Congenital Contractural Arachnodactyly
Synonyms: Beals-Hecht Syndrome, Beals Syndrome
Bert Callewaert, MD, PhD
Center for Medical Genetics
Ghent University Hospital
Ghent, Belgium
Initial Posting: January 23, 2001; Last Revision: July 14, 2022.
Estimated reading time: 28 minutes
Summary
Clinical characteristics.
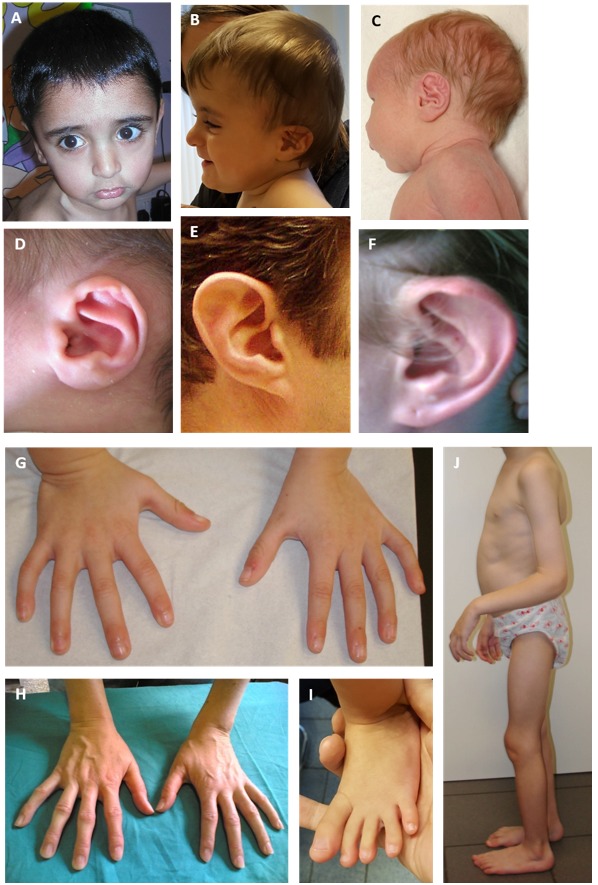
Congenital contractural arachnodactyly (CCA) appears to comprise a broad phenotypic spectrum. Classic CCA is characterized by arachnodactyly; flexion contractures of multiple joints including elbows, knees, hips, ankles, and/or fingers; kyphoscoliosis (usually progressive); a marfanoid habitus (a long and slender build, dolichostenomelia, pectus deformity, muscular hypoplasia, highly arched palate); and abnormal "crumpled" ears. At the mildest end, parents who are diagnosed retrospectively upon evaluation of their more severely affected child may show a lean body build, mild arachnodactyly, mild contractures without impairment, and minor ear abnormalities. At the most severe end is "severe CCA with cardiovascular and/or gastrointestinal anomalies," a rare phenotype in infants with pronounced features of CCA (severe crumpling of the ears, arachnodactyly, contractures, congenital scoliosis, and/or hypotonia) and severe cardiovascular and/or gastrointestinal anomalies. Phenotypic expression can vary within and between families.
Diagnosis/testing.
The diagnosis of CCA can be established in a proband with suggestive findings and a heterozygous FBN2 pathogenic variant identified by molecular genetic testing; however, locus heterogeneity is likely given that only 25%-75% of individuals with clinically diagnosed CCA have an identifiable FBN2 pathogenic variant. Because CCA can be difficult to diagnose clinically, a clinical scoring system based on presence or absence of crumpled ears, musculoskeletal findings, highly arched palate, and micrognathia can be used.
Management.
Treatment of manifestations of classic CCA: Standard management of contractures, clubfeet, kyphoscoliosis including surgical intervention as needed; early physical therapy to improve mobility and occupational therapy to improve camptodactyly. Aortic root dilatation, correction of refractive errors, and palatal abnormalities are managed in a standard manner.
Surveillance for classic CCA: Annual evaluation for kyphosis/scoliosis if not present at initial evaluation; routine measurement of aortic root diameter for evidence of aortic dilatation; routine assessment of visual acuity and refractive error; annual assessment of orthodontic needs after age eight years.
Agents/circumstances to avoid: Contact sports and activities that stress joints; LASIK eye surgery, which may increase the risk for keratoconus in those with predisposing ocular conditions.
Evaluation of relatives at risk: Clarification of the genetic status of apparently asymptomatic or self-reportedly asymptomatic at-risk relatives by molecular genetic testing if the familial FBN2 variant is known, otherwise by clinical examination to identify those with a low – but potential – risk for aortic and/or ocular complications.
Pregnancy management: Although no complications related to pregnancy or delivery have been reported in women with CCA, it is advisable to perform an echocardiography preconceptually and to increase cardiac surveillance during pregnancy in women with dilatation of the aortic root.
Genetic counseling.
CCA is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. While many individuals with CCA have an affected parent, as many as 50% may have a de novo
FBN2 pathogenic variant. If a parent of a proband has clinical features of CCA and/or is known to have the FBN2 pathogenic variant identified in the proband, the risk to sibs of the proband is 50%. Because intrafamilial clinical variability is observed in CCA, a heterozygous sib may have a more or less severe phenotypic presentation than the proband. Once the FBN2 pathogenic variant has been identified in an affected family member, prenatal testing and preimplantation genetic testing are possible.
Diagnosis
Formal diagnostic criteria for congenital contractural arachnodactyly (CCA) have not been established.
Suggestive Findings
Classic CCA should be suspected in individuals with the following:
Arachnodactyly with positive wrist and thumb sign
Flexion contractures of multiple joints including elbows, knees, hips, ankles, and/or fingers
Kyphoscoliosis (usually progressive)
Abnormal pinnae ("crumpled" outer helices)
A marfanoid habitus (a long and slender build, dolichostenomelia, pectus deformity, muscular hypoplasia, highly arched palate)
On rare occasions, infants were reported with the clinical findings of classic CCA as well as the following anomalies [Lipson et al 1974, Currarino & Friedman 1986, Macnab et al 1991, Wang et al 1996, Snape et al 2006]:
Cardiovascular. Interrupted aortic arch and atrial or ventricular septal defects, and/or severe aortic root dilatation (rare)
Gastrointestinal. Duodenal or esophageal atresia and/or intestinal malrotation
Although this phenotype has been referred to as "severe/lethal CCA," its molecular basis has not been unequivocally established and a lethal outcome is not certain; the term "severe CCA with cardiovascular and/or gastrointestinal anomalies" more accurately describes this disorder [Author, personal observation].
