The content of this book is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 Unported license. To view the terms and conditions of this license, visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Varki A, Cummings RD, Esko JD, et al., editors. Essentials of Glycobiology [Internet]. 4th edition. Cold Spring Harbor (NY): Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2022. doi: 10.1101/glycobiology.4e.15
Sialic acids (Sias) are abundant on vertebrate glycoproteins, glycolipids, and milk oligosaccharides, as well as on some microbial surface glycans, mediating diverse functional roles. Originally discovered within the Deuterostome lineage of animals and associated microbes, they are actually a subset of a more ancient family of α-keto acid monosaccharides with a 9-carbon backbone called nonulosonic acids (NulOs), which are also found in some Eubacteria and Archaea. Biosynthesis of all NulO-glycans requires the activation of NulO to a CMP-sugar, before the NulO is transferred to glycan acceptors. NulOs are remarkable for the number and the type of functional groups on one monosaccharide. Further complexity arises from various epimers, modifications, and diverse linkages to other glycans, making these molecules well-suited to carry information for glycan–protein, cell–cell, and pathogen–host recognition. NulOs are among the most rapidly evolving classes of monosaccharides in nature and exist in tremendous variety, particularly in the microbial world. Given their high density and widespread location on vertebrate cells, Sias also exert many functions via electronegative charge, such as repulsion of cell–cell interactions, protein stabilization, ion binding, and ion transport.
DISCOVERY AND GENERAL CLASSIFICATION
Early nomenclature of these molecules was tied to their discovery, being first isolated by Gunnar Blix from salivary mucins in 1936 and independently by Ernst Klenk from brain glycolipids in 1941. Blix named his substance “sialic acid” after the Greek word for saliva (σíαλoν), and Klenk named his “neuraminic acid” for neurons in the brain. By the time the relationship of these substances became evident, both names were already in use and have persisted. Although 5-N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac, sometimes called “NANA”) is the most common sialic acid (Sia) in humans, the Sia family is comprised of related structures (Figure 15.1) that vary at the C-5 carbon, including 5-N-glycolylneuraminic acid (Neu5Gc) and 3-deoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-non-2-ulosonic acid (also known as 3-deoxy-nonulosonic acid, 2-keto-3-deoxy-nononic acid, or Kdn) with a hydroxyl group at C-5. Similar 9-carbon backbone 2-keto acid monosaccharides were later discovered in some bacterial lipopolysaccharides and initially called “bacterial sialic acids.” The resulting confusion was resolved by suggesting that the term “sialic acid” (Sia) be limited to its original use in describing neuraminic acid (Neu), Kdn, and their derivatives in deuterostomes and their pathogens, and that the term “nonulosonic acid” (NulO) be used to encompass the entire group of 9-carbon backbone non-2-ulosonic acids (Figure 15.1). Base structures representing the larger family of NulO molecules are shown in Figure 15.1 for comparison. This chapter will largely deal with the biology, metabolism, and functions of Sias in mammals. The evolution, distribution, and functions of the larger family of NulOs are briefly described toward the end of this chapter.

FIGURE 15.1.
Sialic acids (Sias) and other nonulosonic acids (NulOs). As shown in the figure, Sias are a subset of NulOs. All NulOs carry a negatively charged carboxylate (C-1) and a 3-carbon exocyclic glycerol-like side-chain (C-7 to C-9). The anomeric center (C-2) (more...)

FIGURE 15.2.
Diversity in sialic acid linkages. Sialic acids in vertebrates are commonly (but not exclusively) found in α-glycosidic linkage to the C-3 or C-6 hydroxyl of galactose, the C-6 hydroxyl of N-acetylgalactosamine, the C-8 hydroxyl of another sialic (more...)
THE SIALIC ACID FAMILY
The most common Sia form in humans is Neu5Ac, a relatively strong acid (pKa=2.6) with the electron-withdrawing C-1 carboxylate attached to the C-2 anomeric carbon. The exocyclic glycerol-like side chain (C-7, C-8, and C-9, each carrying a hydroxyl group) provide opportunities for hydrogen bonding. The N-acetyl group facilitates hydrophobic interactions, changing to hydrophilic properties when it is replaced with an N-glycolyl group. Each of these moieties can contribute to binding specificities of Sia-binding proteins and functions of Sia-containing glycans.
SIALOGLYCAN DIVERSITY
Many publications assume that Neu5Ac is the Sia present in a given biological sample, and it is indeed common in vertebrates. But in addition to Neu5Gc, a second level of diversity arises from various natural modifications (e.g., mono- or multiple-O-acetylation at any hydroxyl groups, 8-O-methylation, 8-O-sulfation, and 9-O-lactylation), some of which are also common. The carboxylate group at C-1 can condense with hydroxyl groups of adjacent sugars to form an uncharged lactone, or with a free amino group at C-5 to form an uncharged lactam. Such modifications can determine or modify recognition by Sia-binding proteins and direct Sia function. Despite this complexity, it may be sufficient in some biological studies to simply know that a generic Sia residue is present at the terminal position of a glycan under study (a red diamond in the symbol nomenclature system) (Figure 15.2). Dehydro-Sias also exist in nature. For example, Neu2en5Ac (2,3-dehydro-2-deoxy-N-acetylneuraminic acid, sometimes called DANA) has natural inhibitory properties toward sialidases and was the starting point for the design of more potent inhibitors such as the anti-influenza drug Relenza (Chapter 57).
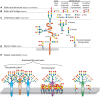
FIGURE 15.3.
Hierarchical levels of sialome complexity. The sialome can vary at the following complexity levels: (A) sialic acid core and core modification: esterification (with various groups), O-methylation, lactonization, or lactamization yielding more than 80 (more...)
The sum total of diverse sialoglycans on a cell is dubbed its “sialome.” As mentioned, Sias are often found as the terminal (outermost) saccharide on branches of N-glycans, O-glycans, glycosphingolipids, milk oligosaccharides, and occasionally capping the side chains of glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchors (Chapter 12). A useful conceptualization of the sialome is as a “forest canopy” of the cell-surface glycan “forest” (the whole glycome) (Figure 15.3). At the outermost level are different Sia structures (leaves and flowers), which are in glycosidic linkage to underlying linear and branched oligosaccharides (stems and branches) (see Figures 15.2 and 15.3), which in turn are components of glycoproteins and glycolipids (the tree trunks). At the cell surface, glycolipids and glycoproteins organize into lateral domains (forests). Just as the forest varies greatly from place to place, the sialome varies among cell types and among domains on a given cell surface, variations that serve specific functions. As with the glycome, each cell type in each species expresses its own distinct sialome. For example, although mammalian liver sialoglycans are most abundant on glycoproteins, brain sialoglycans are much more abundant as sialoglycolipids (Chapter 11), so much so that they are termed “gangliosides” for the nerve ganglia on which they were discovered. The sialome also varies markedly in response to environmental cues.
