NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
About Bookshelf [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010-.
Bookshelf provides free access to the full text of books and documents in the biomedical and life sciences as well as health care and medical humanities and social sciences at the U.S. National Institutes of Health's National Library of Medicine (NIH/NLM). Through integration with other NCBI databases, such as PubMed, Gene, Genetic Testing Registry, and PubChem, Bookshelf also provides reference information for biological, chemical and other biomedical data and facilitates its discovery.
Bookshelf was developed and is managed by NLM’s National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI).
About the Content
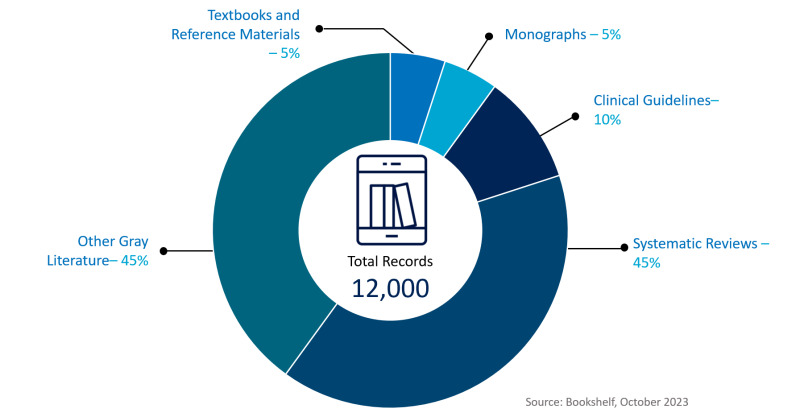
Bookshelf started in 1999 with the third edition of Alberts’ Molecular Biology of the Cell. Since then Bookshelf has grown to 9,000 titles beyond classic textbooks, to include monographs, reference books, systematic reviews, technical reports, clinical guidelines, web materials, grey literature, and other peer-reviewed documents.
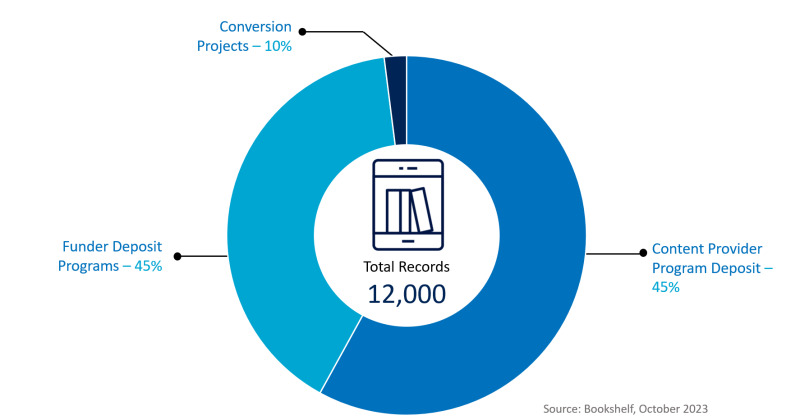
Content is added to the archive through
|
Content Provider and Publisher Program Deposit (45%) |
Funder Program Deposit (45%) |
Conversion Projects (10%) |
|
NLM has agreements with publishers, scholarly societies, and other content owners to deposit books and documents directly to Bookshelf. |
NLM partners with federal agencies, international organizations, and other funding or sponsoring organizations to accept the deposit of health reports, systematic reviews, clinical guidelines, monographs, and related reference works in compliance with funder policies and goals. |
NLM collaborates with NIH or other institutionally-sponsored authors and editors to make available biological, chemical, and other highly regarded biomedical reference materials through conversion of Word documents. |
The resulting collaborations with publishers, societies, funders, sponsors, authors and editors form the foundation of Bookshelf. Bookshelf is not a publisher and does not publish books and documents itself.
About the Archive
NLM’s fundamental responsibility is to permanently preserve periodicals, among other materials, pertinent to medicine. (See the NLM Preservation Policy for more information.) As such, Bookshelf is designed to provide permanent access to all its content, even as technology evolves. To do so,
|
 |
Bookshelf immediately makes all content free to read as NLM believes that the best way to ensure the accessibility and viability of digital material over time is through consistent and active use of the archive. However, free access does not mean that there is no copyright protection (see the Bookshelf Copyright Notice). |
|
 |
Bookshelf stores content in eXtensible Markup Language (XML), which represents the structure and meaning of a document in a relatively simple and human-readable form. All Bookshelf content is converted to and stored in the Book Interchange Tag Suite (BITS) XML format. |
|
 |
Bookshelf leverages the existing PubMed Central® (PMC) software architecture to store and make its content accessible to users. |
|
 |
NLM operates the PMC International network, which provides a framework to maintain copies of the Bookshelf corpus in other reliable international archives that share the goals of PMC and Bookshelf and operate on the same principles. |
Because Bookshelf has the capacity to store and cross reference data from diverse sources in a common format within a central repository, a Bookshelf user can quickly search either the entire collection of full-text books and documents or within a specific book or series to locate all relevant materials. The structure of the Bookshelf archive also supports the integration of the literature with other resources.
Bulk retrieval of files for text mining and other purposes is permitted within a subset of the Bookshelf archive.