Establishing the Diagnosis
The diagnosis of CCA is established in a proband with suggestive findings and a heterozygous FBN2 pathogenic (or likely pathogenic) variant identified by molecular genetic testing (Table 1). However, locus heterogeneity is likely, given that only 25%-75% of individuals clinically diagnosed with CCA have an identifiable FBN2 pathogenic variant [Gupta et al 2002; Callewaert et al 2009; Nishimura et al 2007; Meerschaut et al 2020; Callewaert et al, unpublished data]. Because CCA is difficult to diagnose clinically, Meerschaut et al [2020] developed a clinical scoring system to facilitate the clinical diagnosis of CCA (Table 2).
Note: Per ACMG variant interpretation guidelines, the terms "pathogenic variants" and "likely pathogenic variants" are synonymous in a clinical setting, meaning that both are considered diagnostic and both can be used for clinical decision making. Reference to "pathogenic variants" in this section is understood to include any likely pathogenic variants.
Molecular genetic testing approaches can include a combination of gene-targeted testing (single-gene testing, multigene panel) and comprehensive
genomic testing (exome sequencing, genome sequencing) depending on the phenotype.
Gene-targeted testing requires that the clinician determine which gene(s) are likely involved, whereas genomic testing does not. Because the phenotype of congenital contractural arachnodactyly is broad, individuals with the distinctive findings described in Suggestive Findings are likely to be diagnosed using gene-targeted testing (see Option 1), whereas those in whom the diagnosis of CCA has not been considered because of atypical findings are more likely to be diagnosed using genomic testing (see Option 2).
Option 1
Single-gene testing. Sequence analysis of FBN2 detects small intragenic deletions/insertions and missense, nonsense, and splice site variants; typically, exon or whole-gene deletions/duplications are not detected. Perform sequence analysis first. If no pathogenic variant is found, perform gene-targeted deletion/duplication analysis to detect intragenic deletions or duplications.
A multigene panel that includes FBN2 and other genes of interest (see Differential Diagnosis) is most likely to identify the genetic cause of the condition while limiting identification of variants of uncertain significance and pathogenic variants in genes that do not explain the underlying phenotype. Note: (1) The genes included in the panel and the diagnostic sensitivity of the testing used for each gene vary by laboratory and are likely to change over time. (2) Some multigene panels may include genes not associated with the condition discussed in this GeneReview. Since the differential diagnosis of CCA includes Marfan syndrome and Loeys-Dietz syndrome, clinicians requesting a panel including genes for heritable thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections (HTAD) should be aware that FBN2 may not be included in some panels based on recent recommendations for HTAD genetic testing [Renard et al 2018]. (3) In some laboratories, panel options may include a custom laboratory-designed panel and/or custom phenotype-focused exome analysis that includes genes specified by the clinician. (4) Methods used in a panel may include sequence analysis, deletion/duplication analysis, and/or other non-sequencing-based tests. For CCA a multigene panel that also includes deletion/duplication analysis is recommended (see Table 1).
For an introduction to multigene panels click here. More detailed information for clinicians ordering genetic tests can be found here.
Option 2
When the diagnosis of CCA is not considered because an individual has atypical phenotypic features, comprehensive genomic testing (which does not require the clinician to determine which gene[s] are likely involved) is an option. Exome sequencing is currently the most commonly used genomic testing method; genome sequencing is also possible.
If exome sequencing is not diagnostic, exome array (when clinically available) may be considered to detect (multi)exon deletions or duplications that cannot be detected by sequence analysis.
For an introduction to comprehensive genomic testing click here. More detailed information for clinicians ordering genomic testing can be found here.
Table 1.
Molecular Genetic Testing Used in Congenital Contractural Arachnodactyly
View in own window
| Gene 1 | Proportion of CCA Attributed to Pathogenic Variants in Gene 2 | Method | Proportion of FBN2 Pathogenic Variants 3 Detectable by Method |
|---|
|
FBN2
| 25%-75% | Sequence analysis 4 | ~93% |
| Gene-targeted deletion/duplication analysis 5 | ~7% 6 |
| Unknown | 25%-75% | NA |
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
Sequence analysis detects variants that are benign, likely benign, of uncertain significance, likely pathogenic, or pathogenic. Variants may include small intragenic deletions/insertions and missense, nonsense, and splice site variants; typically, exon or whole-gene deletions/duplications are not detected. For issues to consider in interpretation of sequence analysis results, click here.
- 5.
Gene-targeted deletion/duplication analysis detects intragenic deletions or duplications. Methods used may include a range of techniques such as quantitative PCR, long-range PCR, multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA), and a gene-targeted microarray designed to detect single-exon deletions or duplications. Gene-targeted deletion/duplication testing will detect deletions ranging from a single exon to the whole gene; however, breakpoints of an entire FBN2 deletion and/or deletion of adjacent genes (e.g., those described by Inbar-Feigenberg et al [2014]) may not be detected by these methods.
- 6.
Clinical Scoring System
In the absence of a pathogenic or likely pathogenic FBN2 variant and in the absence of intellectual disability, progressive aortic root dilatation, and/or ectopia lentis, a clinical score of ≥7/20 is suggestive for CCA (sensitivity 95.5%; specificity 17.1%) and a score of ≥11/20 makes the diagnosis of CCA likely (sensitivity 75%; specificity 60%) [Meerschaut et al 2020].
Table 2.
View in own window
| Clinical Feature | Points | Comments |
|---|
| Crumpled ears | 3 | In neonates: a "crumpled ear" often shows underdevelopment & folding of the upper part of the helix w/a prominent helical crus & inferior crus of the antihelix. In older children / adults: ear may "unfold" but the prominence of the crura remains, giving a "tram track" appearance to the ear (see ).
|
| Arachnodactyly | 3 |
|
| Camptodactyly | 3 | |
Large-joint
contractures | 3 | |
| Pectus deformity | 2 | |
| Dolichostenomelia | 2 | Defined as presence of:
|
| Kyphoscoliosis | 1 |
|
| Muscle hypoplasia | 1 | |
| Highly arched palate | 1 | |
| Micrognathia | 1 | |
US/LS = upper segment to lower segment
- 1.
Positive wrist sign: the tip of the thumb covers the entire fingernail of the fifth finger when wrapped around the contralateral wrist [Loeys et al 2010].
- 2.
Positive thumb sign: the entire distal phalanx of the adducted thumb extends beyond the ulnar border of the palm with or without the assistance of the patient or examiner to achieve maximal adduction [Loeys et al 2010].
- 3.
Clinical diagnosis: on bending forward, a vertical difference of ≥1.5 cm between the ribs of the left and right hemithorax is observed [Loeys et al 2010].
- 4.