Sias can also exist as internally linked structures rather than on termini of glycans. In vertebrates, the terminal Sia of a glycan chain is rarely extended further, except with another Sia (Figure 15.3). Among bacteria, Sias and the related NulOs can also be found in diverse cellular structures, including capsular polysaccharides, lipopolysaccharide O-antigens or as part of flagella, pili, or structures such as the cell wall or S-layer (Chapter 21). Bacteria with close relationships to vertebrate hosts often mimic the terminal placement of Sias on capsules and O-antigens. However, many NulOs of bacteria, including Sias, can occur as internal glycan components within repeating units of polysaccharides, which have also been reported in some invertebrates such as echinoderms. In the latter, the C-4 hydroxyl of Neu5Ac is sometimes glycosylated with other monosaccharides such as fucose, galactose, and glucose. Overall, it appears that we do not yet know the full extent of sialoglycan diversity in nature.
POLYSIALIC ACIDS
Polysialic acid (polySia, previously called PSA) is a linear homopolymer of Sias that sometimes reaches lengths of more than 100 residues. Shorter chains of two to three residues, called oligosialic acids, are common components of gangliosides (Figure 15.3 and Chapter 11) and are found occasionally as terminal structures on glycoprotein glycans. PolySia is a prominent structural feature of a highly select group of acceptor proteins, the best studied of which is the neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM). Beginning early in vertebrate brain development, long polySia chains (Neu5Acα2-8)n are added to NCAM (often then called PSA-NCAM), on the termini of two specific N-glycans. The large hydration shell formed by polySia markedly increases the hydrodynamic volume of its protein carrier and interferes with NCAM's natural cell–cell adhesion function. PolySia thus converts an adhesive protein into a repelling one. During brain development, a high level of polySia likely ensures that neural precursors can migrate to their final anatomical sites. Once a destination is reached, polySia is down-regulated and firm adhesion proceeds, keeping the cells in place. When the sialyltransferases (STs) responsible for polySia formation are genetically ablated in mice, some nerve progenitor cells adhere prematurely, become stuck in place and fail to reach their proper destination. In contrast to the above-mentioned “repulsive field effects,” polySia can also act an “attractive field,” binding and locally concentrating neurotrophic factors like BDNF and FGF2. Notably, human genetic and molecular evidence indicate that variations in polysialylation may be a factor in human psychiatric diseases like schizophrenia.
PolySia is found less abundantly on a few other proteins, including another cell adhesion molecule (SynCAM 1), a peptide receptor (neuropilin-2), and on O-glycans of fish egg glycoproteins. It is also a key component of the capsular polysaccharides of certain pathogenic bacteria (e.g., Escherichia coli K1, K92; Neisseria meningitidis serogroups B and C). The linkages between Sia units in polySia chains vary in bacteria, including α2-8, α2-9, and alternating α2-8/α2-9. The α2-8-polySia in E. coli K1 is also called colominic acid, which can be O-acetylated at Sia C-7 or C-9. The α2-9-polySia in N. meningitidis serogroup C can also be O-acetylated at Sia C-7 or C-8. A bacteriophage that attacks polySia-expressing bacteria produces a highly specific endosialidase that only clips chains that are ≥8 residues long. This enzyme (Endo-N) and its inactivated form (which binds polySia) are powerful tools to study polySia functions.
HUMAN LOSS OF N-GLYCOLYLNEURAMINIC ACID
Neu5Gc is common in mammals including human's closest evolutionary relatives (bonobos and chimpanzees). However, it is not synthesized by humans, because of a fixed single-exon deletion mutation in the CMAH gene encoding a hydroxylase that converts CMP-Neu5Ac to CMP-Neu5Gc. Why did the human lineage lose Neu5Gc? Many pathogens use Sias to bind and infect vertebrates (Chapter 42), and some specifically target Neu5Gc. An organism recognizing Neu5Gc may have been the cause of initial selection of the CMAH null state. Subsequent development of anti-Neu5Gc antibodies in CMAH-null females may have then reduced fertility with CMAH-positive males by killing their sperm, possibly serving to speciate the null population. Other lineage-specific losses of Neu5Gc expression may have occurred in a similar fashion. This is part of a broader consideration of Sias as both a pathogen target and a physiological regulator, a combination that apparently contributed to rapid evolution of both Sia expression patterns and Sia-binding proteins, especially of the Siglecs (Chapter 35).
Despite CMAH inactivation in humans, traces of Neu5Gc are found in normal human tissues. This, as well as the presence of Neu5Gc in human tumor cells and tissues, apparently represents metabolic incorporation of Neu5Gc ingested from foods, particularly “red meats.” Most healthy humans have circulating anti-Neu5Gc antibodies, raising the possibility that their subsequent interaction with metabolically incorporated Neu5Gc contributes to inflammation in diseases that correlate with red meat consumption, such as atherosclerosis and epithelial cancers, pathologies uncommon in Neu5Gc-positive primates. Other possible consequences of human Neu5Gc loss include resistance to some Neu5Gc-binding animal pathogens such as E. coli K99, and the emergence of Neu5Ac-preferring pathogens exclusive to human hosts such as the malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum and the toxin from Salmonella Typhi.
An as-yet-unexplained observation is the scarcity of Neu5Gc in the brains of all vertebrates studied to date, including those that have high Neu5Gc levels in other tissues. The evolutionary advantage of excluding Neu5Gc from this vital organ is unknown but may relate to selection pressure by unknown pathogens and/or selective roles of Neu5Ac in optimal brain development and function.
METABOLISM
Synthesis of Sialoglycans
Metabolic pathways of Neu5Ac in vertebrates are shown in Figure 15.4. Neu5Ac is derived by reaction of ManNAc-6-P with phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP). The ManNAc-6-P is produced by a bifunctional enzyme, UDP-GlcNAc-2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase, coded by the GNE gene. Missense, recessive mutations in GNE cause hereditary inclusion body myopathy (HIBM) in humans (Chapter 45), and gene inactivation causes embryonic lethality in mice. Reaction of ManNAc-6-P with PEP yields Neu5Ac-9-P, which is then dephosphorylated by a specific phosphatase to release free Neu5Ac in the cytoplasm. The same pathway can use Man-6-P instead of ManNAc-6-P to generate Kdn. In contrast, Neu5Ac biosynthesis in prokaryotes involves direct reaction of ManNAc with PEP, a pathway that proceeds without a Neu5Ac-9-P intermediate. Many other bacteria synthesize 9-deoxy forms of NulOs using pathways bearing ancient homology to the Neu5Ac synthetic pathways. Notably, synthetic unnatural mannosamine derivatives can enter the Sia biosynthetic pathway in cells, allowing metabolic engineering of the cell surface with modified Sias (Chapter 56).

FIGURE 15.4.
Metabolism of N-acetylneuraminic acid in vertebrate cells. The schematic (left) represents the pathways and compartments of biosynthesis of Neu5Ac in vertebrates: biosynthesized in the cytosolic compartment, converted to activated CMP-Neu5Ac in the nucleus, (more...)
The β-anomers of free Sias are converted to CMP-Sias by reactions with CTP, which occur in the nuclear compartment, for unknown reasons. The CMP-Sia products then return to the cytosol and transported into Golgi compartments by a CMP antiporter, which concentrates them in the Golgi lumen (Chapter 5). In contrast, prokaryotic CMP-Sias are synthesized in the cytoplasm and used without compartmentalization. In eukaryotes, cytosolic CMP-Sia feeds back to inhibit GNE. In a rare human disease called sialuria, dominant mutations in the allosteric site of GNE result in failed feedback regulation and overproduction of Sia.
