This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-.

StatPearls [Internet].
Show detailsContinuing Education Activity
Hemangiomas, colloquially termed "strawberry marks", are the most common benign tumor of infancy and are caused by endothelial cell proliferation. Congenital hemangiomas are visible at birth whereas infantile hemangiomas appear later. This activity describes the evaluation and management of hemangiomas and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in caring for patients with hemangiomas.
Objectives:
- Describe the epidemiology of hemangiomas.
- Describe the histopathology of hemangiomas.
- Explain when hemangiomas should be considered on a differential diagnosis.
- Summarize the treatments of hemangiomas.
Introduction
Hemangiomas, also known as hemangiomas of infancy or infantile hemangiomas (IH), are the most common benign tumor of infancy[1]. They are often called "strawberry marks" due to their clinical appearance. Endothelial cell proliferation results in hemangiomas. There are different types of hemangiomas. Congenital hemangiomas are visible at birth whereas infantile hemangiomas appear later in infancy. Infantile angiomas are characterized by early, rapid growth followed by spontaneous involution.
Etiology
The etiology of infantile hemangiomas is poorly understood, but there are several hypotheses. The most likely hypothesis suggests that hypoxic stress upregulates expression of GLUT 1 and VEGF leading to the mobilization of endothelial progenitor cells. The progenitor cells are positive for CD133 and CD31[2]. Another hypothesis suggests that placental trophoblasts serve as the origin of stem cells for hemangiomas[3]. A third hypothesis suggests that IH development involves vasculogenesis from progenitor cells (de novo formation) as well as the formation of new vessels from existing ones (angiogenesis)[2]. Angiogenic factors have been suggested to act on endothelial cells and pericytes to initiate the formation of a capillary network[4].
Epidemiology
Infantile hemangioma is the most common benign vascular tumor of infancy and affects about 4% to 5 % of newborns[5]. It is due to an abnormal cluster of small blood vessels that occurs during the first year of life. Infantile hemangiomas occur more frequently in Caucasian infants compared to other racial groups. There is also a female predominance with a female to male ratio of up to 5:1. Premature infants, babies born with low birth weights or with prenatal hypoxia are also prone to developing hemangiomas. Infantile hemangiomas are common in infants with elder mothers. The disorder is often seen after post chorionic villus sampling or in multiple births with twins or triplets. Most cases are sporadic but infantile hemangiomas have been seen to run in families. They have been associated with an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance[6] although no specific genes are implicated.[7]
Histopathology
Upon histopathological examination of an infantile hemangioma, a multinodular pattern fed by a single arteriole can be seen[8]. The nodules are composed of hyperplastic endothelial cells, pericytes with and without lumens and prominent basement membranes. The involution stage of the hemangioma is marked by dilated vascular lumens and flattened endothelial cells (which give the IH its lobular architecture). Fibrosis becomes pronounced as involution progresses[9]. During involution, IH expresses a tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase, which also inhibits angiogenesis[4]. Placenta-associated vascular antigens staining, including FcRII, Lewis Y antigen (LeY) and merosin, is also observed during involution. Upon immunohistochemical evaluation of the endothelial cells, they express CD31, von Willebrand factor, and urokinase in all phases. Infantile hemangiomas express glucose transporter protein-1 (GLUT 1) during all phases of their development. Thus, immunohistochemical studies can be used to distinguish the development stages of IH.
History and Physical
Infantile hemangioma is usually absent at birth but can present with several types of precursor lesions. These include a pale area of vasoconstriction, an erythematous macule, a telangiectatic red macule or blue bruise-like patches. Infantile hemangiomas become clinically apparent within 1 to 4 weeks. The localization is ubiquitous, and they may occur on the skin and mucosal surfaces. The majority present as a single localized cutaneous hemangioma but infantile hemangioma may be multifocal or segmental. Hemangiomas occur most commonly on the head and the neck and are seen in 60 % of cases. This is followed by lesions on the trunk in 25% of cases, and least commonly, on the extremities, seen in 15% of cases[6]. Hemangiomas can be superficial, deep or mixed with components of both superficial and deep layers. Superficial lesions involve the superficial dermis and are raised, lobulated and bright red. Deep hemangiomas, also called subcutaneous hemangiomas, arise from the reticular dermis and/or the subcutis layer, and appear as a bluish-hued nodule, plaque or tumor. Mixed hemangiomas have features of both locations.
