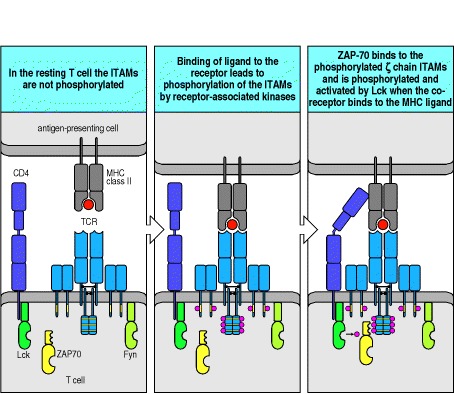
From: Antigen receptor structure and signaling pathways

Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and Disease. 5th edition.
Janeway CA Jr, Travers P, Walport M, et al.
New York: Garland Science; 2001.
Copyright © 2001, Garland Science.
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.