The linkage-specific STs mentioned earlier are type II membrane proteins in animals, with signals leading to their Golgi localization. Animal STs share amino acid sequence motifs (sialylmotifs) that include shared sites for CMP-Sia recognition (Chapters 6 and 8). In contrast, prokaryotic STs emerged independently by convergent evolution, do not have sialylmotifs, and some do not even share homology. In addition to the Sia linkage, several eukaryotic STs show strong preferences for glycolipids versus glycoproteins and/or the terminal saccharides and sequences. Modified Sias, such as Neu5Gc, O-acetylated species, and unnatural synthetic Sias can be used to form activated CMP-Sias, which can serve as donors for STs. Some mammalian STs transfer both Neu5Ac and Kdn, but others transfer only one or the other. All result in α-sialyl linkages. Furthermore, “trans-sialidases” of some pathogenic trypanosome species and some bacteria transfer Sias from one sialoside to form another (Chapter 43). Although trans-sialidases tend to be specific regarding the sialyl linkage they generate, they can be promiscuous toward the donor and acceptor glycans.
Modifications of Sialic Acids
Once CMP-Neu5Ac is converted to CMP-Neu5Gc in the cytosol, there is no known way to reverse the reaction, perhaps explaining the accumulation of diet-derived Neu5Gc in human tissues. Further structural diversity in Sias is generated by enzymatic modification of Neu5Ac, Neu5Gc, and Kdn via reactions that occur in the lumen of the Golgi and related organelles, and on mature sialoglycoconjugates, as well as at the CMP-Sia level. Different enzymes may O-acetylate Sia at C-7/9 (most common) and C-4 (less common). O-Acetyltransferases (some likely yet to be discovered) appear to have specificity for Sias of different glycosidic linkages or carried on different classes of mature glycoconjugates, or on CMP-Neu5Ac. For example, a human O-acetyltransferase (CASD1) acetylates CMP-Neu5Ac using acetyl-CoA as the acetyl donor and the resulting CMP-Sia is then used to transfer O-acetylated Neu5Ac to proteins. In bacteria, Neu5Ac O-acetylation can occur by at least two routes. In group B Streptococcus, O-acetylation occurs intracellularly, prior to CMP-activation via the action of the NeuD enzyme. E. coli K1 also has a NeuD homolog, but it appears to de-O-acetylate prior to capsule assembly, then NeuO O-acetylates the assembled polySia. Other substitutions of the hydroxyl groups arise from the use of appropriate donors (S-adenosylmethionine for methylating Sias or 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphosulfate for sulfating Sias). With the exception of Neu5Gc, other modified Sias do not appear to be very effective substrates for reactivation by vertebrate CMP-Sia synthetases, so their catabolism also involves enzymes like Sia O-acetylesterases.
Enzymatic Release of Sialic Acids
Sias are released from glycoconjugates by sialidases, also historically called “neuraminidases.” The term “sialidase” is now preferred, but influenza virus sialidases are still called neuraminidases because of the use of “N” in their strain designation (e.g., H1N1 influenza), in which N1 refers to its neuraminidase/sialidase. In eukaryotes, sialidases are encoded by NEU genes, of which there are four in the human genome. Although NEU1 and NEU4 are thought to act primarily intracellularly in endosomal/lysosomal compartments to recycle sialoglycans, NEU1 can also be recruited to the cell surface where it may regulate sialylation and modulate receptor-mediated signaling. In contrast, NEU3 appears primarily on the cell-surface and has a preference for cleaving gangliosides, whereas NEU2 exists in the cytosol, presumably to recycle sialoglycans that enter that compartment following autophagy or phagocytosis. Mammalian sialidases have also been implicated in the disordered inflammation seen in colitis and sepsis.
Many microorganisms, including many pathogens, express sialidases. Unlike the case with STs, bacterial, fungal, and invertebrate sialidases are evolutionarily related to their vertebrate counterparts. In contrast, viral sialidases that are essential for their virulence represent distinct families. The 3D structures of pathogen sialidases are used for drug development (Chapter 42). Sialidases vary in their substrate specificity from highly selective (e.g., the α2-3-specific sialidase SpNanB and SpNanC from Streptococcus pneumoniae) to broadly acting (e.g., the α2-3, α2-6, α2-8 sialidase from Arthrobacter ureafaciens and SpNanA from S. pneumoniae). The products of sialidases also differ with free Sias as the most common ones (e.g., released by SpNanA) whereas 2,7-anhydro-Sias (e.g., released by SpNanB) and 2,3-dehydro-2-deoxy-sialic acids (Sia2ens) (e.g., released by SpNanC) are less common. Interestingly, some pathogen sialidases have additional lectin (sugar-binding) domains that appear to direct the action of the enzymes to particular sites.
Some Sia linkages resist release even by sialidases with broad specificity. A branched α2-3Sia on the brain ganglioside GM2 requires a special helper protein (GM2-activator) to facilitate its cleavage, and mutation of GM2-activator protein results in GM2 buildup in the brain (Chapter 44). O-Methylation and O-acetylation of Sias also can hinder or even prevent hydrolysis by sialidases, as is the case for 4-O-acetyl group. These properties are likely biologically significant, but have not been well investigated.
Microbial sialidases and trans-sialidases (see also Chapter 43) can be powerful virulence factors that may promote cellular invasion, unmask potential binding sites, and modulate the immune system. Sias liberated by sialidases at mucosal sites also provide nutrients for some bacteria or provide access to underlying carbohydrates. Viral neuraminidases facilitate release and spreading of newly formed viruses, and specific viral neuraminidase inhibitors are widely used as the antiviral drugs such as anti-influenza A virus drugs Relenza and Tamiflu (Chapter 42).
Sialic Acid Recycling and Degradation
Once a free Sia molecule is released in the lysosome of a vertebrate cell, it is returned to the cytosol by a specific exporter (SLC17A5, also called Sialin), in which it is either reused or degraded. Human mutations in Sialin cause Salla disease and infantile sialic acid storage disease, resulting in accumulation of Sia in lysosomes and excretion of excess Sia in the urine. Some pathogens scavenge Sias from the extracellular space, using high-efficiency transporters to concentrate them from trace levels. In contrast, there is no evidence for plasma membrane Sia transporters in eukaryotic cells. Nevertheless, free Sias can be taken up into mammalian cells via fluid-phase macropinocytosis, eventually arriving in the lysosomes, from which they are exported into the cytoplasm by Sialin. Intact sialoglycans can also be taken up and transported to lysosomes, where sialidases release Sias for delivery to the cytoplasm and then to the nucleus to be reused by the cellular CMP-Sia synthetase. However, at the whole-body level, free Sias in the bloodstream derived from cellular sources or digestive processes are rapidly excreted in the urine. Thus, uptake of sialoglycoproteins (followed by lysosomal release by NEU1 and export by Sialin) may better account for the incorporation of dietary Neu5Gc in human tissues.
