NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
National Center for Biotechnology Information (US). Genes and Disease [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 1998-.
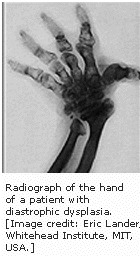
Diastrophic dysplasia (DTD) is a rare growth disorder in which patients are usually short, have club feet, and have malformed handsmand joints. Although found in all populations, it is particularly prevalent in Finland.
The gene whose mutation results in DTD maps to chromosome 5 and encodes a novel sulfate transporter. This ties in with the observation of unusual concentrations of sulfate in various tissues of DTD patients. Sulfate is important for skeletal joints because cartilage—the shock-absorber of joints—requires sulfur during its manufacture. Adding sulfur increases the negative charge within cartilage, which contributes to its shock-absorbing properties.
A great deal of further research must be done before this condition is fully understood and effective therapies are developed.
- Genome view see gene locations
- Entrez Gene collection of gene-related information
- BLink related sequences in different organisms
- Research articles online full text
- Books online books section
- OMIM catalog of human genes and disorders
- GeneReviews a medical genetics resource
- Diastrophic dysplasia - Genes and DiseaseDiastrophic dysplasia - Genes and Disease
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...