Radiographic: a Cobb's angle (angle between a line drawn along the superior-end plate of the superior-end vertebra and a second line drawn along the inferior-end plate of the inferior-end vertebra of the scoliosis measured on anterior-posterior view of the spine) of ≥20° is seen [Loeys et al 2010].
Clinical Characteristics
Clinical Description
Congenital contractural arachnodactyly (CCA) appears to comprise a broad phenotypic spectrum. Phenotypic expression is variable within and between families. At the mildest end, parents who are diagnosed retrospectively upon evaluation of their more severely affected child may show a lean body build, mild arachnodactyly, prominent anterior crus of the antihelix, and/or mild contractures without impairment. At the most severe end is "severe CCA with cardiovascular and/or gastrointestinal anomalies," a rare phenotype in infants with pronounced features of CCA (severe crumpling of the ears, arachnodactyly, contractures, congenital scoliosis, and/or hypotonia) and severe cardiovascular and/or gastrointestinal anomalies. Only one child with the severe form of CCA has been confirmed to have an FBN2 pathogenic variant [Wang et al 1996], but it remains unclear if additional variants affecting other genes could account for this phenotype.
Classic CCA
Table 3.
Selected Clinical Features in Classic Congenital Contractural Arachnodactyly by Frequency
View in own window
| Clinical Feature | Frequency 1, 2 |
|---|
| Arachnodactyly | 98% |
| Small-joint contractures | 92% |
| Large-joint contractures | 88% |
| Crumpled ears | 78% |
| Kyphosis/scoliosis | 62% |
| Muscle hypoplasia | 55% |
| Dolichostenomelia | 50% |
| Pectus deformity | 41% |
| Highly arched palate | 67% |
| Micrognathia | 34% |
- 1.
Features are ordered by frequency.
- 2.
Features seen in individuals with CCA
Arachnodactyly (long slender fingers and toes) caused by overgrowth of the phalanges ()
Joint contractures
Camptodactyly. Contractures of the small joints (metacarpo/tarsophalangeal, proximal, and distal interphalangeal joints)
Large-joint contractures. Limited movement of hips, knees, ankles (clubfoot), shoulders, elbows, and wrists
Contractures of small and large joints usually improve with time, but some limited restriction often remains. Careful assessment is therefore necessary in (older) children and adults.
"Crumpled" ears. Hearing is normal in individuals with CCA.
Kyphosis/scoliosis. Scoliosis can be congenital or develop/worsen during periods of fast growth (6 months – 2 years, pubertal growth spurt), and may cause significant morbidity in CCA.
Muscle hypoplasia. A thin body habitus with relative underdevelopment of the muscular reliefs with reference to age, activity level, and nutritional status. Of note, muscular hypoplasia was more frequently reported in individuals suspected with CCA without a (likely) pathogenic
FBN2 variant (65%) [
Meerschaut et al 2020]. However, this feature is likely underreported ().
Dolichostenomelia. A tall and slender habitus with long-bone overgrowth evoking a marfanoid habitus
Pectus deformity (most frequently pectus excavatum). Due to overgrowth of the ribs, the sternum and anterior thoracic wall are pushed in (pectus excavatum) or out (pectus carinatum).
Craniofacial abnormalities
Other features, not routinely assessed in case reports of CCA
Severe CCA with Cardiovascular and/or Gastrointestinal Anomalies
In addition to the typical skeletal findings in CCA, a few infants with multiple cardiovascular and/or gastrointestinal anomalies requiring surgical correction as early as the first week of life have been reported [Lipson et al 1974, Currarino & Friedman 1986, Macnab et al 1991, Wang et al 1996]. The most common cardiovascular anomalies include interrupted aortic arch and atrial or ventricular septal defects. Gastrointestinal anomalies include esophageal or duodenal atresia and/or intestinal malrotation.
The age of death has ranged from eight days to 11.5 months. Respiratory complications including tracheomalacia and respiratory infections have been the cause of death in most.
Somatic Mosaicism
Somatic mosaicism has been reported in the following instances:
A mother with somatic mosaicism for an
FBN2 variant had features of classic CCA. Her daughter, who inherited the
FBN2 pathogenic variant, had severe CCA with cardiovascular and gastrointestinal anomalies [
Wang et al 1996].
A likely in-frame mosaic intragenic deletion from exons 7-34 spanning the central region of the gene (exons 24-23) that harbors most pathogenic variants was associated with a severe phenotype [
Lavillaureix et al 2017].
Somatic and germline mosaicism were reported in the asymptomatic father of two affected children [
Putnam et al 1997].
Genotype-Phenotype Correlations
No genotype-phenotype correlations have been documented to date.
Some case reports claim a more severe phenotype for deletions [Lavillaureix et al 2017] or splice site variants in the central region of the gene (exons 24-35) (this remains unconfirmed) [Wang et al 1996]. In addition, phenotypic variability between and within families is wide, independent of the variant type (splice site or missense) [Callewaert et al 2009].
Meerschaut et al [2020] state that individuals with a confirmed FBN2 (likely) pathogenic variant have a higher clinical score (Table 2) than those without an FBN2 (likely) pathogenic variant (P<0.001). Nevertheless, persons without an FBN2 (likely) pathogenic variant but with a clinical score as high as 19 have been reported, making it impossible to clinically differentiate between individuals with and without an FBN2 (likely) pathogenic variant.
Penetrance
The penetrance for CCA is likely up to 100%, but some disease manifestations, including the ear and joint manifestations, may become less obvious with age. Nevertheless, upon careful examination, less than 1.2% of the variability of the clinical score (Table 2) could be attributed to age [Meerschaut et al 2020]. Indeed, a previous report indicates that the diagnosis was often retrospectively made in one parent of a proband due to mild features still evident in adulthood (mild contractures without any functional impairment and/or prominent helical crus and anterior antihelical crus ["tram track" ears]) [Callewaert et al 2009]. In addition, long-bone overgrowth and scoliosis may become more prominent with age.
Clinical manifestations are the same in males and females.
Nomenclature
Congenital contractural arachnodactyly (CCA) has been referred to as distal arthrogryposis type 9 (OMIM 121050). This term should be avoided as it puts too much emphasis on the distal contractures while minimizing the significance of other manifestations, including marfanoid habitus, proximal contractures, and aortic and ocular involvement.
Prevalence
The prevalence is not known. To date about 70 probands with CCA have been described. Most described individuals are white, but this likely represents an ascertainment bias [Author, personal observation]. There is no reason to assume that CCA shows any specific geographic or ethnic predilection. Indeed, affected individuals from China [Chen et al 2009, Liu et al 2015, Guo et al 2016], Japan [Takeda et al 2015], India, and the Middle East [Callewaert et al 2009, Mehar et al 2014, Meerschaut et al 2020] have been described.