In vertebrates, O-acetylated Sias are de-O-acetylated by Sia-specific O-acetylesterases, including the human enzyme coded by the SIAE gene, which may regulate B-cell development and immune tolerance by modulating recognition by Siglecs (Chapter 35). Enzymes with Sia 9-O-acetylesterase activity are also found in some bacteria and viruses. Influenza C virus and some coronavirus hemagglutinins bind specifically to 9-O-acetyl Sia for host infection, and their O-acetylesterases help in their further dissemination after newly budded virions are released from host cells. Notably, all known O-acetylesterases specific for C-9 ester are incapable of releasing O-acetyl esters from C-7. However, a 7-O-acetyl group can migrate to C-9 under physiological conditions and thus become a substrate for these enzymes. This process can even result in stepwise de-esterification of 7/8/9-tri-O-acetyl Sias, which do exist in nature. Some vertebrate and viral esterases are specific for 4-O-acetyl groups, but relatively little is known about their functions. Among bacteria, Sia-specific esterases appear to participate in normal processes of mucus turnover in the mammalian gut, but when in excess, they have also been linked to disease states such as colorectal cancer.
If not reused or excreted, Sias are degraded by a cytosolic Sia-specific pyruvate lyase (encoded by NPL) that cleaves the molecule into N-acyl-mannosamine and pyruvate. Such N-acyl-mannosamines may either reenter the Sia biosynthetic pathway after phosphorylation by kinases in eukaryotes, or be further metabolized via conversion to N-acyl-glucosamines and their corresponding phosphates, with eventual deacylation (Figure 15.4). Notably, GlcNGc derived from Neu5Gc can either be de-acylated or converted to UDP-GlcNGc or even to UDP-GalNGc, which can provide donors for glycosyltransferases to incorporate the monosaccharide into glycans, such as chondroitin sulfate with GalNGc instead of GalNAc. Sia-specific pyruvate lyases also exist in various microorganisms, allowing the use of host Sias as a nutrient source. In some bacteria, pathways for Sia biosynthesis and breakdown appear in the same genomes, suggesting that recycling of Sias may also occur in some bacteria. In other bacterial taxa, there is either anabolic or catabolic machinery.
METHODS FOR STUDYING SIALIC ACIDS
Sias are amenable to analysis as components of isolated glycans, as released monosaccharides, and also in situ on cell surfaces. Among animal monosaccharides, Sias have a distinct molecular mass that makes them readily identifiable by mass spectrometry (MS), currently among the most sensitive methods for glycan analysis (Chapters 50 and 51). The glycerol-like side chain of Sias is uniquely sensitive to periodate oxidation under very mild conditions, providing a method to selectively generate aldehyde groups only on sialoglycans (remarkably, this chemical reaction can even show this specificity when applied to some intact cell surfaces). Subsequent addition of a tagged nucleophile (e.g., biotin hydrazide) results in a tag (e.g., biotin) covalently bound to Sia that was originally cleaved by periodate. Selective release of most Sias from intact cells or isolated sialoglycans is accomplished using microbial sialidases. Use of α2-3 or α2-8-specific sialidases can provide some insight on Sia linkages as well. Sia-glycosides are also more susceptible to acid hydrolysis than most other sugars, being released using 0.1 m HCl or even with weak acids like 2 m acetic acid or propionic acid at 80°C (albeit still with some loss or migration of labile modifications). This allows selective release of Sias from complex glycans for subsequent analysis by chromatographic methods. Free Sias react with 1,2-diamino-4,5-methylenedioxybenzene (DMB) to generate fluorescent compounds amenable to qualitative and quantitative high-pressure liquid chromatography. There are still some major limitations to methods available for Sia analysis. For example, some mass spectrometric methods result in selective loss of Sias before mass detection. Some Sia-linkages are partly or completely resistant to sialidases and some are even relatively resistant to acid release. In terms of identifying Sia modifications, the most accurate analysis requires complete release and purification with the modifications intact. The stability of each modification to analytical conditions must be considered—for example, O-acetyl groups are labile to common methods that use alkaline conditions (permethylation and beta-elimination).
Sia-binding lectins are also useful for detecting sialoglycans and their linkages in situ and on isolated sialoglycans. Sambucus nigra (elderberry) lectin binds selectively to α2-6-linked Sias and Maackia amurensis lectins bind selectively to α2-3-linked Sias. Because plants do not express Sias, these lectins may perhaps deter animal ingestion. Alternatively, the natural ligands of these lectins may not be Sias. Improved probes are now being developed, taking advantage of the fact that many microbes have spent millions of years optimizing their binding to vertebrate sialomes (e.g., the B subunits of various toxins). An interesting tool for detecting a specific Sia modification is the hemagglutinin of influenza C or bovine coronavirus, which bind specifically to 9-O-acetyl Sias on isolated sialoglycans, cells, and tissues, if the esterase function is inactivated.
FUNCTIONS OF SIALIC ACIDS
Sias are endowed with a rich diversity of chemical modalities within a single monosaccharide, which evolution uses to modulate the biophysical environment, to mask underlying glycans, and for specific recognition by complementary Sia-binding proteins that mediate biological processes. These functions are not mutually exclusive—for example, highly sialylated molecules with major biophysical roles (such as mucins) may also express specific sialoglycans that serve as ligands in recognition processes. For simplicity, different roles of Sias are addressed separately below.
Biophysical Roles of Sialic Acids
Mucins are heavily glycosylated O-GalNAc-modified sialoglycoproteins secreted or membrane-bound at epithelial surfaces in airways and in the gastrointestinal and urogenital tracts of animals (Chapter 10). Mucins can be remarkably large (several in the range of 5 to >20 MDa). Their dense anionic charge and their propensity to bind water make them efficient as a hydrating and protective barrier at tissue surfaces in contact with the environment. On mucins, as well as other glycoproteins, closely spaced O-GalNAc-linked sialoglycans generate extended polypeptide configurations that would collapse without glycosylation. Clustered sialoglycans along the polypeptide chain can also protect the underlying protein from proteases. Membrane-bound sialoglycans on glycoproteins and glycolipids, which are often quite dense, provide cell surface anionic charge that acts as a barrier and regulates cell surface functions. An extreme example of these biophysical effects is polySia, whose functional impacts are detailed above.
Sialic Acid Recognition by Pathogens and Toxins
Given Sia abundance on cell surfaces (see Figure 15.3), it is not surprising that numerous animal pathogens evolved to target these molecules. Indeed, highly specific Sia-binding proteins were first discovered on human pathogens and their toxins. In the search for host cell receptors for influenza viruses, it was discovered that isolated viruses cross-linked red blood cells, resulting in hemagglutination. Over time, the red cells dispersed and could no longer be agglutinated by fresh viruses. This led to the concept of a viral “hemagglutinin” (a term still used in virus typing; e.g., the “H” in H1N1) that binds to a receptor on the red blood cell, which is also susceptible to a “receptor destroying enzyme” from the virus. The component released by receptor-destroying enzyme was identified as Sia, the hemagglutinin as a Sia-binding protein, and the receptor-destroying enzyme as a sialidase (viral neuraminidase, the “N” in H1N1). Interestingly, the Sia-linkage specificity of the hemagglutinin defines host restrictions; with bird influenza virus preferentially binding to Sias in α2-3-linkage and human virus to Sias in α2-6-linkage. Scientists monitoring influenza virus outbreaks test α2-3- versus α2-6-specificity to detect potential emerging human influenza strains. Molecules designed to block the viral sialidases are useful anti-influenza drugs (Chapter 57).
