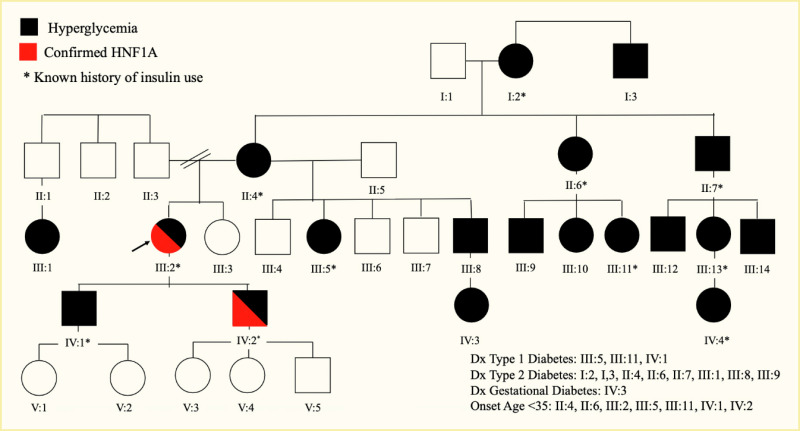
HNF1A Pedigree Shows Diabetes in Multiple Generations (Autosomal Dominant).
A 58-year-old female was initially found to be hyperglycemic at age 19 years with fasting blood glucose of 130 mg/dL. BMI was 19 kg/m2. Blood glucose was retested at age 23 years during pregnancy, and the individual was diagnosed as having gestational diabetes and then type 2 diabetes mellitus. Initially diet-controlled, but transitioned between oral agents (metformin and troglitazone) and insulin due to fluctuating diagnoses of gestational, type 1, and type 2 diabetes. Presented to a new endocrinologist at age 58 years, weight 230 pounds, BMI 40.7 kg/m2, using 90 units/day via an insulin pump. Sulfonylureas were started; A1c improved to the 6% range. Insulin was withdrawn as she lost weight (over 70 pounds). She had euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) after SGLT2i treatment. Conversion formulas for A1c and glucose levels are provided in the Conversions section. A1c, glycated hemoglobin; BMI, body mass index; HNF1A, hepatocyte nuclear factor 1A; SGLT2i, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor.
SOURCE: University of Chicago Monogenic Diabetes Registry Working Group, 2022, unpublished data