Differential Diagnosis
Disorders with features that overlap with those of congenital contractural arachnodactyly (CCA) are summarized in Table 4.
Table 4.
Disorders to Consider in the Differential Diagnosis of Congenital Contractural Arachnodactyly (CCA)
View in own window
Differential
Diagnosis
Disorder | Gene | MOI | Clinical Features of Differential Diagnosis Disorder |
|---|
| Overlapping w/CCA | Distinguishing from CCA |
|---|
|
Marfan syndrome
|
FBN1
| AD | Marfanoid habitus, dolichostenomelia Arachnodactyly Pectus deformity, kyphoscoliosis Muscle hypoplasia Large-joint contractures (mainly elbows) Severe Marfan syndrome 1 may be mistaken for severe CCA as both may have crumpled ears, contractures, & cardiovascular abnormalities. 2
| Lens (sub)luxation High myopia Progressive aortic root dilatation Absence of crumpled ears & joint contractures 3 Neonates w/severe Marfan syndrome are usually very hypotonic & have valvular anomalies ("floppy valves") &/or aortic root dilatation, rather than the septal defects or interrupted aortic arch in severe CCA. Differentiating Marfan syndrome & CCA is most important given the severe cardiovascular complications & cardiac monitoring essential in individuals w/Marfan syndrome.
|
|
Loeys-Dietz syndrome
|
SMAD2
SMAD3
TGFB2
TGFB3
TGFBR1
TGFBR2
| AD | Arachnodactyly Pectus deformity
| Joint laxity Thin skin Hypertelorism, bifid uvula, cleft palate Pectus deformity, scoliosis (Progressive) aortic root dilatation – patent ductus arteriosus
|
|
Stickler syndrome
|
COL2A1
COL9A1
COL9A2
COL9A3
COL11A1
COL11A2
| AD
AR 4 | Marfanoid body habitus (in some affected individuals), but usually secondary to a shortened trunk, rather than long-bone overgrowth | Joint laxity Early-onset & rapidly progressive myopia w/↑ risk of cataract, & retinal detachment Hearing loss (both conductive & sensorineural) Midfacial underdevelopment & cleft palate Mild spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia &/or precocious arthritis
|
|
Homocystinuria
|
CBS
| AR | Limited joint mobility Dolichostenomelia Arachnodactyly Kyphoscoliosis
|
|
Distal arthrogryposes
(DA) (OMIM PS108120) |
ECEL1
MYBPC1
MYH3
MYH8
PIEZO2
TNNI2
TNNT3
TPM2
| AD
AR 5 | Medially overlapping fingers Clenched fists Ulnar deviation of fingers Camptodactyly Positional foot deformities Clubfoot Scoliosis
| Absence of marfanoid habitus, arachnodactyly, contractures of knees & elbows, & crumpled ears Additional features depending on DA subtype Often pursed lips
|
| Bethlem myopathy (See Collagen Type VI-Related Disorders & OMIM 616471.) |
COL6A1
COL6A2
COL6A3
COL12A1
| AD
AR | Joint contractures Muscular hypoplasia
| Absence of marfanoid habitus, arachnodactyly, & crumpled ears |
| Van den Ende - Gupta syndrome (OMIM 600920) |
SCARF2
| AR | Contractures Arachnodactyly Pectus excavatum Femoral bowing
| Normal ears Interdigital webbing Cleft palate Craniosynostosis
|
| Bruck syndrome (OMIM 259450 & 609220) |
FKBP10
PLOD2
| AR | Contractures Pectus deformity Bowed long bones Clubfeet
|
|
| Congenital contractures of the limbs & face, hypotonia & DD (OMIM 616266) |
NALCN
| AD | Contractures Hypotonia Micrognathia Scoliosis
|
|
AD = autosomal dominant; AR = autosomal recessive; DD = developmental delay; MOI = mode of inheritance
- 1.
Neonatal Marfan syndrome is at the most severe end of the spectrum of Marfan syndrome.
- 2.
In neonatal Marfan syndrome, cardiovascular abnormalities include mitral and tricuspid valve anomalies and dilated aorta. In severe/lethal CCA, cardiovascular abnormalities include atrial and/or ventricular septal defects and interrupted aortic arch.
- 3.
Joint contractures are seen at birth in individuals with CCA.
- 4.
Stickler syndrome caused by pathogenic variants COL2A1, COL11A1, or COL11A2 is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner; Stickler syndrome caused by pathogenic variants in COL9A1, COL9A2, or COL9A3 is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner.
- 5.
Distal arthrogryposes is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner with the exception of ECEL1-related distal arthrogryposis, which is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner.
Fetal akinesia sequence. Any disorder resulting in fetal akinesia either through severe (central) nervous system impairment or mechanical constraint will result in neonatal contractures. These individuals may have ear deformities and a small jaw, but usually do not present with arachnodactyly. Therefore, a pregnancy history (oligohydramnios) and workup with a brain MRI is necessary to differentiate between possible causes of the contractures.
Management
Evaluations Following Initial Diagnosis
To establish the extent of disease in an individual diagnosed with congenital contractural arachnodactyly (CCA), the evaluations summarized in Table 5 (if not performed as part of the evaluation that led to the diagnosis) are recommended.
Table 5.
Recommended Evaluations Following Initial Diagnosis in Individuals with Classic Congenital Contractural Arachnodactyly
View in own window
| System/Concern | Evaluation | Comment |
|---|
|
Musculoskeletal
| Orthopedics: joint contractures, bowed long bones; kyphoscoliosis | Kyphoscoliosis may be congenital, is progressive, & warrants early eval. |
| Assessment by physiatrist, OT/PT of fine motor & gross motor skills related to contractures & muscular hypotonia | |
|
Cardiovascular
| Assessment for aortic root dilatation | The risk for aortic root dilatation is low & progression uncommon; but assessing aortic root dilatation at an early stage is important for determining frequency of further cardiovascular follow up. |
|
Ophthalmologic
| Flat cornea / keratoconus | Low risk |
|
Orthodontic
| Highly arched palate, dental crowding | A highly arched palate is also assoc w/↑ incidence of middle ear infections. |
Miscellaneous/
Other
| Consultation w/clinical geneticist &/or genetic counselor | |
OT = occupational therapy; PT = physical therapy
Table 6.