Sia-specific binding proteins are widespread in pathogens and include numerous viral hemagglutinins, bacterial adhesins, bacterial toxins, and parasite-binding proteins (see Table 15.1 for a few examples). Helicobacter pylori causes stomach ulcers and cancers. It expresses a Sia-specific adhesin called SabA, which contributes to its chronic colonization of the stomach lining. The merozoite stage of the malarial parasite P. falciparum can bind to erythrocyte sialoglycans to initiate cell entry. Several bacterial toxins also target sialoglycans. Cholera toxin and the structurally related E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin both bind to Sias on ganglioside GM1 on the intestinal epithelium, whereas tetanus and related botulinum toxins bind to more complex gangliosides (Chapter 37). The toxin from the human pathogen Salmonella Typhi binds specifically to Neu5Ac on glycans but not Neu5Gc; influenza C virus expresses a hemagglutinin that binds only to 9-O-acetylated Sias. The complexities of Sia diversification are thought to be the outcome of an ongoing evolutionary “arms race” between animals and microbial pathogens (Chapter 20). In this regard, it is notable that O-acetyl and N-glycolyl groups on Sias can limit action of bacterial sialidases and block the binding of some pathogens. Alternately, the same modifications may facilitate binding of pathogens that have adapted to them. Sialoglycans at environmental surfaces (like mucins) or free in biological fluids might provide protection by virtue of their “decoy” inhibition of microbial adherence and/or sialidases. The evolutionary persistence of sialoglycans despite their role in virulent diseases suggests critical physiological roles, some of which are addressed below.
TABLE 15.1.
A few classic examples of sialic acid–binding proteins in nature
Sialic Acid Recognition within Vertebrates
Sias in vertebrates can act as “biological masks,” preventing recognition of underlying glycans (especially β-linked Gal residues) by intrinsic and extrinsic glycan-binding proteins. They are also essential components of recognition molecules, with roles that vary according to cell type, tissue type, and species. The first mammalian Sia-binding protein found was the complement regulatory molecule factor H, a soluble serum factor that binds cell-surface Sias and protects cells from autoimmune attack, providing recognition of “self-associated molecular patterns” (SAMPs), which are also recognized by CD33-related Siglecs (Chapter 35). Human mutations in the Sia-binding site of factor H result in atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome in humans, a disease caused by excessive complement activation, because of the failure of factor H function. Other variations of the factor H polyanion binding region increase the risk of age-dependent macular degeneration, a common cause of blindness resulting from inflammation in the eye retina.
Sias are also involved in interactions of white blood cells with the endothelial lining of blood vessels. Circulating neutrophils must bind to and move across the blood vessel wall to clear bacterial infections in tissues. Endothelial cells respond to nearby bacterial infection and quickly send Sia-binding lectins to their surface. E- and P-selectins (Chapter 34) connect with passing neutrophils, which have the complementary sialoglycans on their surface lipids or proteins. Initially rolling, and finally snagged, neutrophils then respond to other signals (including cytokines presented by GAGs; Chapter 17) and work their way into the tissue to fight bacteria. Without Sia-dependent binding by E- and P-selectins, inflammation is compromised and persistent tissue infections ensue. A related lectin, L-selectin, is also involved in trafficking of lymphocytes from blood to lymph.
Siglecs (Sia-binding immunoglobulin-like lectins) constitute a Sia-binding family within the I-type lectins (Chapter 35). In humans, there are 14 Siglecs with sialic acid–dependent functions (13 and 17 are missing in humans and 12 does not bind sialic acid), all but one of which are found on the surface of different blood cell types. In several cases, binding of Siglecs to their sialoglycan targets on other cells or their own cell surface modulates ongoing immune responses, either damping them to protect from hyperimmune reactions or activating them. The one Siglec not found in the immune system, Siglec-4 (myelin-associated glycoprotein), is in the nervous system, where it aids cell–cell interactions between nerve cells and myelin, the protective and insulating membrane sheath essential to rapid nerve conduction.
Notably, all the above examples of vertebrate Sia-recognizing proteins were discovered serendipitously, via the unexpected abrogating effect of sialidases on a biological process. To date, there has been no systematic effort to search for other examples, but other likely vertebrate Sia-binding lectins are PECAM-1, PILRs, L1-CAM, HMGB-1, and an as-yet-unidentified uterine agglutinin.
The many functions of Sias in vertebrates make these molecules particularly attractive targets for microbes that co-exist with the host, whether harmoniously or not. As discussed elsewhere, there are several independent mechanisms of Sia mimicry, which promote bacterial interactions with host factor H and Siglecs to enable survival in the host.
Lectins in Organisms without Sialic Acids
Some Sia-binding lectins are found in organisms that do not themselves appear to express Sias (see Table 15.1 for examples). In these cases, Sia binding may defend against sialylated pathogens, such as the protein limulin in the hemolymph (blood-like fluid) of the horseshoe crab, which can trigger foreign cell lysis. Sia-binding lectins in plants, such as elderberry shrubs, may suppress consumption by animals. Of course, some of these Sia-binding properties might be incidental, with the true lectin ligands being related to prokaryotic NulOs such as Leg or Pse, and/or Kdo, which is also found in some plants.
SIALIC ACIDS IN DEVELOPMENT AND MALIGNANCY
Although cell lines deficient in Sias grow in culture, disruption of Sia synthesis in mice results in lethality at embryonic day 8.5, with poor differentiation of nerve cells as well as cardiac and skeletal muscle cells. In contrast, disruption of some ST genes in mice is relatively well tolerated, in some cases because of complementarity among related genes. For example, both St8sia2 and St8sia4 must be deleted in mice to fully eliminate polySia, resulting in severe developmental deficits in the brain. Likewise, both St3sia2 and St3sia3 must be deleted to fully block terminal sialylation of brain gangliosides, resulting in early motor and behavioral deficits. Deleting both St3gal4 and St3gal6, but not either one separately, results in loss of leukocyte rolling on selectins. One benefit of having multiple genes and enzymes that make a Sia linkage (see Figure 15.2) is that the results of single gene mutations are tempered. In contrast, human mutations in ST3GAL5 alone result in severe early seizures with profound deficits in postnatal cognitive and motor development, mutations in the ST3GAL3 gene result in intellectual impairment, and mutation of human ST8SIA2 is associated with mental illness. Mutations of other STs in mice cause defects in immune system development and function and/or fertility. In Drosophila, mutation of the single ST results in severe phenotypes.
Cellular and environmental regulation of Sia fine-structure implies roles for Sia modifications. Certain classes of lymphocytes have O-acetylated Sias, and mutations in a sialic acid esterase results in altered immune function. Expression of polySia and O-acetylation of brain gangliosides varies with developmental stage and location. Differences in O-acetylation of brain gangliosides are reported between cold- and warm-blooded species and between awake and hibernating animals. Developmental regulation of Neu5Gc expression and O-acetylation expression in the gut mucosa occurs in response to microbial colonization and has been suggested to protect against microorganisms. Similarly, although adult bovine submandibular glands produce large amounts of highly O-acetylated mucins, this modification is scarcely present in the corresponding fetal tissue. The types and linkages of endothelial, plasma protein, and erythrocyte Sias can undergo marked changes in responses to inflammatory stimuli. Abnormalities have also been reported in mice depleted in 9-O-acetyl Sias (transgenic for a viral 9-O-acetylesterase). The physiological roles of these Sia modifications are not well-established, and there is much yet to be learned.
