From: The destruction of antibody-coated pathogens via Fc receptors

NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
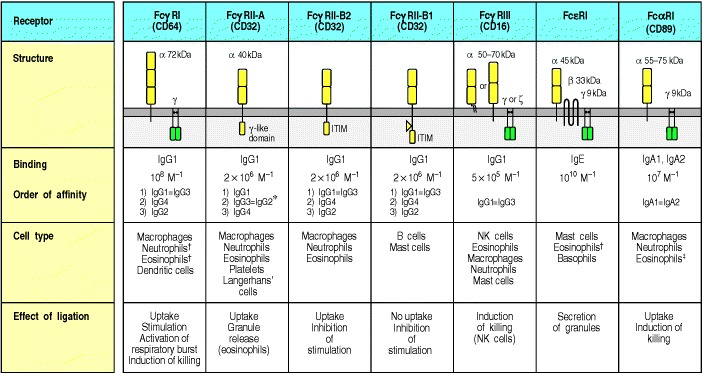
The subunit structure and binding properties of these receptors and the cell types expressing them are shown. The complete multimolecular structure of most receptors is not yet known but they might all be multichain molecular complexes similar to the Fcε receptor I (FcεRI). The exact chain composition of any receptor can vary from one cell type to another. For example, FcγRIII in neutrophils is expressed as a molecule with a glycophosphoinositol membrane anchor, without γ chains, whereas in NK cells it is a transmembrane molecule associated with γ chains as shown. The FcγRII-B1 differs from the FcγRII-B2 by the presence of an additional exon in the intracellular region. This exon prevents the FcγRII-B1 from being internalized upon cross-linking. The binding affinities are taken from data on human receptors. *Only some allotypes of FcγRII-A bind IgG2. †In these cases Fc receptor expression is inducible rather than constitutive. ‡In eosinophils, the molecular weight of CD89α is 70–100 kDa.
From: The destruction of antibody-coated pathogens via Fc receptors

NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.