Recommended Evaluations Following Initial Diagnosis in Infants with Severe Congenital Contractural Arachnodactyly
View in own window
| System/Concern | Evaluation | Comment |
|---|
|
Constitutional
| Assess nutritional status, growth. | |
|
Musculoskeletal
| Orthopedics: joint contractures, bowed long bones; kyphoscoliosis | Kyphoscoliosis is congenital, progressive, & warrants early eval. |
| Assessment by physiatrist, OT/PT of fine motor & gross motor skills related to contractures & muscular hypotonia | |
|
Cardiovascular
| Assess for congenital heart disease. | Commonly atrial or ventricular septal defect, interrupted aortic arch; rarely aortic root dilatation. Valvular insufficiency may occur. |
Gastrointestinal/
Feeding
| Assess for GI malformation: a "double bubble" sign on abdominal ultrasound is indicative of a duodenal atresia/obstruction. | Duodenal or esophageal atresia & intestinal malrotation |
|
Respiratory
| Assess for respiratory insufficiency. | Most common cause of death, often resulting from tracheomalacia (due to pressure from vascular anomalies) & respiratory infections. It is unclear if hypotonia, emphysema, &/or left-sided congestive heart failure may contribute to the respiratory problems. |
|
Ophthalmologic
| Flat cornea / keratoconus | Low risk |
Miscellaneous/
Other
| Consultation w/clinical geneticist &/or genetic counselor | |
OT = occupational therapy; PT = physical therapy
Treatment of Manifestations
Table 7.
Treatment of Manifestations in Individuals with Classic Congenital Contractural Arachnodactyly
View in own window
Manifestation/
Concern | Treatment | Considerations/Other |
|---|
|
Musculoskeletal
| By orthopedist | Contractures may require surgical release. Clubfeet may require casting. Progressive kyphoscoliosis may require bracing &/or surgical intervention.
|
| By physiatrist, OT/PT | Early PT in children helps ↑ joint mobility & counteract muscle hypoplasia (usually calf muscles). Camptodactyly & large-joint contractures may spontaneously improve over time. Swimming reinforces the musculature w/out taxing joints. Cycling may benefit those w/patellar hypermobility by ↓ risk for patellar luxation.
|
|
Cardiovascular
| By cardiologist/
cardiovascular surgeon | Aortic root dilatation is managed in a standard manner. See Marfan Syndrome & Milewicz et al [2005] (full text). |
|
Ophthalmologic
| By ophthalmologist |
|
|
Orthodontic
| By orthodontist/dentist |
|
OT = occupational therapy; PT = physical therapy
Table 8.
Treatment of Manifestations in Individuals with Severe/Lethal CCA
View in own window
Manifestation/
Concern | Treatment | Considerations/Other |
|---|
|
Musculoskeletal
| By orthopedist | Contractures may require surgical release. Clubfeet may require casting. Progressive kyphoscoliosis may require bracing &/or surgical intervention. Severe pectus excavatum may rarely cause restrictive lung disease or cardiac displacement & thus require surgical treatment (Nüss procedure).
|
By physiatrist,
OT/PT |
|
|
Cardiovascular
| By cardiologist /
cardiovascular surgeon | Hypoplastic aortic arch or interrupted aortic arch, a ductus-dependent heart defect, requires intervention shortly after birth (incl prostaglandins while awaiting surgery). For septal defects, treatment is either conservative (by percutaneous closure) or surgical following standard guidelines.
|
|
Gastrointestinal
| By abdominal/
pediatric surgeon |
|
|
Ophthalmologic
| By ophthalmologist |
|
|
Respiratory
| By neonatologist/
pulmonologist/
anesthesiologist | Tracheomalacia requires bronchoscopy &/or vascular imaging to determine cause & best treatment options. Aggressive treatment of pulmonary infections Respiratory physiotherapy may be necessary in case of severe hypotonia & reduced coughing. As it is unclear if pulmonary emphysema may develop, positive pressure ventilation should be kept to a minimum.
|
OT = occupational therapy; PT = physical therapy
Surveillance
Table 9.
Recommended Surveillance for Individuals with Classic Congenital Contractural Arachnodactyly
View in own window
| System/Concern | Evaluation | Frequency |
|---|
|
Musculoskeletal
| If not present at initial eval: evaluate for kyphosis/scoliosis clinically. | At least annually |
| If present at initial eval: monitor kyphosis/scoliosis (clinically &/or radiologically). | Per treating orthopedist |
|
Cardiovascular
| Measurement of aortic root diameter for evidence of aortic dilatation | Every 2 yrs until end of puberty; then every 3-5 yrs if aortic measurements are well below upper limit for age, sex, & body surface area (z-score <2) & no major valvular involvement (mitral valve prolapse) |
|
Ocular
| Visual acuity & assessment of refractive error | Upon clinical guidance (or at least every 2 yrs in young children) |
| Keratometry | Every 3 yrs, especially in those w/difficult-to-correct refractive errors |
|
Orthodontic
| From age 8 yrs | Annually |
Agents/Circumstances to Avoid
Avoid contact sports and activities that stress joints. Individuals should remain active but avoid high-intensity aerobic activities.
LASIK eye surgery may increase the risk for keratoconus in individuals with predisposing ocular conditions.
Evaluation of Relatives at Risk
It is appropriate to clarify the genetic status of apparently asymptomatic or self-reportedly asymptomatic at-risk relatives of an affected individual. Some parents have been unaware of their clinical status. In those individuals, evaluation of their status is necessary to reveal a low but potential risk for aortic and/or ocular complications.
Evaluations can include:
See Genetic Counseling for issues related to testing of at-risk relatives for genetic counseling purposes.
Pregnancy Management
There are no reported complications related to pregnancy or delivery in females with CCA. It is advisable to perform an echocardiography preconceptually and to increase cardiac surveillance during pregnancy in women with dilatation of the aortic root.
Therapies Under Investigation
Search ClinicalTrials.gov in the US and EU Clinical Trials Register in Europe for access to information on clinical studies for a wide range of diseases and conditions. Note: There may not be clinical trials for this disorder.
Genetic Counseling
Genetic counseling is the process of providing individuals and families with
information on the nature, mode(s) of inheritance, and implications of genetic disorders to help them
make informed medical and personal decisions. The following section deals with genetic
risk assessment and the use of family history and genetic testing to clarify genetic
status for family members; it is not meant to address all personal, cultural, or
ethical issues that may arise or to substitute for consultation with a genetics
professional. —ED.
Mode of Inheritance
Congenital contractural arachnodactyly (CCA) is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner.
Risk to Family Members
Parents of a proband
Many individuals diagnosed with CCA have an affected parent.
A proband with CCA may have the disorder as the result of a
de novo
FBN2 pathogenic variant. The proportion of cases caused by a
de novo pathogenic variant is unknown but likely nears 50% [
Callewaert et al 2009; Callewaert, unpublished data].
Molecular genetic testing (if the FBN2 pathogenic variant in the proband has been identified) and physical examination are recommended for the parents of a proband with an apparent negative family history.