Certain changes in Sias are also characteristic of cancer. In general, total Sia increases and there are quantitative changes in linkages, with α2-6Gal(NAc) linkages becoming particularly prominent. O-Acetylation of Sia at C-9 can disappear (colon carcinomas) in concert with increased levels of O-acetylesterase activity in fecal specimens. Alternatively, 9-O-acetyl-GD3 becomes more prominent in melanomas and basal cell carcinomas. Increased expression of polySia may also facilitate cell migration by some cancers. The precise mechanisms by which Sia changes enhance tumorigenesis and/or invasive behavior remain uncertain, although it has been proposed that tumor sialoglycans enhance metastatic dissemination by their ability to alter functions of galectins (Chapter 36) and by enhancing the binding of tumor cells to endothelial, leukocyte, and platelet selectins (Chapter 34). Increased sialylation may also mask antigenic sites on tumor cells, which also become more like “self” and evade immune surveillance by engaging factor H and/or Siglecs. Regardless of the mechanisms involved, certain sialylated molecules are also specific markers for some cancers and potential ligands for targeted therapies (Chapter 47).
SIALIC ACIDS IN PHARMACOLOGY
Each role of Sias in physiology and pathology provides opportunities for therapeutic development. Best known are competitive inhibitors of viral sialidases (Relenza and Tamiflu), which hinder budding and spreading of susceptible strains of influenza A and B viruses (Chapters 42 and 57). Another strategy to block Sia-binding pathogens has been to engineer therapeutic sialidases to remove pathogen-binding sites on human tissues. Efforts to use sialoglycans themselves as anti-infectives have not been as successful, although sialylated milk oligosaccharides have been claimed to have some value. Sia-mimetic drugs designed to bind to and block selectins (e.g., rivipansel) have shown promise in human trials as anti-inflammatory drugs. Strategies are also under study for inducing immune attack of cancer cells with sialoglycoconjugates and for suppressing antibody responses by engaging Siglecs on B cells.
Many sialoglycoproteins have been developed as drugs, including erythropoietin to enhance blood cell production and monoclonal antibodies to target various diseases including cancers (Chapter 57). In these cases, appropriate sialylation is a desired goal, not only to optimize serum half-life, stability, and receptor binding, but also to assure FDA approval. Chemical, recombinant, and other methods are thus in use to maintain appropriate sialylation on biological drugs, and efforts are underway to engineer “humanized” glycosylation (including sialylation) in yeast, insect, or plant cells (that do not typically express Sias but are more economical sources of expressed glycoproteins) (Chapter 56). Notably, differences in sialylation of endogenous and exogenous erythropoietin are used by the World Anti-Doping Agency to detect illicit administration, and have resulted in rescinding of many Olympic and Tour de France medals.
The presence of Neu5Gc is of potential importance in biotherapeutics, because humans have circulating anti-Neu5Gc antibodies, with marked variations in levels and isotypes. The use of animal-derived proteins in biopharmaceutical development can lead to Neu5Gc incorporation, with unwanted results. Similarly, cell therapies under development often use animal sera or support cells, which can provide Neu5Gc to the cell products. Finally, Neu5Gc on animal organs likely contributes to the failure of xenotransplantation (use of animal organs in humans), which led to engineering of CMAH knockout pigs.
EVOLUTIONARY DISTRIBUTION OF SIALIC ACIDS
Early studies suggested species specificity in the occurrence of specific Sia variants. With analytical improvements, it became evident that Sia variations are more widely expressed across species but occur at differing levels. Sias are prominent in the deuterostome lineage (Chapter 27), which comprises vertebrates and some “higher” invertebrates (such as echinoderms). Indeed, with exceptions, Sias are not generally reported in plants or invertebrates. This may change as molecular techniques improve. For example, insects were believed to be free of Sias until their discovery in cicada Malpighian tubules and Drosophila brains, and later identification of a single Drosophila gene (SiaT) with sequence similarities to mammalian STs. When SiaT is inactivated, flies suffer locomotor abnormalities and defects in neuromuscular junctions. Although of very low abundance, Sias are both present and crucial to the survival of Drosophila. Sias have also been reported in the nervous systems of behaviorally complex protostomes like octopus and squid. On the other hand, no Sias or ST genes were found in the well-studied round worm, Caenorhabditis elegans (Chapter 25).
It appears that Sias (other than Kdn, which probably appeared earlier) were “invented” in a common ancestor of protostomes and deuterostomes and then became essential in deuterostomes, while being partially or completely discarded in some protostome lineages. Interestingly, there is wide variation in Sia expression and complexity within deuterostomes, with the sialome of echinoderms appearing very complex and that of humans being among the simplest. Although expression of Neu5Gc and 9-O-acetylated Sias is very common in deuterostomes, exceptions exist, such as independent loss of Neu5Gc biosynthesis in humans, New World monkeys, Sauropsids (birds and reptiles, the descendants of dinosaurs), the Pinnipedia and Musteloidia members of the Carnivora, and likely in Monotremes.
Sias in capsular polysaccharides and lipopolysaccharides can have beneficial effects for microbes in their hosts, protecting them from complement activation and/or antibody recognition of underlying glycans, also sometimes engaging the Siglec family receptors (Chapter 35) to dampen innate immune cell reactivity. The bacterial enzymes involved in synthesizing and metabolizing Sias do not appear to be the result of lateral transfer of genes from animals, but evolved independently, apparently being “reinvented” at least twice from a more ancient prokaryotic NulO pathway. In fact, Sias that are synthesized by some present-day vertebrate pathogens share closer phylogenetic relationships to biosynthetic pathways for legionaminic acids than to Sia pathways of vertebrates. Other microbes “steal” Sias from their host using various mechanisms to achieve “molecular mimicry.” Neisseria gonorrheae even has a remarkably efficient surface ST that can scavenge trace amounts of CMP-Neu5Ac from body fluids of its exclusive host, humans.
PROKARYOTIC NONULOSONIC ACIDS
A diverse array of Sia-like molecules (see Figure 15.1) with ancient evolutionary roots has been described in Bacteria and archaea and the relevant biosynthetic pathways are predicted to occur in ∼20% of prokaryotes. These molecules differ from Sias in several ways. First, they lack a hydroxyl group at C9 and nearly all described forms have amino functions at C7 that are often decorated with substituents.