The natural history of infantile hemangioma has a triphasic evolution:
- Early proliferative or growth phase: Usually, there is rapid growth during the first three months and gradual growth in months five to eight of life. Deep infantile hemangiomas tend to proliferate for a longer period and can be seen doing so until the ninth or twelfth month of life[3].
- Plateau phase: The lesion remains stable and quiescent for a period of months (between 6 and 12 months of life).
- Involution phase: This may occur within the first year of life and can continue for several years. The regressive infantile hemangiomas become softer and more compressible, and the color changes from bright red to purple or gray. The skin may return to normal, but often there are residual changes (excessive fibrofatty tissue, telangiectasia, skin laxity)[3][7].
Evaluation
Most Infantile hemangiomas are diagnosed clinically. A skin biopsy can be performed if there is any doubt. Infantile hemangiomas stain positive for GLUT 1. Imaging studies like ultrasonography, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are indicated to confirm the diagnosis and the extent of deep IH without superficial changes. This is done to rule out associated anomalies and to differentiate proliferating IH from other tumors.
Treatment / Management
Most infantile hemangiomas do not require treatment because they resolve on their own. Complicated infantile hemangiomas requires treatment. Recently, beta blockers such as oral propranolol (2mg/kg/day) have been shown to be effective as first line therapy. However, the side effect profile of propanolol includes bradycardia, hypotension, bronchospasm, and hypoglycemia. Oral prednisone (2-4mg/kg/day) is an alternative therapy that can be used. The high dose of prednisone would have to be slowly tapered over weeks to months. Prednisone's adverse reactions would include irritability, sleep disturbance, hypertension, bone demineralization, cardiomyopathy, and growth retardation. The topical beta blocker, timolol, is used for smaller,superficial, and uncomplicated, infantile hemangiomas.
Intralesional and topical corticosteroids can be used to treat small focal lesions[3]. Otherwise, surgical excision may be considered to prevent complications. Surgical excision involves removing the residual fibrofatty tissue and this improves treatment outcomes.
Pulsed dye laser (PDL) is indicated for telangiectasia, but PDL remains controversial for infantile hemangiomas that are deep[10].
Differential Diagnosis
When considering hemangiomas, there are various differentials that fall into this category. It is important to consider each of them to obtain the accurate diagnosis.
- Congenital hemangioma
- Pyogenic granuloma
- Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma
- Tufted hemangioma
- Venous malformation
- Capillary malformation: port wine stain
- Macrocystic lymphatic malformation
- Malignant tumors: sarcoma, a cutaneous location of neuroblastoma or lymphoma
Prognosis
The prognosis is very good for uncomplicated IH and there is complete involution in the majority of cases. 50% of hemangiomas will resolve in 5 years, 70% by 7 years and 90% by 9 years. Approximately 8% of IH leave cosmetic disfigurement and require some intervention.
Complications
The complications depend on the patient's age and on the hemangioma's size and location. The complications of IH are listed below.
- Ulceration is the most common complication and occurs in up to 10% of cases. Locations with higher risk of ulceration include the anogenital area, lower lip, axilla, and neck.
- Ophthalmologic complications include amblyopia, astigmatism, myopia, retrobulbar involvement and tear duct obstruction.
- Airway obstruction can be seen in nasal, subglottic and laryngeal passages.
- Difficulties feeding can be seen with perioral or lip hemangiomas.
- Visceral hemangiomatosis, especially multifocal hemangiomas (greater than or equal to 5 skin lesions), may be associated with liver or gastrointestinal involvement.
- Cosmetic disfigurement can be seen with large facial area involvement or involvement of the nasal tip (called Cyrano nose), ears and perioral area.
- PHACES syndrome manifests with a large segmental facial hemangioma (greater than or equal to 5 cm). The PHACES syndrome acronym stands for posterior fossa malformations, hemangioma of the cervicofacial region, arterial anomalies, cardiac anomalies, eye anomalies, and Sternal or abdominal clefting[3].
- LUMBAR syndrome manifests with lumbosacral hemangiomas and may be associated with underlying developmental anomalies. The LUMBAR syndrome acronym represents lumbosacral hemangioma, urogenital anomalies, myelopathy, bony deformities, anorectal or arterial, and renal anomalies[3]
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
The goal in identifying hemangiomas and treating them is to prevent their complications. One of the most serious complications includes permanent cosmetic disfigurement that may have a psychosocial impact on the patient and the family.