If the
FBN2 pathogenic variant found in the proband cannot be detected in the leukocyte DNA of either parent, possible explanations include a
de novo pathogenic variant in the proband or somatic/germline mosaicism in a parent; somatic/germline mosaicism has been suggested or confirmed in three families [
Wang et al 1996,
Putnam et al 1997,
Callewaert et al 2009]. In one family, an
FBN2 pathogenic variant identified in two sibs was detectable in DNA derived from buccal cells and hair bulbs from the father, but not in DNA derived from paternal leukocytes [
Putnam et al 1997].
The family history of some individuals diagnosed with CCA may appear to be negative because of failure to recognize the disorder in family members. Therefore, an apparently negative family history cannot be confirmed unless appropriate clinical evaluation and/or molecular genetic testing has been performed on the parents of the proband.
Note: If the parent is the individual in whom the
FBN2 pathogenic variant first occurred, the parent may have somatic mosaicism for the variant and may have a less severe phenotypic presentation than the proband. In one report, a mother with somatic and germline mosaicism had features of classic CCA, while her daughter, who inherited the
FBN2 pathogenic variant, had severe CCA with cardiovascular and gastrointestinal anomalies [
Wang et al 1996].
Sibs of a proband. The risk to the sibs of the proband depends on the clinical/genetic status of the parents:
If a parent of the proband has clinical features of CCA and/or is known to have the
FBN2 pathogenic variant identified in the proband, the risk to the sibs is 50%. Because intrafamilial clinical variability is observed in CCA, a heterozygous sib may have a more or less severe phenotypic presentation than the proband (see
Genotype-Phenotype Correlations).
If neither parent is clinically affected and if the
FBN2 pathogenic variant identified in the proband cannot be detected in the leukocyte DNA of either parent, the recurrence risk to sibs is slightly greater than that of the general population because of the possibility of parental germline mosaicism (confirmed or suspected germline mosaicism has been reported in three unrelated families; in one family, an unaffected father had two children with CCA) [
Putnam et al 1997].
Offspring of a proband. Each child of an individual with CCA has a 50% chance of inheriting the FBN2 pathogenic variant.
Other family members. The risk to other family members depends on the status of the proband's parents: if a parent is affected or has an FBN2 pathogenic variant, the parent's family members are at risk.
Prenatal Testing and Preimplantation Genetic Testing
Molecular genetic testing. Once the FBN2 pathogenic variant has been identified in an affected family member, prenatal testing and preimplantation genetic testing are possible.
Fetal ultrasound examination. While joint contractures may be identified by ultrasound examination of an at-risk fetus, a normal fetal ultrasound examination does not exclude the diagnosis of CCA.
Note: Prenatal suspicion of contractures without a known familial history of CCA can be complemented by fetal brain MRI and or prenatal molecular testing in order to differentiate between possible causes of contractures, mostly with the purpose of excluding disorders with central nervous system involvement such as fetal akinesia deformation sequence.
Differences in perspective may exist among medical professionals and within families regarding the use of prenatal testing. While most centers would consider use of prenatal testing to be a personal decision, discussion of these issues may be helpful.
Resources
GeneReviews staff has selected the following disease-specific and/or umbrella
support organizations and/or registries for the benefit of individuals with this disorder
and their families. GeneReviews is not responsible for the information provided by other
organizations. For information on selection criteria, click here.
National Library of Medicine Genetics Home Reference
Genetic Aortic Disorders Association (GADA) Canada
Centre Plaza Postal Outlet
128 Queen Street South
PO Box 42257
Mississauga Ontario L5M 4Z0
Canada
Phone: 866-722-1722 (toll free); 905-826-3223
National Marfan Foundation (NMF)
22 Manhasset Avenue
Port Washington NY 11050
Phone: 800-862-7326 (toll-free); 516-883-8712
Fax: 516-883-8040
Molecular Genetics
Information in the Molecular Genetics and OMIM tables may differ from that elsewhere in the GeneReview: tables may contain more recent information. —ED.
Table A.
Congenital Contractural Arachnodactyly: Genes and Databases
View in own window
Data are compiled from the following standard references: gene from
HGNC;
chromosome locus from
OMIM;
protein from UniProt.
For a description of databases (Locus Specific, HGMD, ClinVar) to which links are provided, click
here.
Molecular Pathogenesis
FBN2 encodes fibrillin-2, a large extracellular matrix protein that multimerizes in linear structures, called microfibrils. These calcium-binding structures have some intrinsic stretchiness, and can further associate with elastin to form elastic fibers. Microfibrils provide support in both elastic and non-elastic connective tissue, are involved in cell-matrix communication, and contribute to extracellular growth factor sequestration and regulation.
Fibrillin-2 is homologous to fibrillin-1, encoded by FBN1 (pathogenic variants in which cause Marfan syndrome), but its expression begins earlier in embryonic development. Mouse studies have shown that fibrillin-1 may partially compensate for fibrillin-2 deficiency [Carta et al 2006] during embryonic development, at least in the aorta. In mice, contractures disappear around the time that fetal fbn2 expression is replaced by postnatal fbn1 expression. Fbn2 is involved in murine limb patterning, and both FBN1 and FBN2 are expressed in bone and tendons and control bone growth and density, suggesting overlapping and diverse roles for FBN1 and FBN2 in TGFβ and BMP growth factor sequestration and bioavailability [Nistala et al 2010, Smaldone et al 2011].
Of note, disease-associated variants in FBN2 are located in the central region of the gene (exons 24-35) encoding a central stretch of calcium-binding epidermal growth factor-like (cbEGF-like) domains. Pathogenic variants in the homologous central region of FBN1 (also called the "neonatal" region) typically cause a more severe Marfan syndrome phenotype [Faivre et al 2009]. In contrast to fibrillin-1, however, only one reported fibrillin-2 missense variant, p.Gly925Arg, located outside this region, caused a classic CCA phenotype [Meerschaut et al 2020].
Mechanism of disease causation. Both dominant-negative and loss-of-function mechanisms may be at play in the pathogenesis. Most disease-associated variants are missense or splice site variants that cluster in the central region of the gene (exons 24-35, which encode a stretch of calcium-binding epidermal growth factor-like [cbEGF-like] domains) and result in an in-frame mutated gene product. In addition, in-frame multiexon deletions outside the central region of FBN2 produce stably expressed mRNA. Since fibrillin-2 multimerizes in microfibrils, this suggests that most phenotypic effects of FBN2 pathogenic variants result from a dominant-negative effect.
Nevertheless, identification of an FBN2 nonsense variant and the 5q23.3 microdeletion syndrome encompassing FBN2 in individuals with features reminiscent of CCA suggest that a loss-of-function mechanism may contribute to the disease mechanism.
Table 10.