Di-N-acetyllegionaminic acid (Leg5,7Ac2) is a common well-characterized microbial NulO initially discovered in the LPS of Legionella pneumophila. Like Neu5Ac, it has a D-glycero-D-galacto stereochemistry in the backbone, but with an amino function instead of a hydroxyl at C-7 and no hydroxyl at C-9. Di-N-acetylpseudaminic acid (Pse5,7Ac2), first described in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, has a similar structure to Leg5,7Ac2 but with opposite stereochemical configurations at C-5, C-7, and C-8 (Figure 15.1). Later discoveries of NulOs include 4epi-di-N-acetyllegionaminic acid (4eLeg5,7Ac2), 8epi-di-N-acetyllegionaminic acid (8eLeg5,7Ac2), di-N-acetylacinetaminic acid (Aci5,7Ac2), 8epi-di-N-acetylacinetaminic acid (Figure 15.1). Following the earlier tradition of naming NulO classes by the organism in which they were first reported, acinetaminic acid was first described in Acinetobacter baumannii. Recently, another novel NulO was reported in Fusobacterium nucleatum. Although the configuration is still tentatively defined, “fusaminic acid” was coined to refer to the new NulO—a 4-epimer of pseudaminic acid with a hydroxyl instead of an amino function at C7. NulOs are rather unusual among monosaccharides in being activated as CMP-linked sugars. Interestingly, the 8-carbon α-keto acid monosaccharide 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonic acid (Kdo; see Chapter 21) is also activated in a CMP-linked form and the enzymes involved in activation are homologous. Although the distribution of Kdo is limited to Gram-negative bacteria and plants, NulOs are more widespread among bacterial taxa and archaea. Together, the evidence suggests that NulO biosynthetic pathways are an ancient invention by the common ancestor of all life-forms, but persisted only in some taxa. Sias were likely “invented” early in life on earth. They appear in bacteria from diverse taxa with varied lifestyles in the environment or with animals, including “lower” animals often in internally linked positions that do not mimic known structures in “higher” animals. Sias became prominent in animals when the Deuterostome lineage emerged at the Cambrian Explosion ∼530 million years ago. Sequence homology suggests that ancient prokaryotic NulO biosynthetic pathways later became an evolutionary template that allowed some microbes to reinvent Sias of “higher” animals by convergent evolution. Many important commensals and pathogens use Sia mimicry to evade the vertebrate immune system by one or more of several established mechanisms. Some of the prokaryotic NulOs that share the same stereochemistry as Sias can engage in mechanisms of Sia mimicry, at times conveying pathogenic properties in unintended hosts following environmental exposure or zoonosis. Some examples of bacterial NulO-containing structures are provided (Figure 15.5).
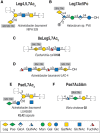
FIGURE 15.5.
Examples of legionaminic and pseudaminic acid–containing glycans in bacteria and Archaea, selected from the Bacterial Carbohydrate Structure Database (BCSDB). The sialic acid–like monosaccharides legionaminic acid (Leg) (A,B), 8-epi-legionaminic (more...)
ABBREVIATED NAMES OF NONULOSONIC ACIDS
Complete chemical names of NulOs are rather cumbersome for routine use. For example, the name of the closed ring Neu5Ac is 5-acetamido-3,5-dideoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-non-2-ulopyranosonic acid. Beyond the currently known core units (Figure 15.1), additional substitutions are designated by letter codes (Ac, acetyl; Gc, glycolyl; Me, methyl; Lt, lactyl; and S, sulfate), and these are listed along with numbers indicating their location relative to the carbons (e.g., 9-O-acetyl-8-O-methyl-N-acetylneuraminic acid is Neu5,9Ac28Me). Among NulOs as a whole, there are now at least 138 known structural variants. If one is uncertain of the exact type of molecule present, the generic abbreviations Sia or NulO should be used. Partial structural information can also be incorporated. For example, a Sia of otherwise unknown type with an O-acetyl substitution at the C-9 position could be written as Sia9Ac. With regard to the bacterial NulOs, the names Leg, Pse, 4eLeg, 8eLeg, and Aci are often used synonymously with the 5,7-di-N-acetylated forms of these molecules (Figure 15.1). To be consistent with Sia nomenclature (as with Neu) and to avoid confusion, it is recommended that the substituted forms be specified whenever possible (e.g., Leg5,7Ac2). Free amino forms of the prokaryotic NulOs have not to our knowledge been reported in nature. Instead, many different types of substitutions of the C-5 and C-7 positions have been reported for the exclusively prokaryotic NulOs, including acetyl (Ac), formyl (Fo), (R)-hydroxybutyryl (3RHb), (S)-3-hydroxybutyryl (3SHb), 4-hydroxybutyryl (4Hb), 3,4-dihydroxybutyryl (3,4Hb), acetimidoyl (Am), N-methyl-acetimidoyl (AmMe), methyl (Me), D-alanyl (Ala), N-acetyl-D-alanyl (AlaNAc), N-methyl-5-glutamyl (GluNMe), L-glyceryl (Gr), and/or 2,3-di-O-methyl-glyceryl (Me2Gr) groups. Additional variety derives from acetyl groups at O4 and O8, as well as acetyl, N-acetyl-glutaminyl (GlnNAc), and glycyl (Gly) substitutions at O8.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors acknowledge contributions to previous versions of this chapter by the late Roland Schauer and appreciate helpful comments and suggestions from Hamed Jafar-Nejad.
FURTHER READING
- Blix FG, Gottschalk A, Klenk E. 1957. Proposed nomenclature in the field of neuraminic and sialic acids. Nature 179: 1088. doi:10.1038/1791088b0 [PubMed: 13430805] [CrossRef]
- Schauer R. 1982. Chemistry, metabolism, and biological functions of sialic acids. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem 40: 131–234. doi:10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60109-2 [PubMed: 6762816] [CrossRef]
- Taylor G. 1996. Sialidases: structures, biological significance and therapeutic potential. Curr Opin Struct Biol 6: 830–837. doi:10.1016/s0959-440x(96)80014-5 [PubMed: 8994884] [CrossRef]
- Kelm S, Schauer R. 1997. Sialic acids in molecular and cellular interactions. Int Rev Cytol 175: 137–240. doi:10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62127-0 [PMC free article: PMC7133163] [PubMed: 9203358] [CrossRef]
- Knirel YA, Shashkov AS, Tsvetkov YE, Jansson PE, Zãhringer U. 2003. 5,7-Diamino-3,5,7,9-tetradeoxynon-2-ulosonic acids in bacterial glycopolymers: chemistry and biochemistry. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem 58: 371–417. doi:10.1016/s0065-2318(03)58007-6 [PubMed: 14719362] [CrossRef]
- Toukach P, Joshi H, Ranzinger R, Knirel Y, von der Leith C. 2007. Sharing of worldwide distributed carbohydrate-related digital resources: online connection of the Bacterial Carbohydrate Structure Database and GLYCOSCIENCES.de. Nucleic Acids Res 35: D280–D286. doi:10.1093/nar/gkl883 [PMC free article: PMC1899093] [PubMed: 17202164] [CrossRef]
