient education for Segond fractures and ACL ruptures is very challenging. Most injuries are caused by recreational or sporting injuries. Females, in particular, can decrease the risk of ligamentous injury to the knee by hamstring strengthening exercises and improved landing mechanics. Generally speaking, recreational activity should not be limited to prevent ligamentous injury, as exercise plays an important role in mental wellbeing and cardiovascular health.[14]
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Segond fractures will require input from multiple members of the interprofessional team. Diagnosticians and radiologists must recognize Segond fractures and other avulsion fractures from the posterolateral corner of the knee as being pathognomonic for a more sinister soft tissue injury warranting further evaluation. Surgical repair of ligamentous injuries requires a dedicated OR team to optimize patient outcomes. Finally, therapists and surgeons must work together to provide the appropriate rehabilitation protocol for each individual patient to assist in maximal return to function. [Level V]
Review Questions
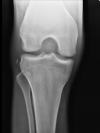
Figure
Segond fracture Case courtesy of Dr Maulik S Patel
References
- 1.
- Davis DS, Post WR. Segond fracture: lateral capsular ligament avulsion. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 1997 Feb;25(2):103-6. [PubMed: 9007767]
- 2.
- Ferretti A, Monaco E, Wolf MR, Guzzini M, Carli A, Mazza D. Surgical Treatment of Segond Fractures in Acute Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. Orthop J Sports Med. 2017 Oct;5(10):2325967117729997. [PMC free article: PMC5637969] [PubMed: 29051899]
- 3.
- Sferopoulos NK, Rafailidis D, Traios S, Christoforides J. Avulsion fractures of the lateral tibial condyle in children. Injury. 2006 Jan;37(1):57-60. [PubMed: 16246341]
- 4.
- Vincent JP, Magnussen RA, Gezmez F, Uguen A, Jacobi M, Weppe F, Al-Saati MF, Lustig S, Demey G, Servien E, Neyret P. The anterolateral ligament of the human knee: an anatomic and histologic study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012 Jan;20(1):147-52. [PubMed: 21717216]
- 5.
- Shaikh H, Herbst E, Rahnemai-Azar AA, Bottene Villa Albers M, Naendrup JH, Musahl V, Irrgang JJ, Fu FH. The Segond Fracture Is an Avulsion of the Anterolateral Complex. Am J Sports Med. 2017 Aug;45(10):2247-2252. [PubMed: 28499093]
- 6.
- Arneja SS, Furey MJ, Alvarez CM, Reilly CW. Segond fractures: not necessarily pathognemonic of anterior cruciate ligament injury in the pediatric population. Sports Health. 2010 Sep;2(5):437-9. [PMC free article: PMC3445053] [PubMed: 23015973]
- 7.
- Yoon KH, Kim JS, Park SY, Park SE. The Influence of Segond Fracture on Outcomes After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. Arthroscopy. 2018 Jun;34(6):1900-1906. [PubMed: 29487001]
- 8.
- Sanders TL, Maradit Kremers H, Bryan AJ, Larson DR, Dahm DL, Levy BA, Stuart MJ, Krych AJ. Incidence of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears and Reconstruction: A 21-Year Population-Based Study. Am J Sports Med. 2016 Jun;44(6):1502-7. [PubMed: 26920430]
- 9.
- Gaunder CL, Bastrom T, Pennock AT. Segond Fractures Are Not a Risk Factor for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Failure. Am J Sports Med. 2017 Dec;45(14):3210-3215. [PubMed: 28949245]
- 10.
- Melugin HP, Johnson NR, Wu IT, Levy BA, Stuart MJ, Krych AJ. Is Treatment of Segond Fracture Necessary With Combined Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction? Am J Sports Med. 2018 Mar;46(4):832-838. [PubMed: 29286825]
- 11.
- Slagstad I, Parkar AP, Strand T, Inderhaug E. Incidence and Prognostic Significance of the Segond Fracture in Patients Undergoing Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2020 Apr;48(5):1063-1068. [PMC free article: PMC7163245] [PubMed: 32119785]
- 12.
- Friel NA, Chu CR. The role of ACL injury in the development of posttraumatic knee osteoarthritis. Clin Sports Med. 2013 Jan;32(1):1-12. [PMC free article: PMC6548436] [PubMed: 23177457]
- 13.
- Jameson SS, Dowen D, James P, Serrano-Pedraza I, Reed MR, Deehan D. Complications following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in the English NHS. Knee. 2012 Jan;19(1):14-9. [PubMed: 21216599]
- 14.
- Sadoghi P, von Keudell A, Vavken P. Effectiveness of anterior cruciate ligament injury prevention training programs. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012 May 02;94(9):769-76. [PubMed: 22456856]
Disclosure: Edward Skinner declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Donald Davis declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Matthew Varacallo declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
- Far Posterior Approach for Rib Fracture Fixation: Surgical Technique and Tips.[JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2024]Far Posterior Approach for Rib Fracture Fixation: Surgical Technique and Tips.Manes TJ, DeGenova DT, Taylor BC, Patel JN. JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2024 Oct-Dec; 14(4). Epub 2024 Dec 6.
- Stress Reaction and Fractures.[StatPearls. 2025]Stress Reaction and Fractures.Kiel J, Kaiser K. StatPearls. 2025 Jan
- The presence of a Segond fracture in ACL-injured patients is associated with increased internal tibial rotation on preoperative MRIs.[J Orthop Surg Res. 2024]The presence of a Segond fracture in ACL-injured patients is associated with increased internal tibial rotation on preoperative MRIs.Zhang ZY, Wang HD, Wang SY, Maimaitijiang P, Wang C. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Dec 4; 19(1):824. Epub 2024 Dec 4.
- Review FBN1-Related Marfan Syndrome.[GeneReviews(®). 1993]Review FBN1-Related Marfan Syndrome.Dietz H. GeneReviews(®). 1993
- Review Citrullinemia Type I.[GeneReviews(®). 1993]Review Citrullinemia Type I.Quinonez SC, Lee KN. GeneReviews(®). 1993
- Segond Fracture - StatPearlsSegond Fracture - StatPearls
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...