Notable FBN2 Pathogenic Variants
View in own window
Reference
Sequences | DNA
Nucleotide
Change | Predicted
Protein
Change | Comment [Reference] |
|---|
|
NM_001999.3
| c.4346-2A>T | | Severe CCA in a proband w/this heterozygous variant whose mother had classic CCA w/mosaicism for the variant [Wang et al 1996] |
| c.2773G>A | p.Gly925Arg | Located outside the FBN1 homologous region but assoc w/severe phenotype [Meerschaut et al 2020] |
Variants listed in the table have been provided by the author. GeneReviews staff have not independently verified the classification of variants.
GeneReviews follows the standard naming conventions of the Human Genome Variation Society (varnomen.hgvs.org). See Quick Reference for an explanation of nomenclature.
Chapter Notes
Author Notes
Dr Bert Callewaert ([email protected]) is actively involved in clinical research regarding individuals with congenital contractural arachnodactyly. He would be happy to communicate with persons who have any questions regarding diagnosis of congenital contractural arachnodactyly or other considerations.
Contact Dr Callewaert at [email protected] to inquire about the interpretation of FBN2 variants of uncertain significance.
Dr Callewaert ([email protected]) is also interested in hearing from clinicians treating families affected by congenital contractural arachnodactyly in whom no causative variant has been identified through molecular genetic testing.
Author History
Bert Callewaert, MD, PhD (2019-present)
Maurice Godfrey, PhD; University of Nebraska Medical Center (2001-2019)
Revision History
14 July 2022 (bc) Revision: contact information for questions about congenital contractural arachnodactyly added to
Author Notes21 October 2019 (bp) Comprehensive update posted live
23 February 2012 (me) Comprehensive update posted live
4 May 2007 (me) Comprehensive update posted live
5 April 2006 (cd) Revision: FBN2 testing clinically available
29 December 2004 (me) Comprehensive update posted live
5 February 2003 (me) Comprehensive update posted live
23 January 2001 (me) Review posted live
June 2000 (mg) Original submission
References
Literature Cited
Callewaert BL, Loeys BL, Ficcadenti A, Vermeer S, Landgren M, Kroes HY, Yaron Y, Pope M, Foulds N, Boute O, Galán F, Kingston H, Van der Aa N, Salcedo I, Swinkels ME, Wallgren-Pettersson C, Gabrielli O, De Backer J, Coucke PJ, De Paepe AM. Comprehensive clinical and molecular assessment of 32 probands with congenital contractural arachnodactyly: report of 14 novel mutations and review of the literature.
Hum Mutat. 2009;30:334–41. [
PubMed: 19006240]
Carmical SG, Gupta P, Milewicz DM, Putnam EA. FBN2 mutations identified in congenital contractural arachnodactyly patients with aortic root dilatation. Am J Hum Genet. 1999;65S:A6.
Carta L, Pereira L, Arteaga-Solis E, Lee-Arteaga SY, Lenart B, Starcher B, Merkel CA, Sukoyan M, Kerkis A, Hazeki N, Keene DR, Sakai LY, Ramirez F. Fibrillins 1 and 2 perform partially overlapping functions during aortic development.
J Biol Chem. 2006;281:8016–23. [
PMC free article: PMC3052983] [
PubMed: 16407178]
Chen Y, Lei YP, Zheng HX, Wang W, Cheng HB, Zhang J, Wang HY, Jin L, Li H. A novel mutation (C1425Y) in the FBN2 gene in a father and son with congenital contractural arachnodactyly.
Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2009;13:295–300. [
PubMed: 19473076]
Courtens W, Tjalma W, Messiaen L, Vamos E, Martin JJ, Van Bogaert E, Keersmaekers G, Meulyzer P, Wauters J. Prenatal diagnosis of a constitutional interstitial deletion of chromosome 5 (q15q31.1) presenting with features of congenital contractural arachnodactyly.
Am J Med Genet. 1998;77:188–97. [
PubMed: 9605585]
Currarino G, Friedman JM. A severe form of congenital contractural arachnodactyly in two newborn infants.
Am J Med Genet. 1986;25:763–73. [
PubMed: 3789025]
Faivre L, Collod-Beroud G, Callewaert B, Child A, Binquet C, Gautier E, Loeys BL, Arbustini E, Mayer K, Arslan-Kirchner M, Stheneur C, Kiotsekoglou A, Comeglio P, Marziliano N, Wolf JE, Bouchot O, Khau-Van-Kien P, Beroud C, Claustres M, Bonithon-Kopp C, Robinson PN, Adès L, De Backer J, Coucke P, Francke U, De Paepe A, Jondeau G, Boileau C. Clinical and mutation-type analysis from an international series of 198 probands with a pathogenic FBN1 exons 24-32 mutation.
Eur J Hum Genet. 2009;17:491–501. [
PMC free article: PMC2734964] [
PubMed: 19002209]
Garcia-Miñaur S, Ramsay J, Grace E, Minns RA, Myles LM, FitzPatrick DR. Interstitial deletion of the long arm of chromosome 5 in a boy with multiple congenital anomalies and mental retardation: molecular characterization of the deleted region to 5q22.3q23.3.
Am J Med Genet A. 2005;132A:402–10. [
PubMed: 15742475]
Guo X, Song C, Shi Y, Li H, Meng W, Yuan Q, Xue J, Xie J, Liang Y, Yuan Y, Yu B, Wang H, Chen Y, Qi L, Li X. Whole exome sequencing identifies a novel missense FBN2 mutation co-segregating in a four-generation Chinese family with congenital contractural arachnodactyly.
BMC Med Genet. 2016;17:91. [
PMC free article: PMC5135809] [
PubMed: 27912749]
Gupta PA, Putnam EA, Carmical SG, Kaitila I, Steinmann B, Child A, Danesino C, Metcalfe K, Berry SA, Chen E, Delorme CV, Thong MK, Ades LC, Milewicz DM. Ten novel FBN2 mutations in congenital contractural arachnodactyly: delineation of the molecular pathogenesis and clinical phenotype.
Hum Mutat. 2002;19:39–48. [
PubMed: 11754102]
Inbar-Feigenberg M, Meirowitz N, Nanda D, Toi A, Okun N, Chitayat D. Beals syndrome (congenital contractural arachnodactyly): prenatal ultrasound findings and molecular analysis.
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2014;44:486–90. [
PubMed: 24585410]
Lavillaureix A, Heide S, Chantot-Bastaraud S, Marey I, Keren B, Grigorescu R, Jouannic JM, Gelot A, Whalen S, Héron D, Siffroi JP. Mosaic intragenic deletion of FBN2 and severe congenital contractural arachnodactyly.
Clin Genet. 2017;92:556–8. [
PubMed: 28762477]
Lipson EH, Viseskul C, Herrmann J. The clinical spectrum of congenital contractural arachnodactyly. A case with congenital heart disease.