- Lewis AL, Desa N, Hansen EE, Knirel YA, Gordon JI, Gagneux P, Nizet V, Varki A. 2009. Innovations in host and microbial sialic acid biosynthesis revealed by phylogenomic prediction of nonulosonic acid structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106: 13552–13557. doi:10.1073/pnas.0902431106 [PMC free article: PMC2726416] [PubMed: 19666579] [CrossRef]
- Schauer R. 2009. Sialic acids as regulators of molecular and cellular interactions. Curr Opin Struct Biol 19: 507–514. doi:10.1016/j.sbi.2009.06.003 [PMC free article: PMC7127376] [PubMed: 19699080] [CrossRef]
- Chen X, Varki A. 2010. Advances in the biology and chemistry of sialic acids. ACS Chem Biol 5: 163–176. doi:10.1021/cb900266r [PMC free article: PMC2825284] [PubMed: 20020717] [CrossRef]
- Xu G, Kiefel MJ, Wilson JC, Andrew PW, Oggioni MR, Taylor GL. 2011. Three Streptococcus pneumoniae sialidases: three different products. J Am Chem Soc 133: 1718–1721. doi:10.1021/ja110733q [PubMed: 21244006] [CrossRef]
- Li Y, Chen X. 2012. Sialic acid metabolism and sialyltransferases, natural functions and applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 94: 887–905. doi:10.1007/s00253-012-4040-1 [PMC free article: PMC3534974] [PubMed: 22526796] [CrossRef]
- Miyagi T, Yamaguchi K. 2012. Mammalian sialidases: physiological and pathological roles in cellular functions. Glycobiology 22: 880–896. doi:10.1093/glycob/cws057 [PubMed: 22377912] [CrossRef]
- Varki A, Gagneux P. 2012. Multifarious roles of sialic acids in immunity. Ann NY Acad Sci 1253: 16–36. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06517.x [PMC free article: PMC3357316] [PubMed: 22524423] [CrossRef]
- Petit D, Teppa RE, Petit JM, Harduin-Lepers A. 2013. A practical approach to reconstruct evolutionary history of animal sialyltransferases and gain insights into the sequence–function relationships of Golgi-glycosyltransferases. Methods Mol Biol 1022: 73–97. doi:10.1007/978-1-62703-465-4_7 [PubMed: 23765655] [CrossRef]
- Tiralongo J, Martinez-Duncker I. 2013. Sialobiology: structure, biosynthesis and function. Bentham, Oak Park, IL. doi:10.2174/97816080538651130101 [CrossRef]
- Schnaar RL, Gerardy-Schahn R, Hildebrandt H. 2014. Sialic acids in the brain: gangliosides and polysialic acid in nervous system development, stability, disease, and regeneration. Physiol Rev 94: 461–518. doi:10.1152/physrev.00033.2013 [PMC free article: PMC4044301] [PubMed: 24692354] [CrossRef]
- Stencel-Baerenwald JE, Reiss K, Reiter DM, Stehle T, Dermody TS. 2014. The sweet spot: defining virus–sialic acid interactions. Nat Rev Microbiol 12: 739–749. doi:10.1038/nrmicro3346 [PMC free article: PMC4791167] [PubMed: 25263223] [CrossRef]
- Chen X. 2015. Human milk oligosaccharides (HMOS): structure, function, and enzyme-catalyzed synthesis. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem 72: 113–190. doi:10.1016/bs.accb.2015.08.002 [PMC free article: PMC9235823] [PubMed: 26613816] [CrossRef]
- Lundblad A. 2015. Gunnar Blix and his discovery of sialic acids. Fascinating molecules in glycobiology. Ups J Med Sci 120: 104–112. doi:10.3109/03009734.2015.1027429 [PMC free article: PMC4463483] [PubMed: 25921326] [CrossRef]
- Toukach PV, Egoroca KS. 2016. Carbohydrate structure database merged from bacterial, archaeal, plant and fungal parts. Nucleic Acids Res 44: D1229–D1236. doi:10.1093/nar/gkv840 [PMC free article: PMC4702937] [PubMed: 26286194] [CrossRef]
- Pearce OM, Läubli H. 2017. Sialic acids in cancer biology and immunity. Glycobiology 26: 111–128. doi:10.1093/glycob/cwv097 [PubMed: 26518624] [CrossRef]
- Wasik BR, Barnard KN, Parrish CR. 2017. Effects of sialic acid modifications on virus binding and infection. Trends Microbiol 24: 991–1001. doi:10.1016/j.tim.2016.07.005 [PMC free article: PMC5123965] [PubMed: 27491885] [CrossRef]
- Sato C, Kitajima K. 2020. Polysialylation and disease. Mol Aspects Med 27: 100892. doi:10.1016/j.mam.2020.100892 [PubMed: 32863045] [CrossRef]
- DISCOVERY AND GENERAL CLASSIFICATION
- THE SIALIC ACID FAMILY
- SIALOGLYCAN DIVERSITY
- POLYSIALIC ACIDS
- HUMAN LOSS OF N-GLYCOLYLNEURAMINIC ACID
- METABOLISM
- METHODS FOR STUDYING SIALIC ACIDS
- FUNCTIONS OF SIALIC ACIDS
- SIALIC ACIDS IN DEVELOPMENT AND MALIGNANCY
- SIALIC ACIDS IN PHARMACOLOGY
- EVOLUTIONARY DISTRIBUTION OF SIALIC ACIDS
- PROKARYOTIC NONULOSONIC ACIDS
- ABBREVIATED NAMES OF NONULOSONIC ACIDS
- ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- FURTHER READING
- Review Sialic Acids and Other Nonulosonic Acids.[Essentials of Glycobiology. 2015]Review Sialic Acids and Other Nonulosonic Acids.Varki A, Schnaar RL, Schauer R. Essentials of Glycobiology. 2015
- Cataloging natural sialic acids and other nonulosonic acids (NulOs), and their representation using the Symbol Nomenclature for Glycans.[Glycobiology. 2023]Cataloging natural sialic acids and other nonulosonic acids (NulOs), and their representation using the Symbol Nomenclature for Glycans.Lewis AL, Toukach P, Bolton E, Chen X, Frank M, Lütteke T, Knirel Y, Schoenhofen I, Varki A, Vinogradov E, et al. Glycobiology. 2023 Mar 6; 33(2):99-103.
- Tannerella forsythia strains display different cell-surface nonulosonic acids: biosynthetic pathway characterization and first insight into biological implications.[Glycobiology. 2017]Tannerella forsythia strains display different cell-surface nonulosonic acids: biosynthetic pathway characterization and first insight into biological implications.Friedrich V, Janesch B, Windwarder M, Maresch D, Braun ML, Megson ZA, Vinogradov E, Goneau MF, Sharma A, Altmann F, et al. Glycobiology. 2017 Apr 1; 27(4):342-357.
- Genomic and metabolic profiling of nonulosonic acids in Vibrionaceae reveal biochemical phenotypes of allelic divergence in Vibrio vulnificus.[Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011]Genomic and metabolic profiling of nonulosonic acids in Vibrionaceae reveal biochemical phenotypes of allelic divergence in Vibrio vulnificus.Lewis AL, Lubin JB, Argade S, Naidu N, Choudhury B, Boyd EF. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Aug 15; 77(16):5782-93. Epub 2011 Jul 1.
- Review Structural and Biosynthetic Diversity of Nonulosonic Acids (NulOs) That Decorate Surface Structures in Bacteria.[Trends Microbiol. 2021]Review Structural and Biosynthetic Diversity of Nonulosonic Acids (NulOs) That Decorate Surface Structures in Bacteria.McDonald ND, Boyd EF. Trends Microbiol. 2021 Feb; 29(2):142-157. Epub 2020 Sep 17.
- Sialic Acids and Other Nonulosonic Acids - Essentials of GlycobiologySialic Acids and Other Nonulosonic Acids - Essentials of Glycobiology
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...