The management of IH is best done with an interprofessional approach. This would consist of a team with pediatricians, dermatologists, ophthalmologists, and other specialists.
Review Questions
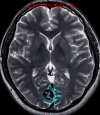
Figure
Cerebral Cavernous Hemangioma. Image demonstrating a cerebral cavernous malformation, also known as cavernous hemangiomas. Contributed by S Bhimji, MD
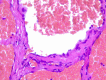
Figure
Hemangioma, H/E 20x. The image shows flattened endothelium lining a dilated vessel, engorged with erythrocytes. Contributed by Fabiola Farci, MD
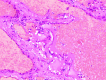
Figure
Hemangioma, H/E 10x. Vascular neoplastic lesion, benign. Cavernous hemangioma is lined by normal and mature endothelial cells. Contributed by Fabiola Farci, MD
References
- 1.
- Hemangioma Investigator Group. Haggstrom AN, Drolet BA, Baselga E, Chamlin SL, Garzon MC, Horii KA, Lucky AW, Mancini AJ, Metry DW, Newell B, Nopper AJ, Frieden IJ. Prospective study of infantile hemangiomas: demographic, prenatal, and perinatal characteristics. J Pediatr. 2007 Mar;150(3):291-4. [PubMed: 17307549]
- 2.
- Yu Y, Flint AF, Mulliken JB, Wu JK, Bischoff J. Endothelial progenitor cells in infantile hemangioma. Blood. 2004 Feb 15;103(4):1373-5. [PubMed: 14576053]
- 3.
- Holland KE, Drolet BA. Infantile hemangioma. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2010 Oct;57(5):1069-83. [PubMed: 20888458]
- 4.
- Takahashi K, Mulliken JB, Kozakewich HP, Rogers RA, Folkman J, Ezekowitz RA. Cellular markers that distinguish the phases of hemangioma during infancy and childhood. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jun;93(6):2357-64. [PMC free article: PMC294441] [PubMed: 7911127]
- 5.
- Léauté-Labrèze C, Harper JI, Hoeger PH. Infantile haemangioma. Lancet. 2017 Jul 01;390(10089):85-94. [PubMed: 28089471]
- 6.
- Bruckner AL, Frieden IJ. Hemangiomas of infancy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003 Apr;48(4):477-93; quiz 494-6. [PubMed: 12664009]
- 7.
- Margileth AM, Museles M. Cutaneous hemangiomas in children. Diagnosis and conservative management. JAMA. 1965 Nov 01;194(5):523-6. [PubMed: 5897362]
- 8.
- TOMPKINS VN, WALSH TS. Some observations on the strawberry nevus of infancy. Cancer. 1956 Sep-Oct;9(5):869-904. [PubMed: 13364872]
- 9.
- Tan ST, Velickovic M, Ruger BM, Davis PF. Cellular and extracellular markers of hemangioma. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000 Sep;106(3):529-38. [PubMed: 10987458]
- 10.
- Stier MF, Glick SA, Hirsch RJ. Laser treatment of pediatric vascular lesions: Port wine stains and hemangiomas. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008 Feb;58(2):261-85. [PubMed: 18068263]
Disclosure: Amal Chamli declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Payal Aggarwal declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Radia Jamil declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Noureddine Litaiem declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
- Capillary Infantile Hemangiomas.[StatPearls. 2025]Capillary Infantile Hemangiomas.Koka K, Zeppieri M, Patel BC. StatPearls. 2025 Jan
- Oral Hemangiomas.[StatPearls. 2025]Oral Hemangiomas.Lyssy LA, Puckett Y. StatPearls. 2025 Jan
- Peer Play.[StatPearls. 2025]Peer Play.Scott HK, Cogburn M. StatPearls. 2025 Jan
- Review Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency.[GeneReviews(®). 1993]Review Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency.Lichter-Konecki U, Caldovic L, Morizono H, Simpson K, Ah Mew N, MacLeod E. GeneReviews(®). 1993
- Review Adenosine Deaminase Deficiency.[GeneReviews(®). 1993]Review Adenosine Deaminase Deficiency.Hershfield M, Tarrant T. GeneReviews(®). 1993
- Hemangioma - StatPearlsHemangioma - StatPearls
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...