Z Kinderheilkd. 1974;118:1–8. [
PubMed: 4432555]
Liu W, Zhao N, Li XF, Wang H, Sui Y, Lu YP, Feng WH, Ma C, Han WT, Jiang M. A novel FBN2 mutation in a Chinese family with congenital contractural arachnodactyly.
FEBS Open Bio. 2015;5:163–6. [
PMC free article: PMC4359973] [
PubMed: 25834781]
Loeys BL, Dietz HC, Braverman AC, Callewaert BL, De Backer J, Devereux RB, Hilhorst-Hofstee Y, Jondeau G, Faivre L, Milewicz DM, Pyeritz RE, Sponseller PD, Wordsworth P, De Paepe AM. The revised Ghent nosology for the Marfan syndrome.
J Med Genet. 2010;47:476–85. [
PubMed: 20591885]
Macnab AJ, D'Orsogna L, Cole DE, Baguley PE, Adderley RJ, Patterson MW. Cardiac anomalies complicating congenital contractural arachnodactyly.
Arch Dis Child. 1991;66:1143–6. [
PMC free article: PMC1590273] [
PubMed: 1750764]
Meena JP, Gupta A, Mishra D, Juneja M. Beals-Hecht syndrome (congenital contractural arachnodactyly) with additional craniospinal abnormality: a case report.
J Pediatr Orthop B. 2015;24:226–9. [
PubMed: 25493702]
Meerschaut I, De Coninck S, Steyaert W, Barnicoat A, Bayat A, Benedicenti F, Berland S, Blair EM, Breckpot J, de Burca A, Destrée A, García-Miñaúr S, Green AJ, Hanna BC, Keymolen K, Koopmans M, Lederer D, Lees M, Longman C, Lynch SA, Male AM, McKenzie F, Migeotte I, Mihci E, Nur B, Petit F, Piard J, Plasschaert FS, Rauch A, Ribaï P, Pacheco IS, Stanzial F, Stolte-Dijkstra I, Valenzuela I, Varghese V, Vasudevan PC, Wakeling E, Wallgren-Pettersson C, Coucke P, De Paepe A, De Wolf D, Symoens S, Callewaert B. A clinical scoring system for congenital contractural arachnodactyly.
Genet Med. 2020;22:124–31. [
PubMed: 31316167]
Mehar V, Yadav D, Kumar R, Yadav S, Singh K, Callewaert B, Pathan S, De Paepe A, Coucke PJ. Congenital contractural arachnodactyly due to a novel splice site mutation in the FBN2 gene.
J Pediatr Genet. 2014;3:163–6. [
PMC free article: PMC5020994] [
PubMed: 27625873]
Milewicz DM, Dietz HC, Miller DC. Treatment of aortic disease in patients with Marfan syndrome.
Circulation. 2005;111:e150–7. [
PubMed: 15781745]
Monies D, Maddirevula S, Kurdi W, Alanazy MH, Alkhalidi H, Al-Owain M, Sulaiman RA, Faqeih E, Goljan E, Ibrahim N, Abdulwahab F, Hashem M, Abouelhoda M, Shaheen R, Arold ST, Alkuraya FS. Autozygosity reveals recessive mutations and novel mechanisms in dominant genes: implications in variant interpretation.
Genet Med. 2017;19:1144–50. [
PubMed: 28383543]
Nishimura A, Sakai H, Ikegawa S, Kitoh H, Haga N, Ishikiriyama S, Nagai T, Takada F, Ohata T, Tanaka F, Kamasaki H, Saitsu H, Mizuguchi T, Matsumoto N. FBN2, FBN1, TGFBR1, and TGFBR2 analyses in congenital contractural arachnodactyly.
Am J Med Genet. 2007;143A:694–8. [
PubMed: 17345643]
Nistala H, Lee-Arteaga S, Smaldone S, Siciliano G, Carta L, Ono RN, Sengle G, Arteaga-Solis E, Levasseur R, Ducy P, Sakai LY, Karsenty G, Ramirez F. Fibrillin-1 and -2 differentially modulate endogenous TGF-β and BMP bioavailability during bone formation.
J Cell Biol. 2010;190:1107–21. [
PMC free article: PMC3101602] [
PubMed: 20855508]
Park ES, Putnam EA, Chitayat D, Child A, Milewicz DM. Clustering of FBN2 mutations in patients with congenital contractural arachnodactyly indicates an important role of the domains encoded by exons 24 through 34 during human development.
Am J Med Genet. 1998;78:350–5. [
PubMed: 9714438]
Putnam EA, Park ES, Aalfs CM, Hennekam RC, Milewicz DM. Parental somatic and germ-line mosaicism for a FBN2 mutation and analysis of FBN2 transcript levels in dermal fibroblasts.
Am J Hum Genet. 1997;60:818–27. [
PMC free article: PMC1712457] [
PubMed: 9106527]
Renard M, Francis C, Ghosh R, Scott AF, Witmer PD, Adès LC, Andelfinger GU, Arnaud P, Boileau C, Callewaert BL, Guo D, Hanna N, Lindsay ME, Morisaki H, Morisaki T, Pachter N, Robert L, Van Laer L, Dietz HC, Loeys BL, Milewicz DM, De Backer J. Clinical validity of genes for heritable thoracic aortic aneurysm and dissection.
J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;72:605–15. [
PMC free article: PMC6378369] [
PubMed: 30071989]
Smaldone S, Carta L, Ramirez F. Establishment of fibrillin-deficient osteoprogenitor cell lines identifies molecular abnormalities associated with extracellular matrix perturbation of osteogenic differentiation.
Cell Tissue Res. 2011;344:511–7. [
PMC free article: PMC3214762] [
PubMed: 21538048]
Snape KM, Fahey MC, McGillivray G, Gupta P, Milewicz DM, Delatycki MB. Long-term survival in a child with severe congenital contractural arachnodactyly, autism and severe intellectual disability.
Clin Dysmorphol. 2006;15:95–9. [
PubMed: 16531736]
Takeda N, Morita H, Fujita D, Inuzuka R, Taniguchi Y, Imai Y, Hirata Y, Komuro I. Congenital contractural arachnodactyly complicated with aortic dilatation and dissection: case report and review of literature.
Am J Med Genet A. 2015;167A:2382–7. [
PubMed: 25975422]
Wang M, Clericuzio CL, Godfrey M. Familial occurrence of typical and severe lethal congenital contractural arachnodactyly caused by missplicing of exon 34 of fibrillin-2.
Am J Hum Genet. 1996;59:1027–34. [
PMC free article: PMC1914850] [
PubMed: 8900230]